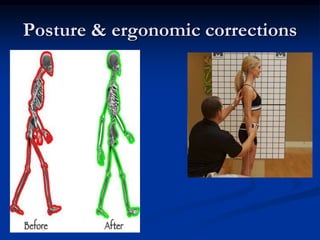
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, is a primary health care profession that treats a variety of medical conditions through movement and exercise. Physiotherapists diagnose issues, develop treatment plans which may include exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy, and education, and help patients achieve the best possible physical function and mobility. They are university-trained health professionals that work in various settings like hospitals, private clinics, and patients' homes to improve patients' pain, function, and quality of life for conditions like injuries, arthritis, strokes, and respiratory diseases.