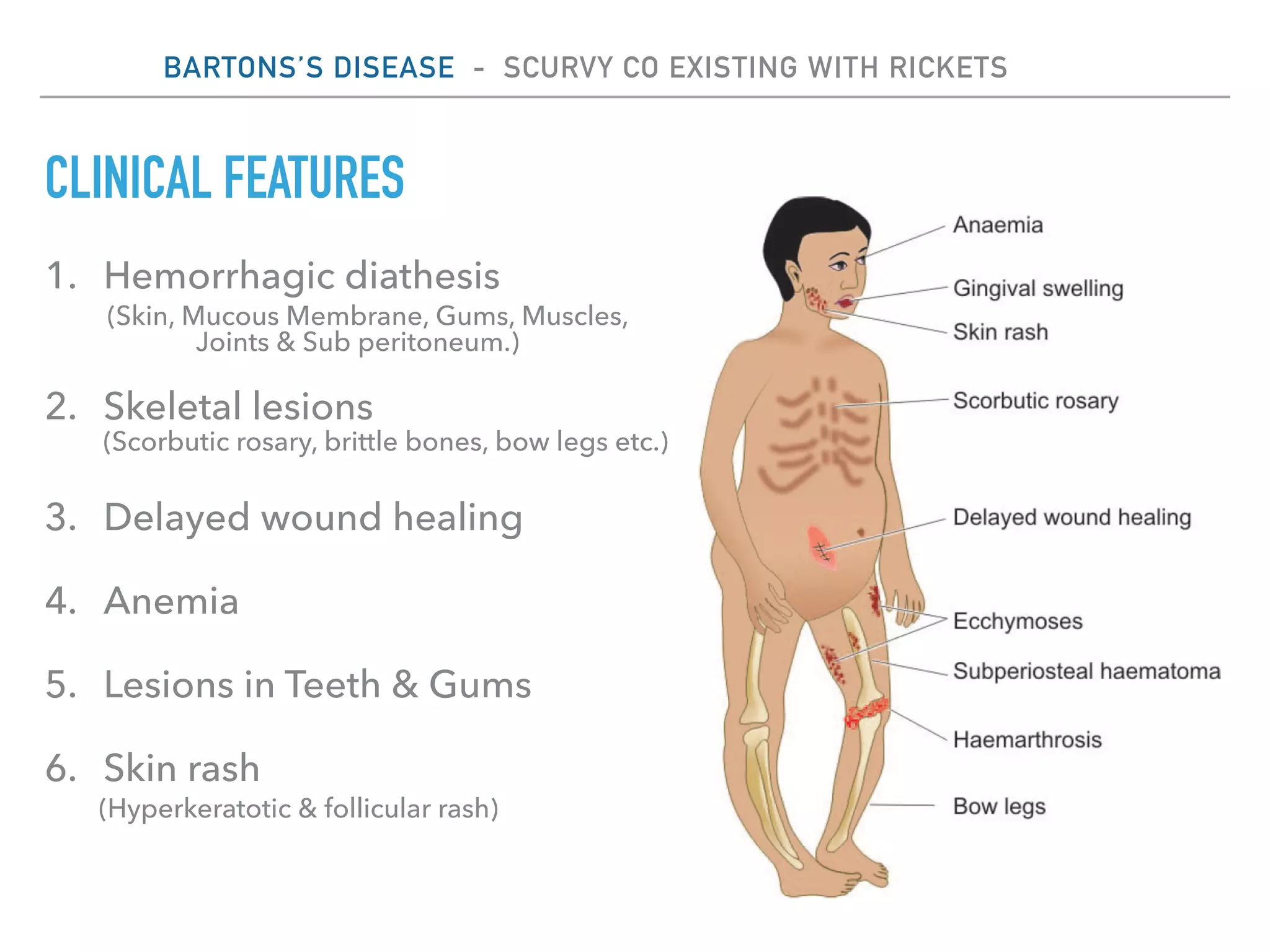
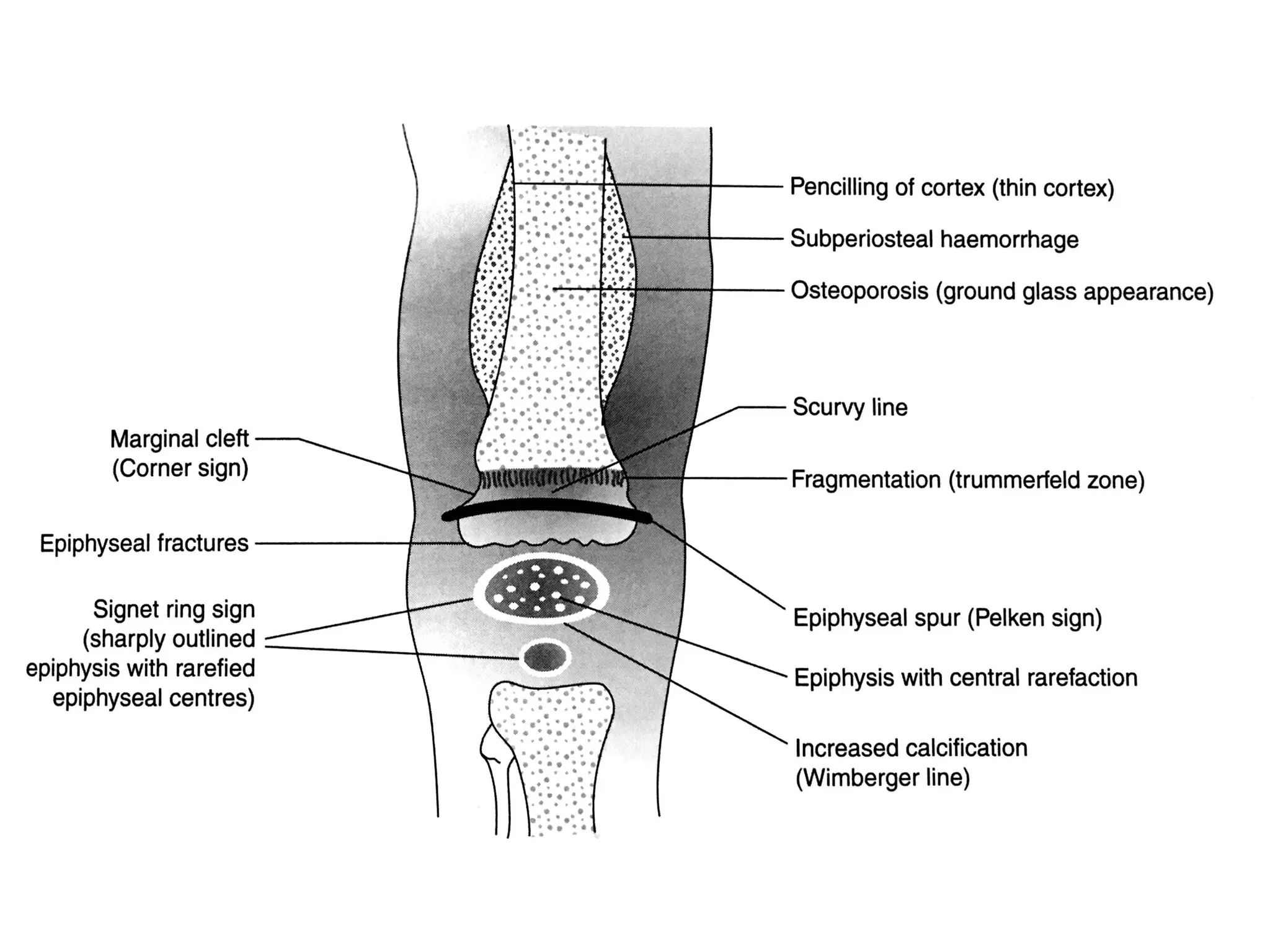
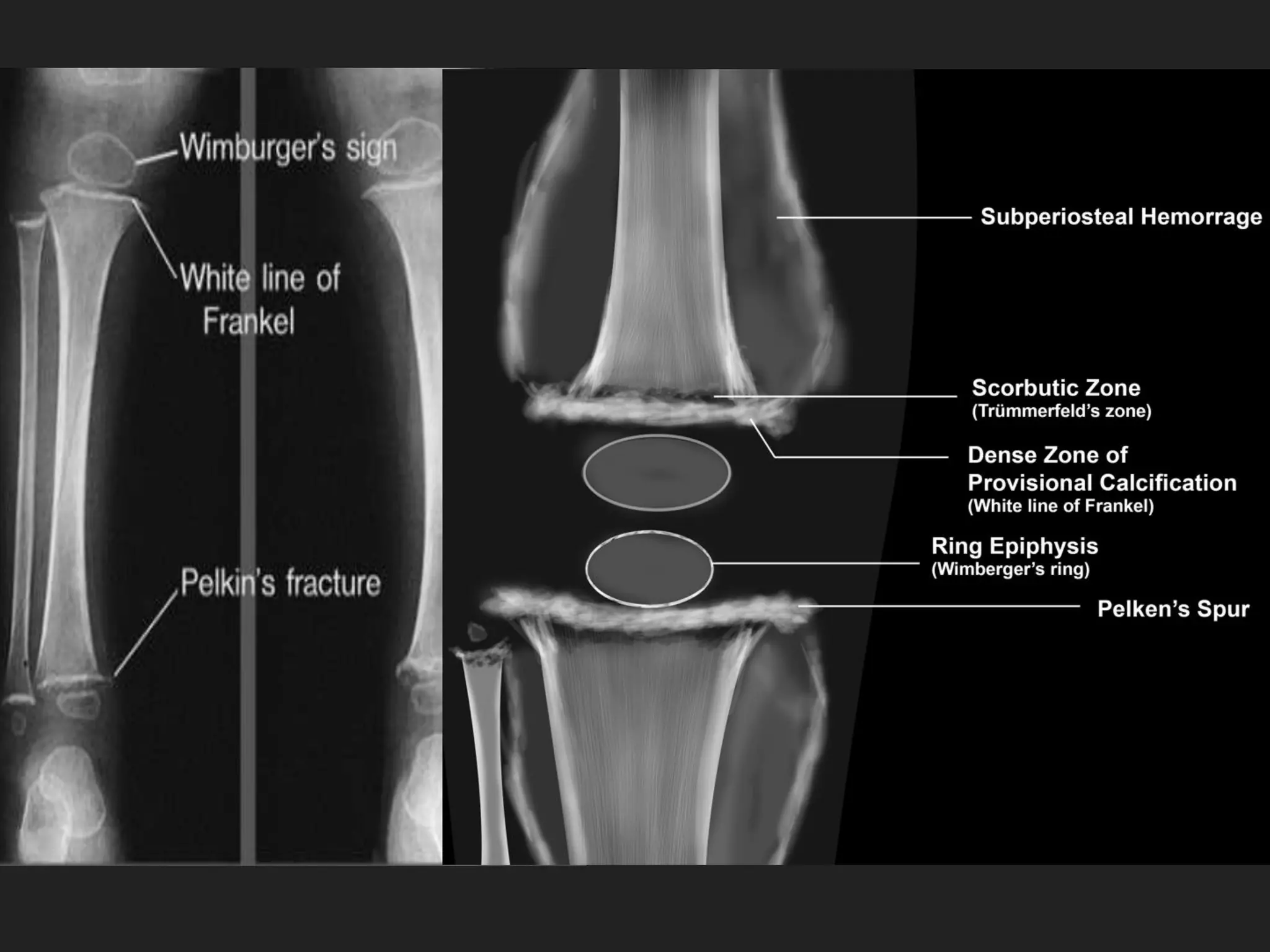
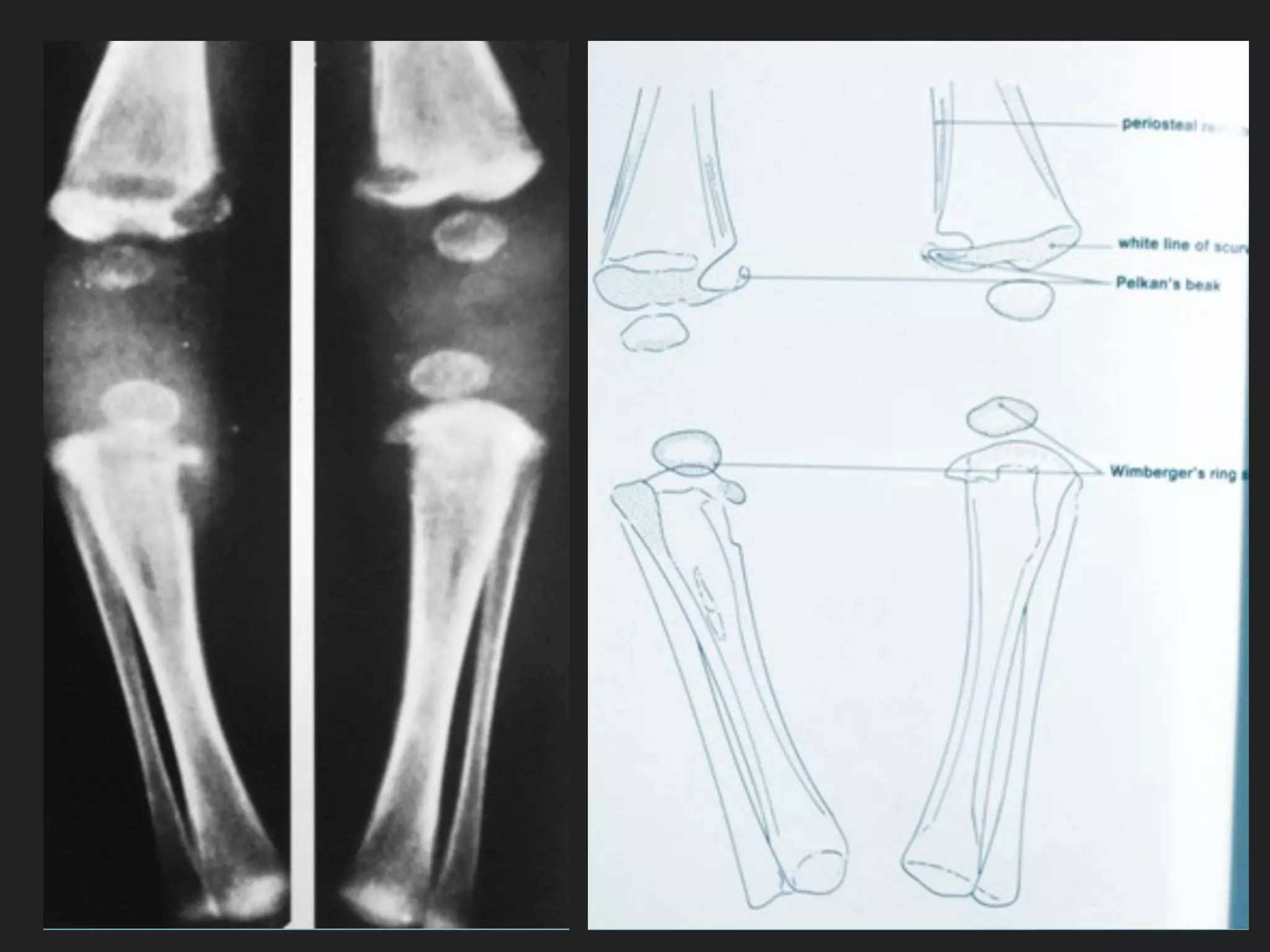
