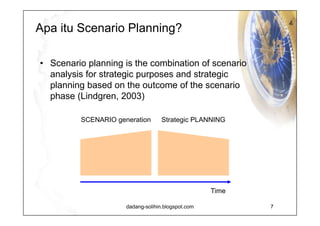
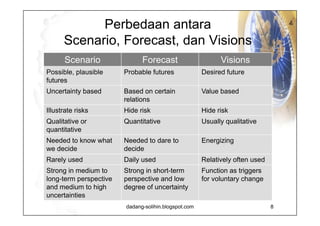
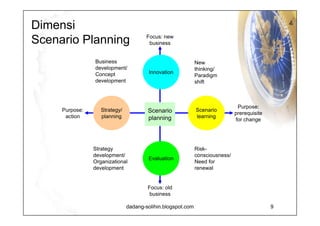
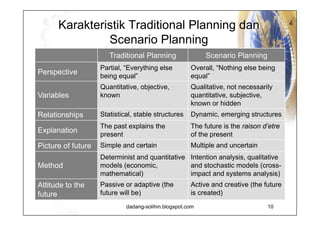
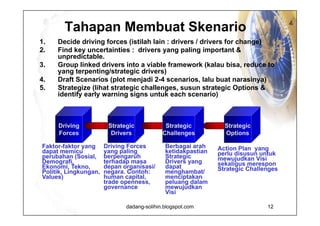
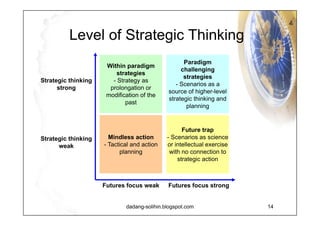
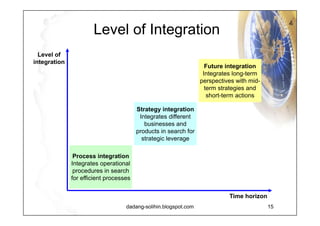
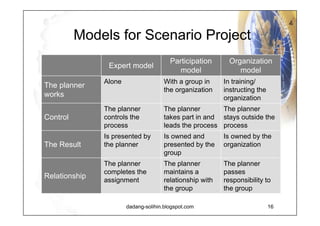
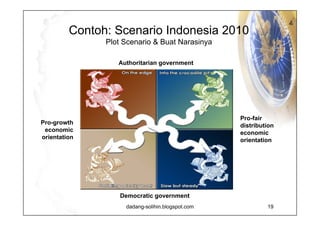
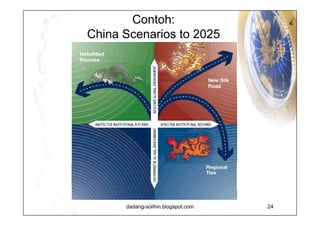
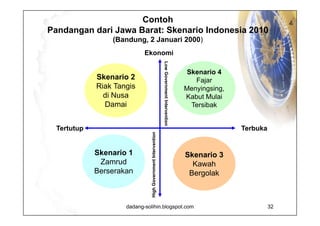
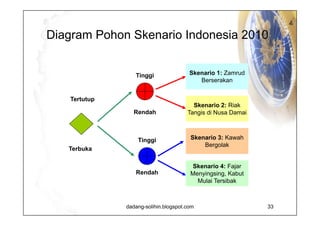
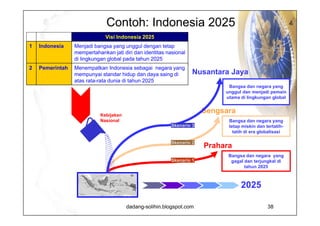
The document elaborates on scenario planning as a strategic management tool used to create and analyze diverse future scenarios, linking them to business decisions. It highlights the differences between scenario planning and traditional forecasting, integrating uncertainties and driving forces to craft comprehensive narratives. Examples from Indonesia, China, and India are provided to illustrate potential future scenarios and their implications on strategic thinking and decision-making processes.


![Apa itu Scenario Planning? “ An internally consistent view of what the future might turn out to be” (Michael Porter, 1985). “ A tool [for] ordering one’s perceptions about alternative future environments in which one’s decision might be played out right” (Peter Schwartz, 1991). “ That part of strategic planning which relates to the tools and technologies for managing the uncertainties of the future” (Gill Ringland, 1998). “ A disciplined method for imaging possible futures in which organizational decisions may be played out” (Paul Shoemaker, 1995).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scenario-planning3119/85/Scenario-Planning-3-320.jpg)