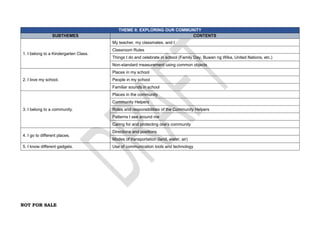
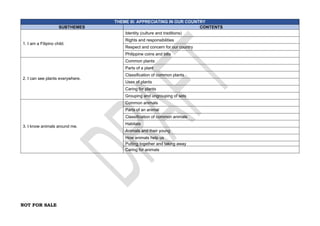
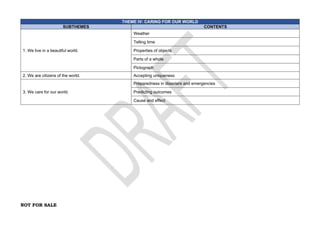
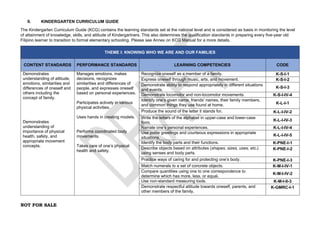
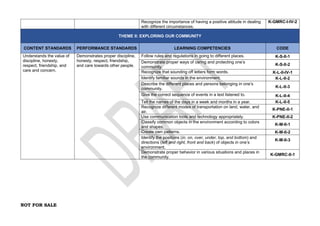
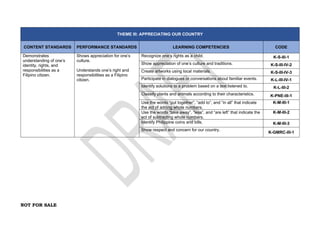
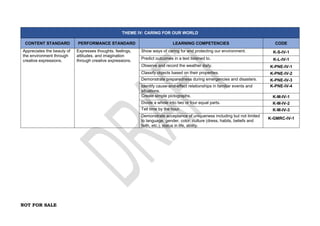
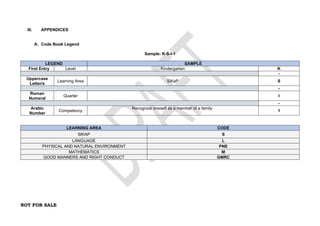
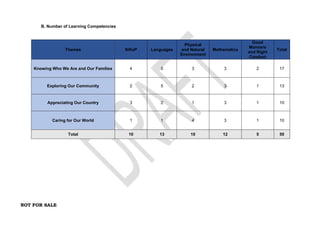
The document provides an overview of the Kindergarten curriculum guide for the Philippines, including scope and sequence, themes, standards, and competencies. It contains 4 themes that explore various topics like self, family, community, country, and world. Each theme has subthemes and associated learning competencies. The guide is intended to help Kindergarten learners attain knowledge, skills, and attitudes to transition successfully to elementary school.