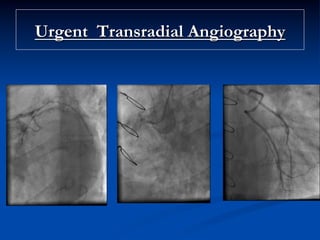
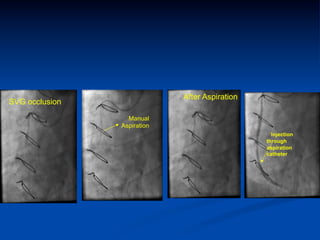
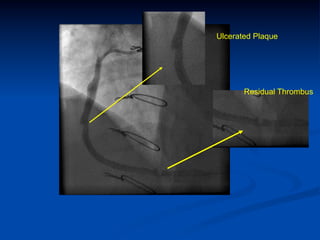
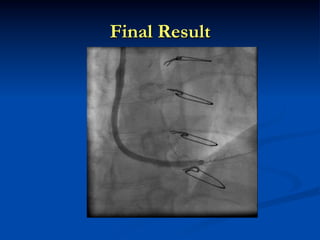
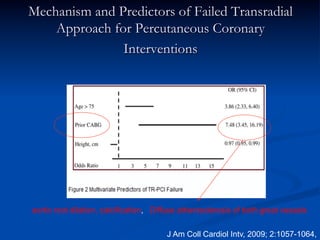
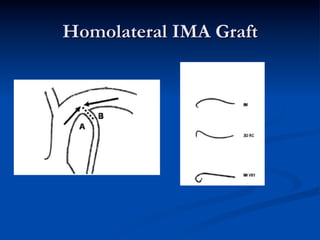
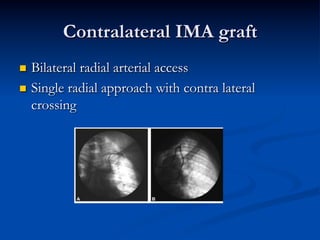
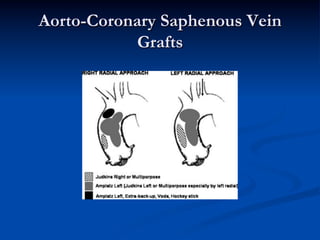
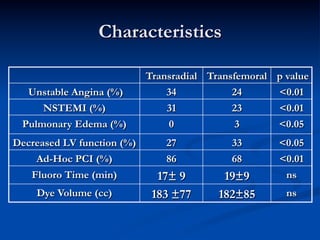
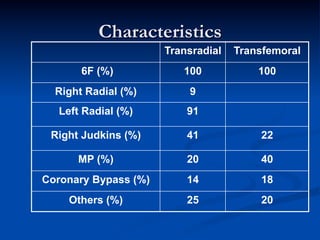
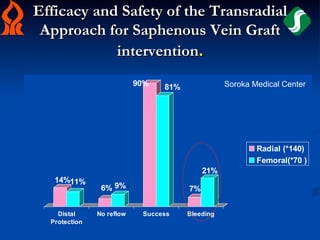
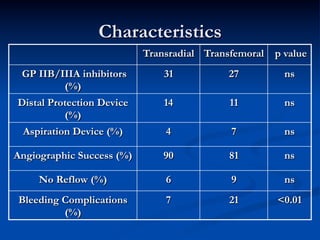
This study compared outcomes of 140 patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of saphenous vein grafts via the transradial approach versus 70 patients undergoing PCI of saphenous vein grafts via the transfemoral approach. The transradial group had a lower rate of bleeding complications compared to the transfemoral group (7% vs 21%, p<0.01), with similar rates of angiographic success (90% vs 81%, ns) and no reflow (6% vs 9%, ns). The study supports broader use of the transradial approach for saphenous vein graft intervention due to its association with fewer bleeding complications compared to the transfemoral approach.