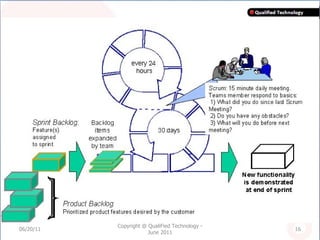
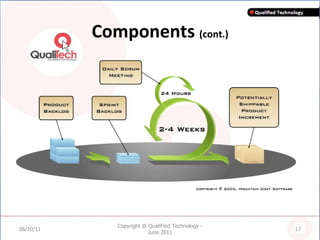
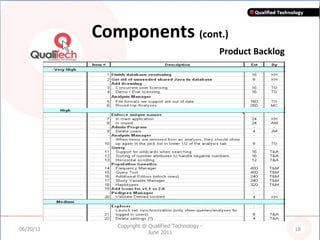
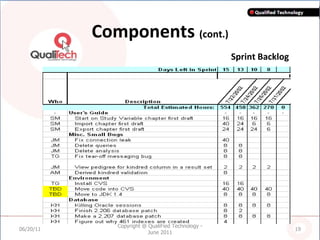
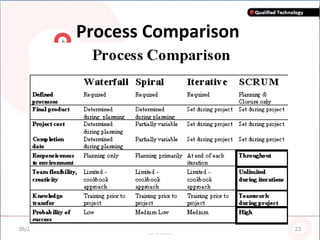
SCRUM is an agile software development methodology where self-organizing teams work in short cycles called sprints to build functionality incrementally from a product backlog. It is based on iterative development and aims to respond to change quickly. Key components include roles like the Scrum Master, sprints that last 2-4 weeks to deliver an increment, and daily stand-up meetings to track progress. SCRUM aims to improve productivity, flexibility, and quality through principles like empowered teams and frequent delivery of working software.