Embed presentation





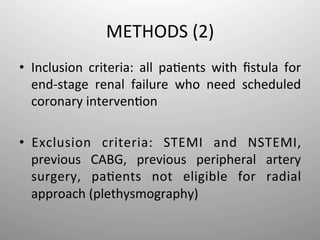



The COFIDIS study aims to prove the superiority of the radial approach compared to the femoral approach for coronary interventions in patients with fistulas for dialysis in terms of vascular and bleeding complications. The study is a prospective, multicenter, randomized trial that will enroll 784 patients undergoing planned coronary interventions who will be randomized 1:1 to either radial or femoral access. The primary endpoint is the total in-hospital vascular and bleeding complications. Secondary endpoints include major and minor bleeding, vascular complications, radial occlusion rates, and outcomes at 6 months. The results of this study could demonstrate that the radial approach reduces complications in dialysis patients undergoing coronary procedures.









