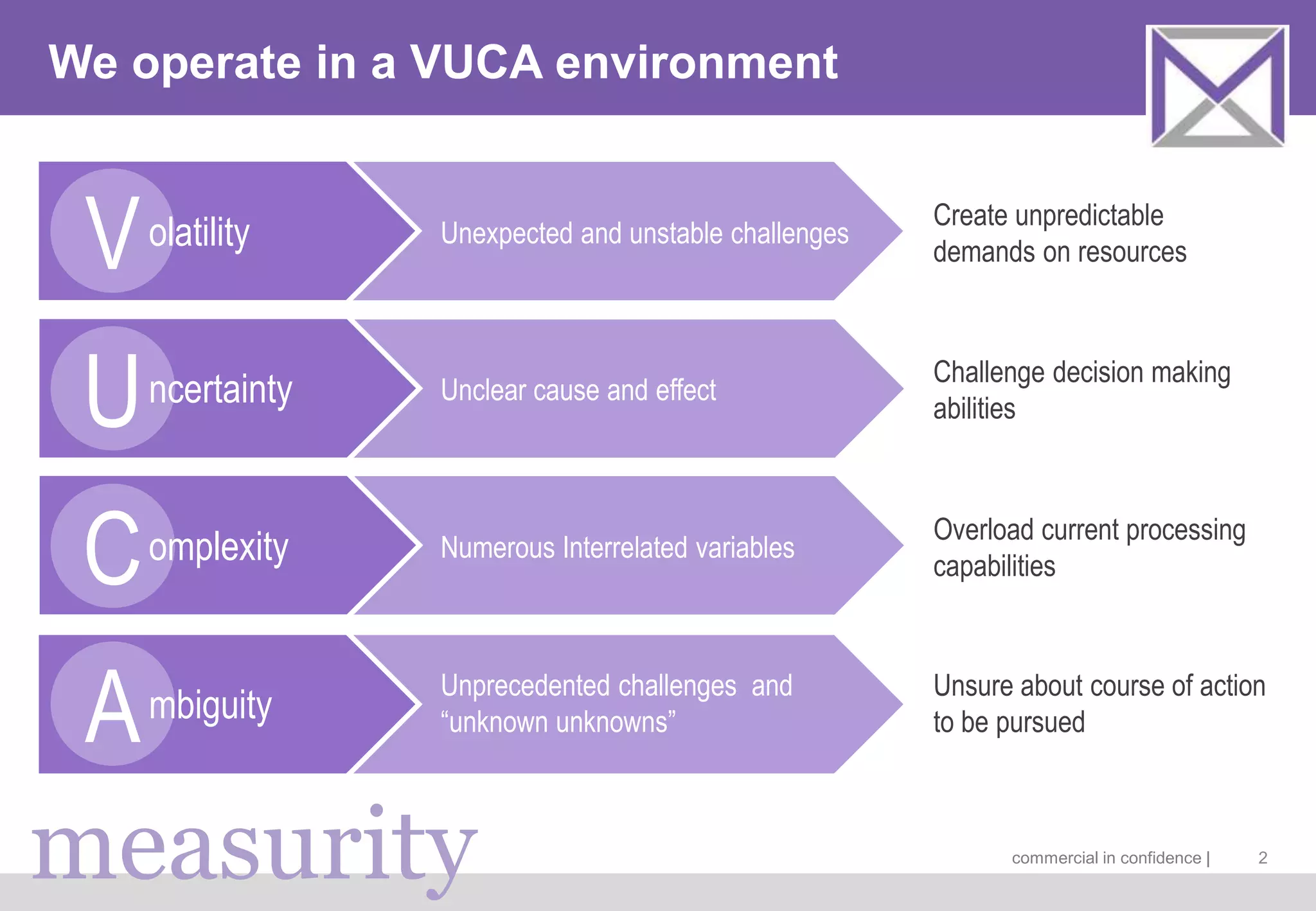
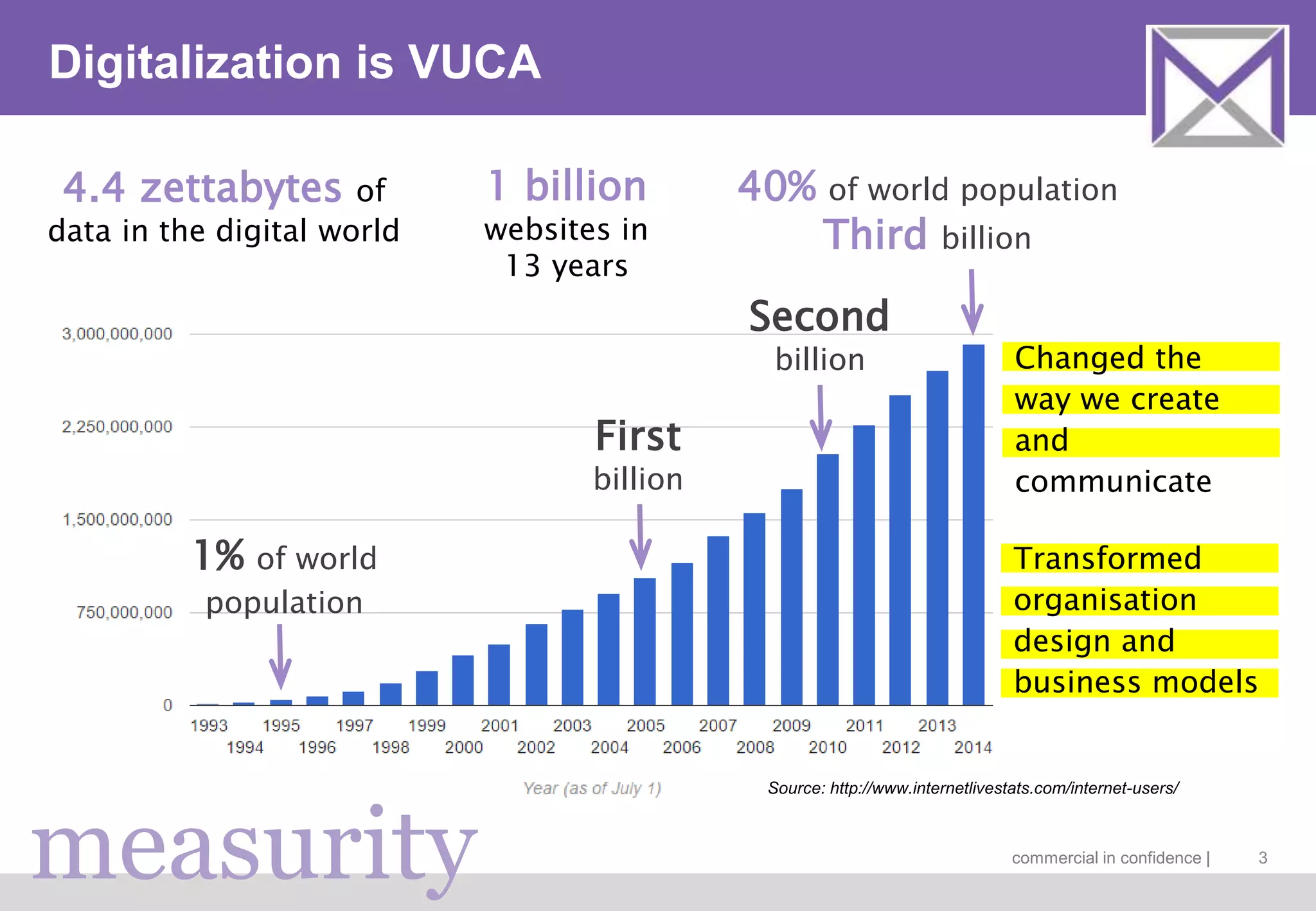
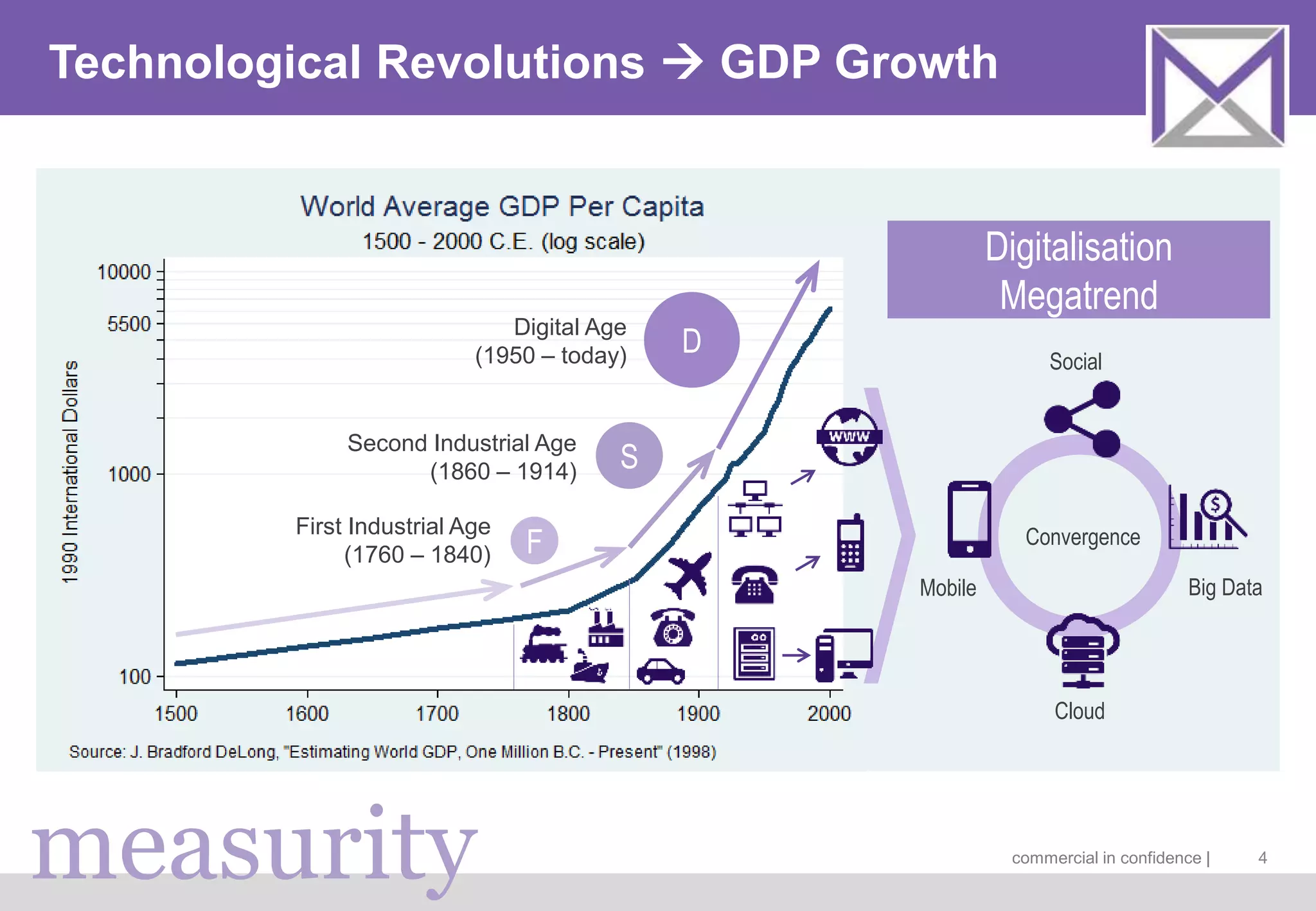
