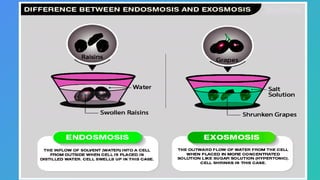
The document describes osmosis as the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a low concentration solution to a high concentration solution. It explains the effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions on cells, highlighting that isotonic solutions maintain cell size, hypotonic solutions may cause cells to swell, and hypertonic solutions lead to cell shrinkage. An experiment using raisins and apricots illustrates osmosis, showing how these fruits swell in pure water and shrink in a concentrated sugar and salt solution.