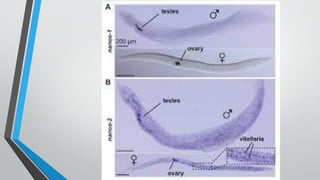
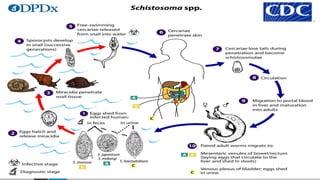
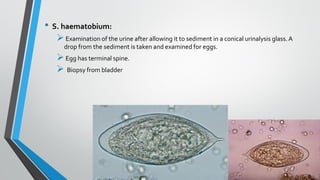
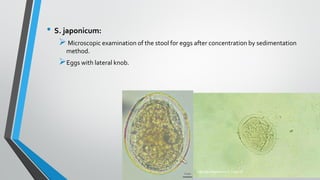
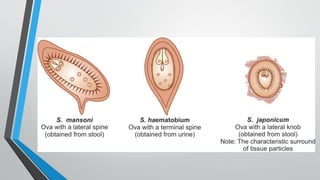
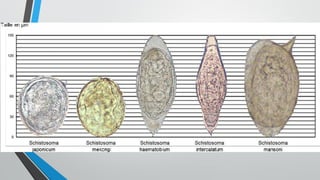
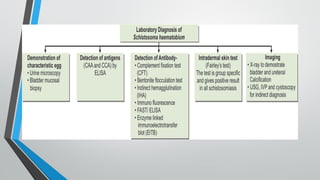
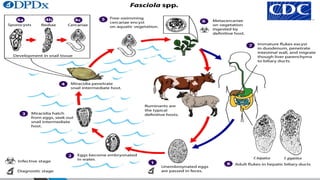
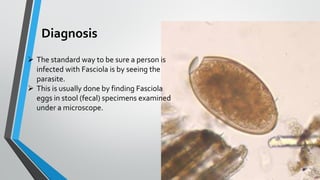
Trematodes, a group of parasitic flatworms from the phylum Platyhelminthes, inhabit various organs in vertebrates, with significant types including blood, intestinal, liver, and lung flukes. Notably, schistosomiasis affects around 600 million people, caused by different species of schistosomes, leading to various health complications. The lifecycle of schistosomes involves freshwater snails as intermediate hosts, and diagnosis typically requires microscopic examination of eggs in stool or urine.