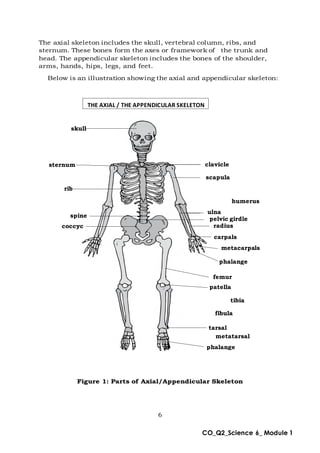
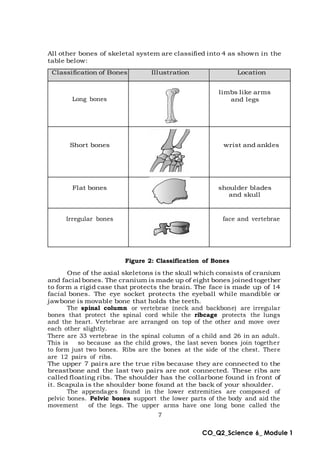
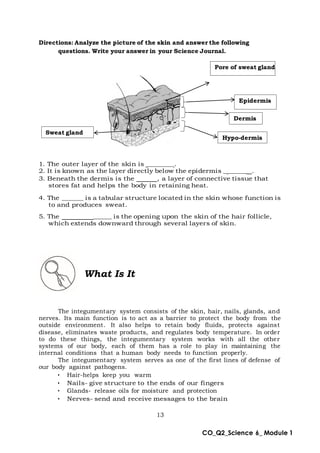
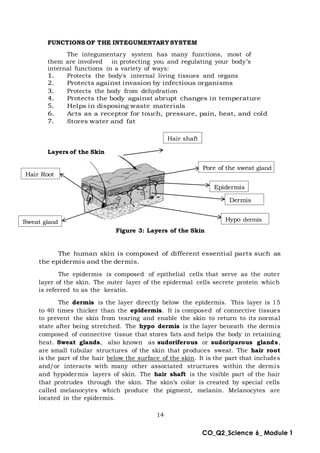
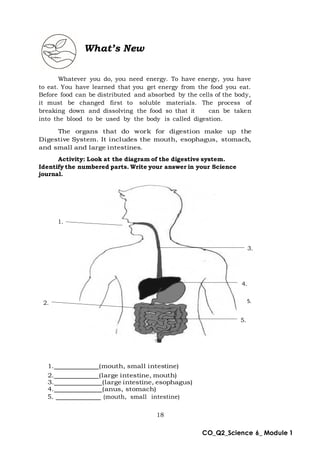
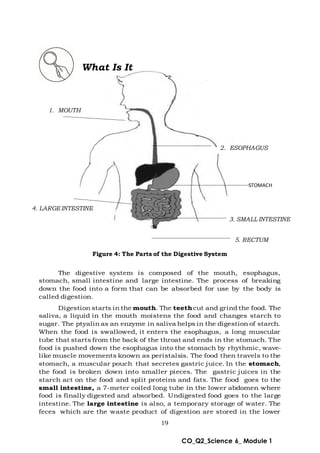
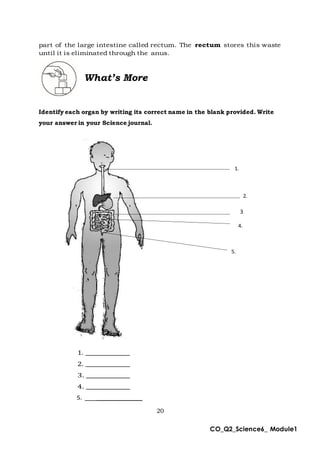
This document provides an overview of a science module that covers the skeletal, integumentary, and digestive systems. It includes 3 lessons that identify the major parts of each system and explain how the parts work together. The module is intended to help students learn the key structures and functions of the human body systems.