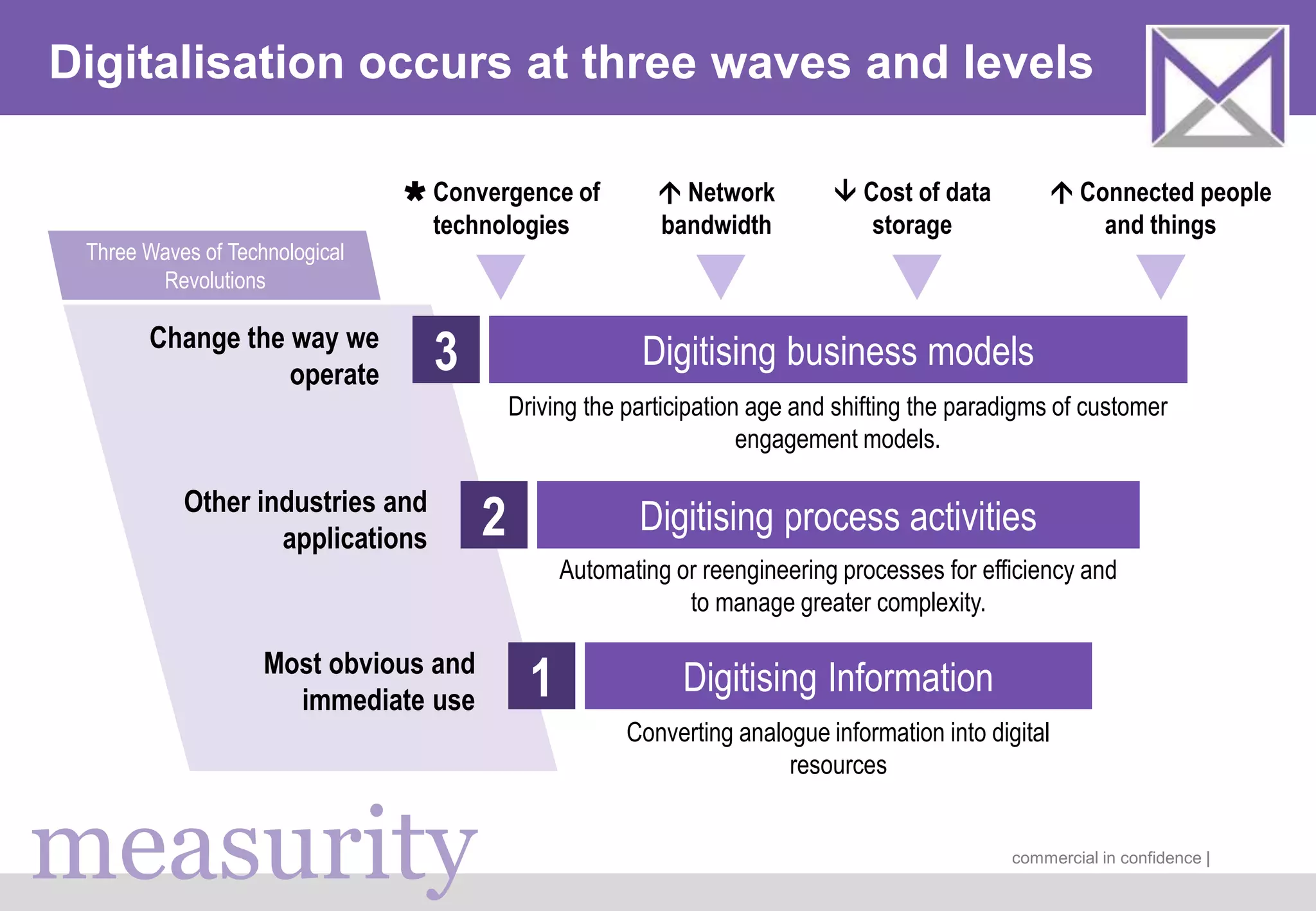
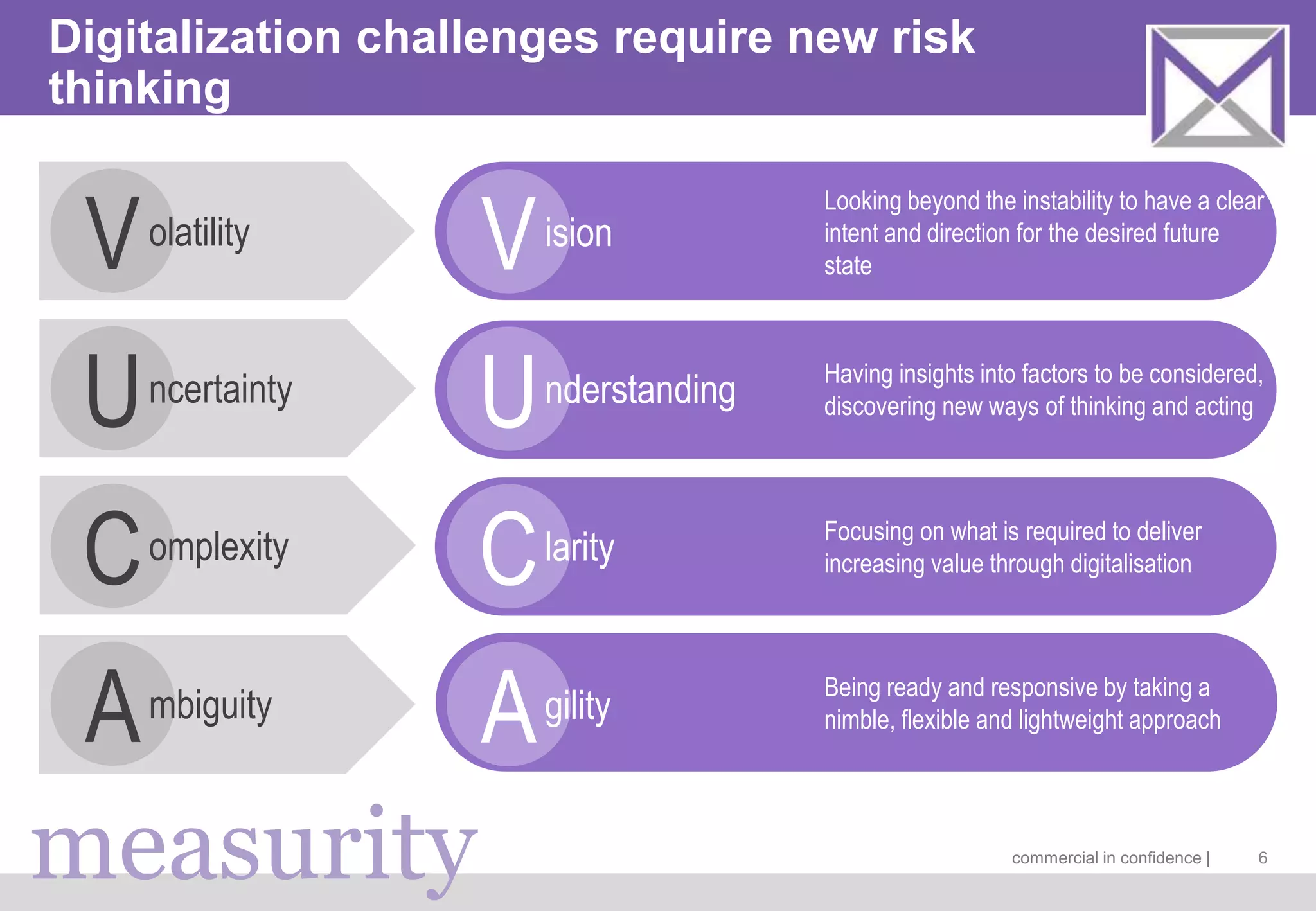
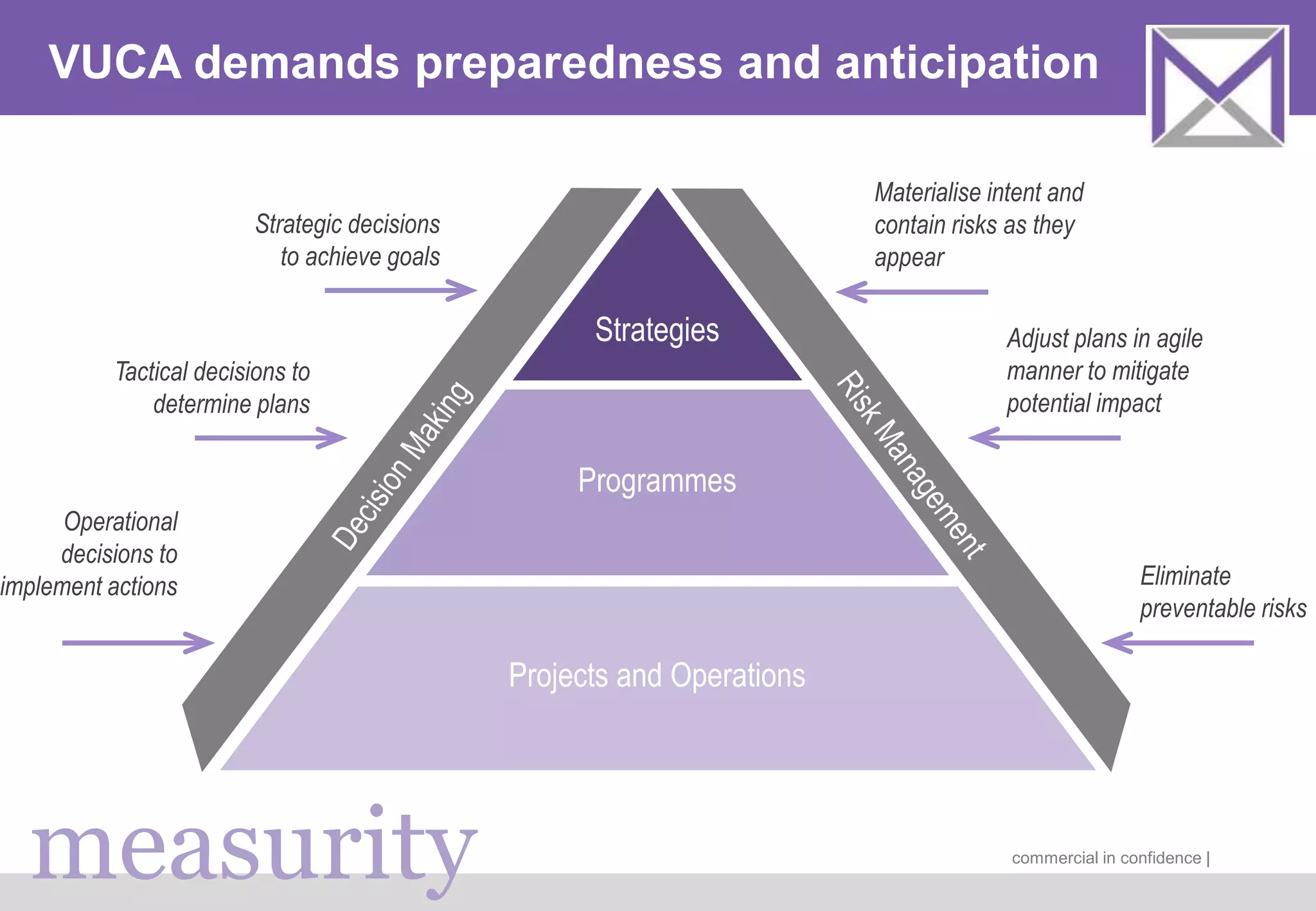
