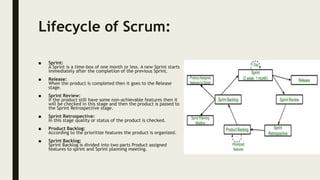
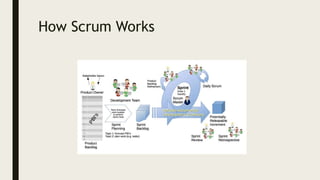
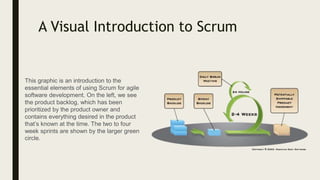
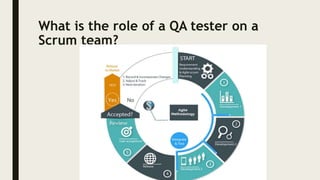
The role of a QA tester on a Scrum team includes:
1) Participating in sprint planning and retrospectives to provide input on testing needs and improvements.
2) Testing software increments throughout the sprint to find issues early.
3) Communicating regularly with developers through daily standups and demos.
4) Ensuring quality by developing test cases, conducting exploratory testing, and automating tests.
5) Helping clarify requirements and identify ambiguities.