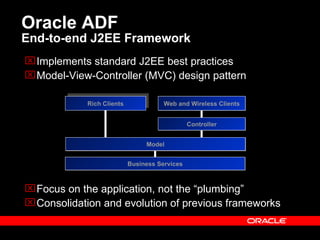
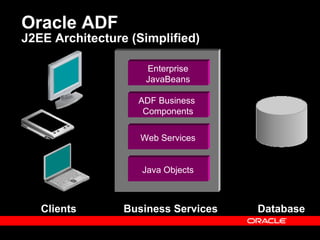
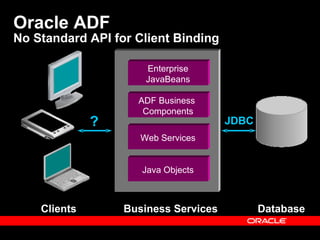
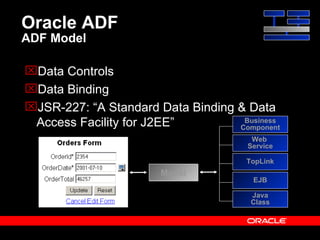
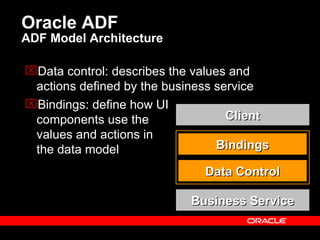
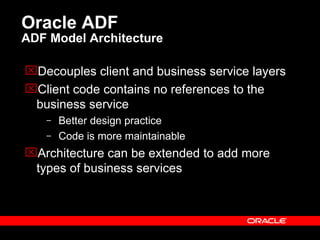
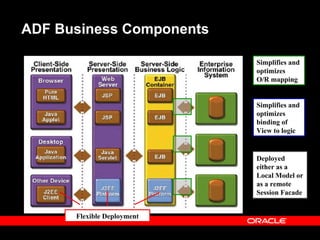
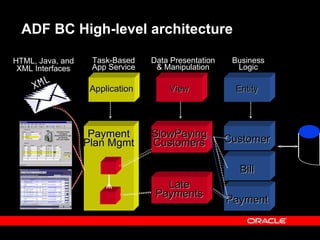
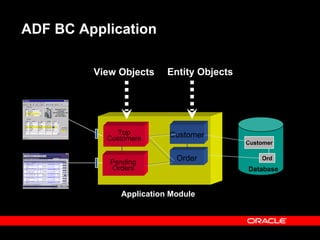
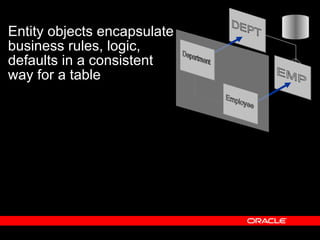
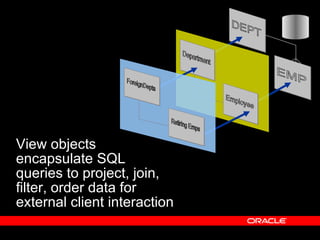
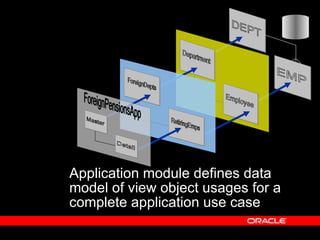
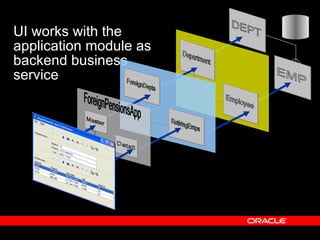
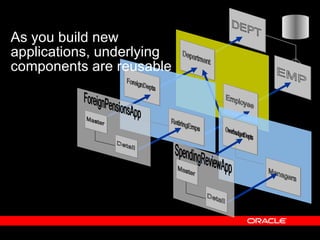
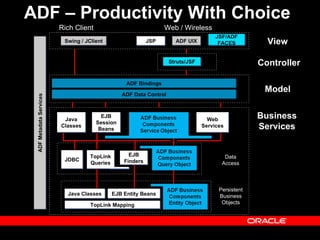
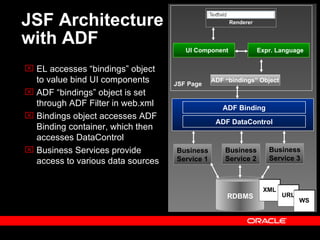
Oracle ADF is a Java EE framework that aims to reduce the complexity of developing Java EE applications by providing visual and declarative development tools, increasing productivity by reducing coding needs and focusing on the application logic rather than infrastructure code, and encouraging best practices through implementation of standard patterns like MVC. It provides an end-to-end solution for building rich web, desktop and mobile clients that access business services using data binding and visual development.