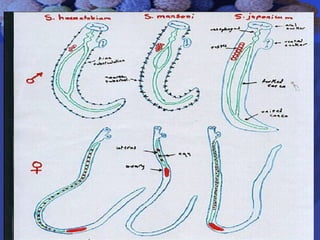
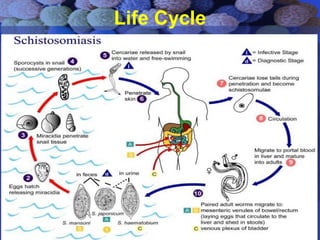
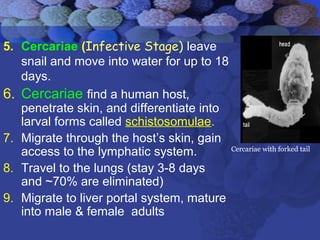
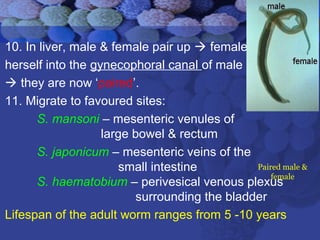
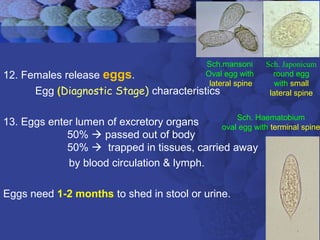
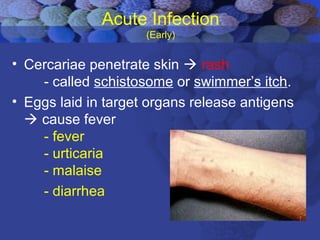
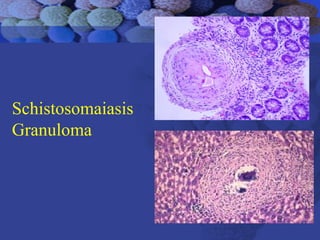
This document summarizes information about Schistosoma worms and Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia). It describes the classification, morphology, and life cycle of Schistosoma, which involves a snail intermediate host and human final host. Symptoms in humans include acute infection reactions or chronic complications in organs like the liver, intestines, bladder due to egg-induced immune responses. Diagnosis involves microscopic detection of eggs in stool/urine or other tests. Praziquantel is the primary treatment, while prevention focuses on avoiding contaminated freshwater sources.