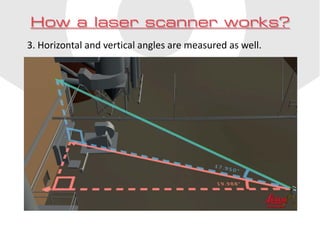
Laser scanning is a technique that can quickly and accurately capture existing structures and objects with a high level of detail. It works by sending out laser beams and measuring the distance, horizontal and vertical angles of reflected beams to calculate XYZ coordinates of up to 1 million points per second. Multiple scans may be required to fully capture the object or structure, and they are then registered into a single point cloud. This scan data can be used to build a Building Information Model (BIM) in Autodesk Revit, with the scan-to-BIM process involving scanning the site, cleaning up the point cloud data, and constructing a model from the point cloud.