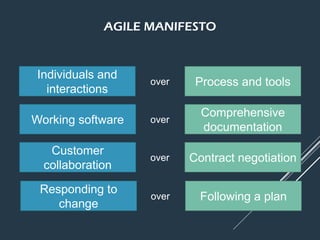
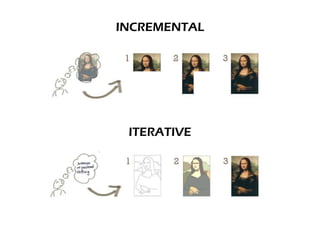
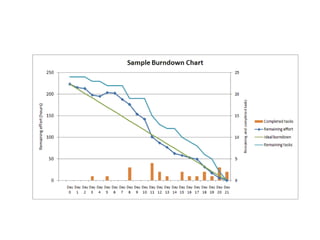
Scrum is an agile framework for managing complex product development, originally formalized for software projects but adaptable to various scopes. It involves specific roles such as the Product Owner, Development Team, and Scrum Master, and emphasizes collaboration, flexibility in response to changing customer needs, and iterative completion of work through defined events like sprints and daily meetings. Key artifacts include the product backlog, sprint backlog, and sprint burndown chart, which help teams manage work progress and deliver value effectively.