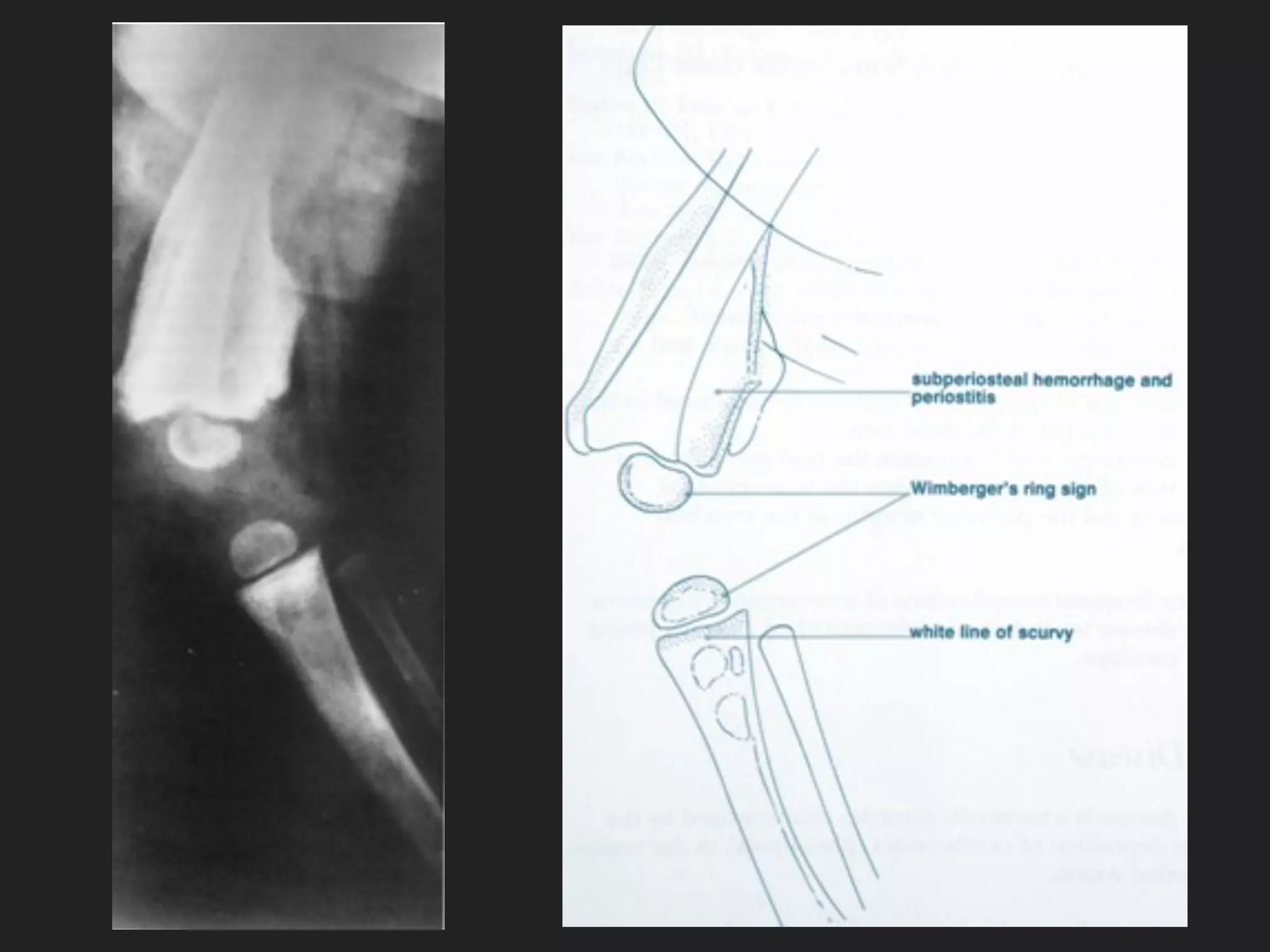
This document discusses scurvy, a nutritional disorder caused by vitamin C deficiency. It presents the clinical features and radiological findings of scurvy, including generalized hemorrhage, skeletal lesions, delayed wound healing, and anemia. Radiological findings include osteoporosis, subperiosteal hemorrhage, increased calcification around the epiphysis (Wimberger's ring sign), cortical thinning (pencil point cortex), and fragmentation above the calcified cartilage in the metaphysis (Trummerfeld's zone). Treatment involves oral or parenteral vitamin C, with loading doses of 500-1000 mg daily for one week for clinical scurvy.