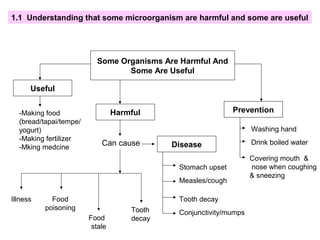
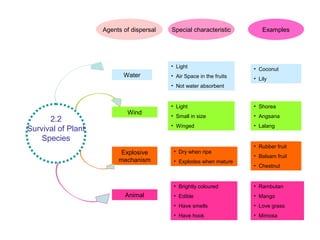
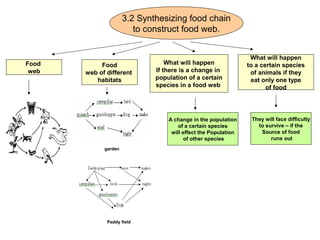
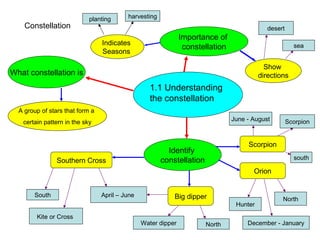
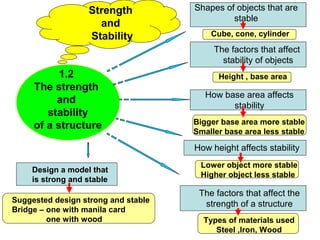
Microorganisms are tiny living things that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Some microorganisms are useful, like those that help make bread rise, while others are harmful and can cause illness. Animals and plants have various survival strategies to ensure their species continue, such as caring for offspring or having mechanisms to disperse seeds. Food chains show the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, and food webs illustrate the complex interactions between multiple food chains.