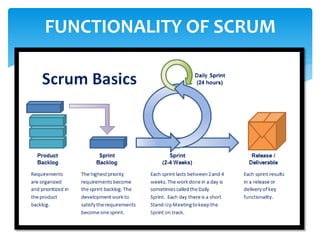
This document discusses the Scrum framework. Scrum is an agile process for managing complex product development. It uses self-organizing cross-functional teams, sprints, daily stand-ups, and artifacts like a product backlog and sprint backlog. The key components of Scrum include roles like the Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Scrum Team. The Scrum process involves sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and producing an increment of work each sprint.