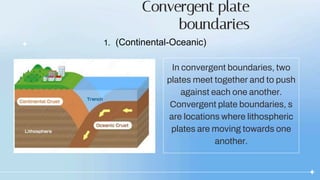
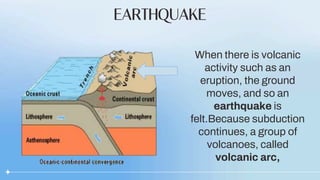
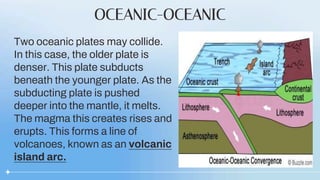
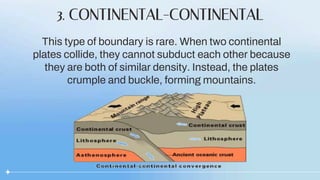
There are three types of convergent plate boundaries: continental-oceanic, oceanic-oceanic, and continental-continental. At a continental-oceanic boundary, an oceanic plate subducts under a continental plate, forming a trench where earthquakes often occur. As the oceanic plate subducts into the mantle, it melts and rises as magma, forming volcanic arcs at the surface. At an oceanic-oceanic boundary, the older, denser oceanic plate subducts under the younger plate, creating volcanic island arcs. A continental-continental boundary results in crustal crumpling and mountain formation as the plates cannot subduct through each other.