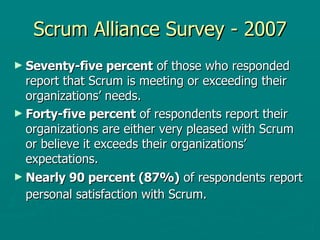
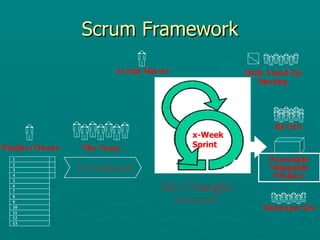
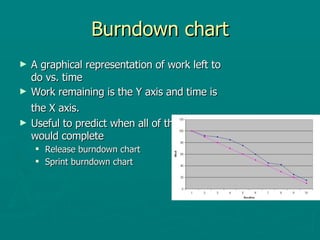
The document introduces Scrum as an agile software development framework aimed at effectively managing complex problems and maximizing productivity. It outlines the roles, ceremonies, and artifacts involved in Scrum, emphasizes the importance of collaboration and communication, and highlights survey results indicating high satisfaction with Scrum among organizations. The document also discusses potential challenges in adopting Scrum and concludes with its successful application in notable companies.