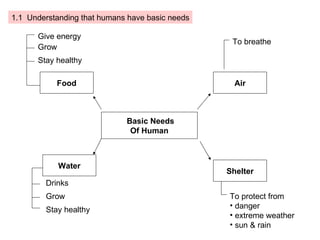
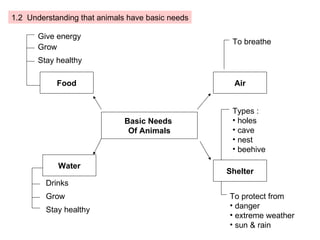
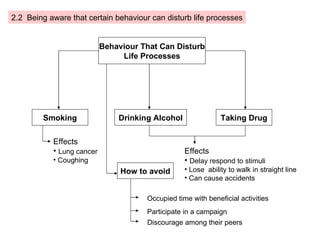
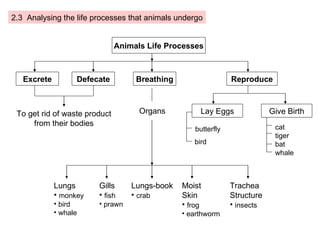
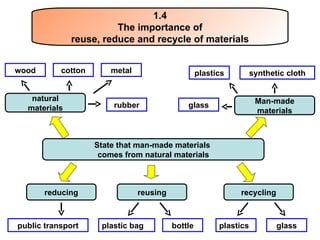
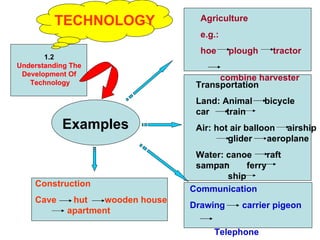
The document provides information about a mind map for Year 4 on investigating living things. It discusses the basic needs of humans and animals, as well as the basic needs of plants. It also analyzes various life processes that humans, animals, and plants undergo, such as breathing, excreting, and reproducing. The document discusses characteristics and behaviors that help protect animals from dangers, extreme weather, and enemies. It also discusses characteristics that help plants protect themselves from enemies and dry regions/strong winds. Finally, it covers investigating force and energy, including measurement units and properties of materials.