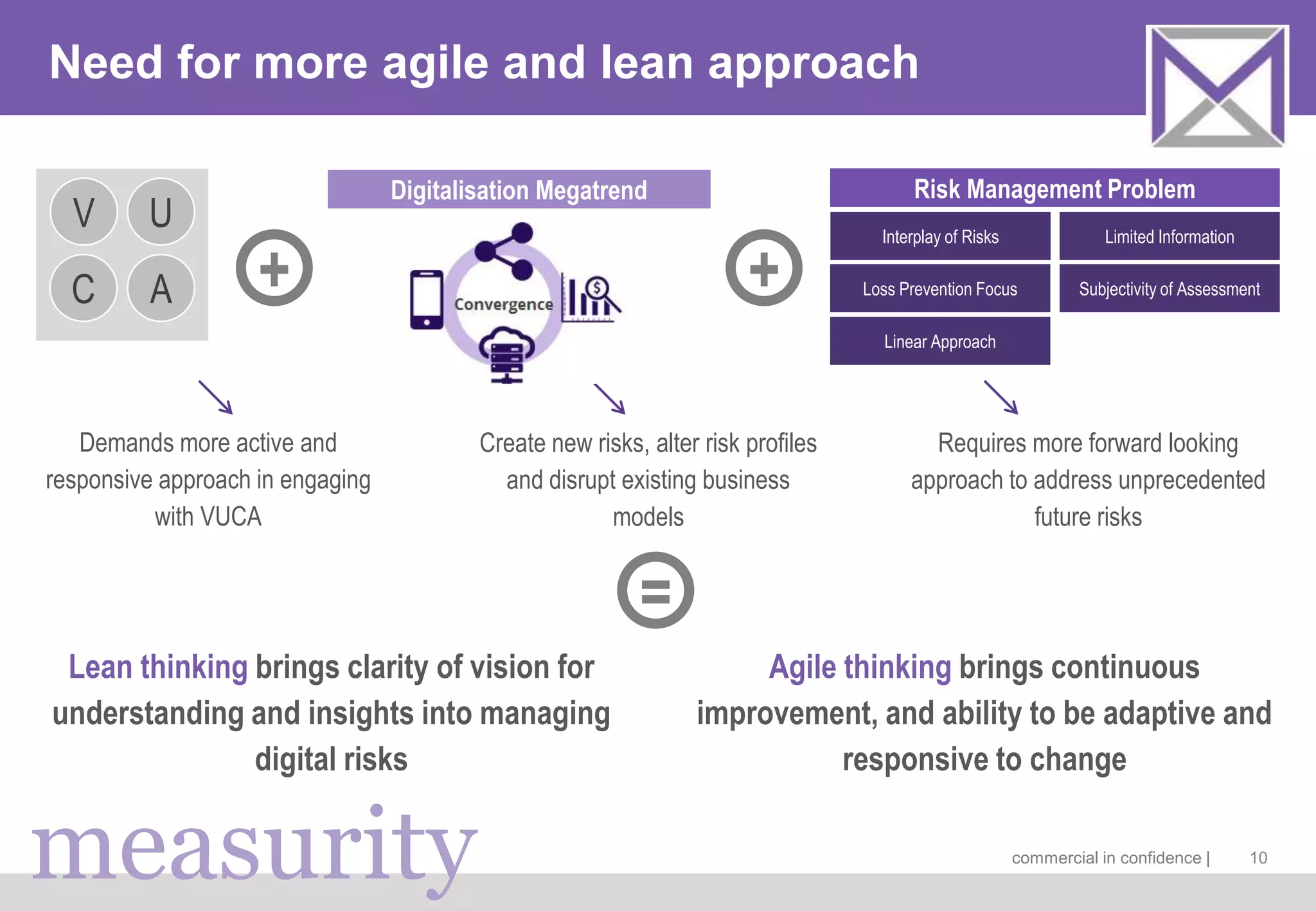
The document discusses managing digitalization risks in a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) environment, emphasizing the need for agile and lean thinking. It criticizes traditional risk management approaches for inadequately handling the complexities of digitalization and promotes a more dynamic strategy focused on value creation and adaptability. Key recommendations include fostering collaboration, taking iterative approaches, and evolving risk assessment methods to better respond to the challenges posed by digital transformation.