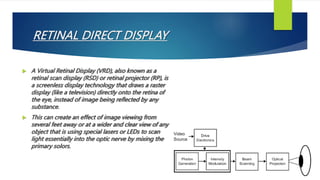
Screenless display technology (STD) transmits information without a physical screen, utilizing methods like visual image displays, retinal direct displays, and synaptic interfaces. Key applications include the medical field for virtual x-rays, manufacturing for virtual blueprints, and transportation systems for virtual maps. While STD offers advantages such as low power requirements and high-resolution images, it also presents challenges including high costs and developmental limitations.