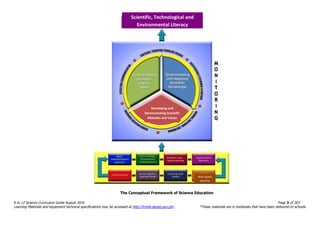
The document is the K to 12 Science Curriculum Guide published by the Department of Education of the Philippines in August 2016. It lays out the conceptual framework and standards for science education from Kindergarten to Grade 10. The goals are to develop scientific literacy, technological literacy, and environmentally literate citizens. The curriculum is inquiry-based and organized around understanding science concepts, performing scientific processes and skills, and developing scientific attitudes and values. It presents concepts in a spiral progression with increasing complexity from grade to grade.