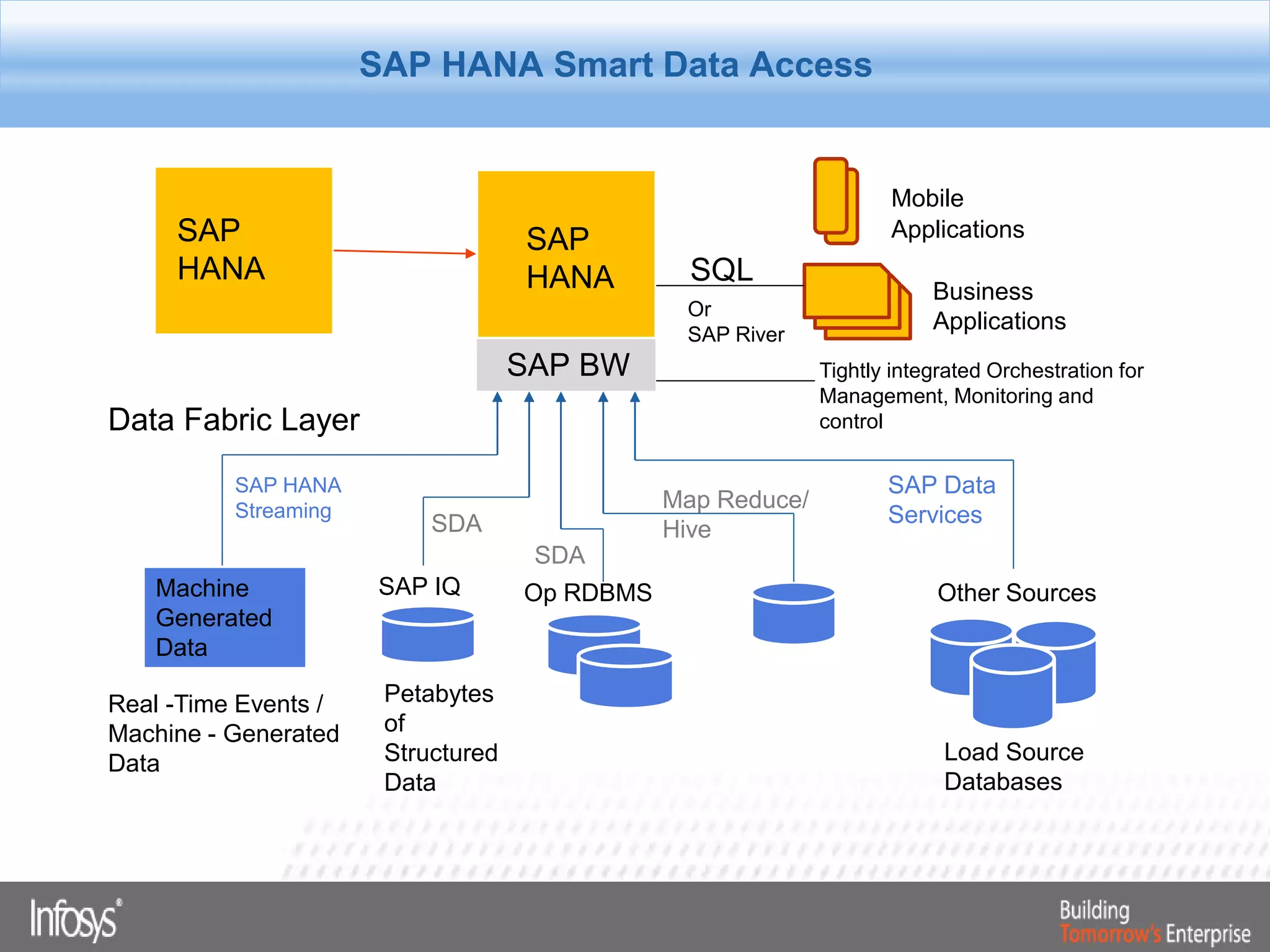
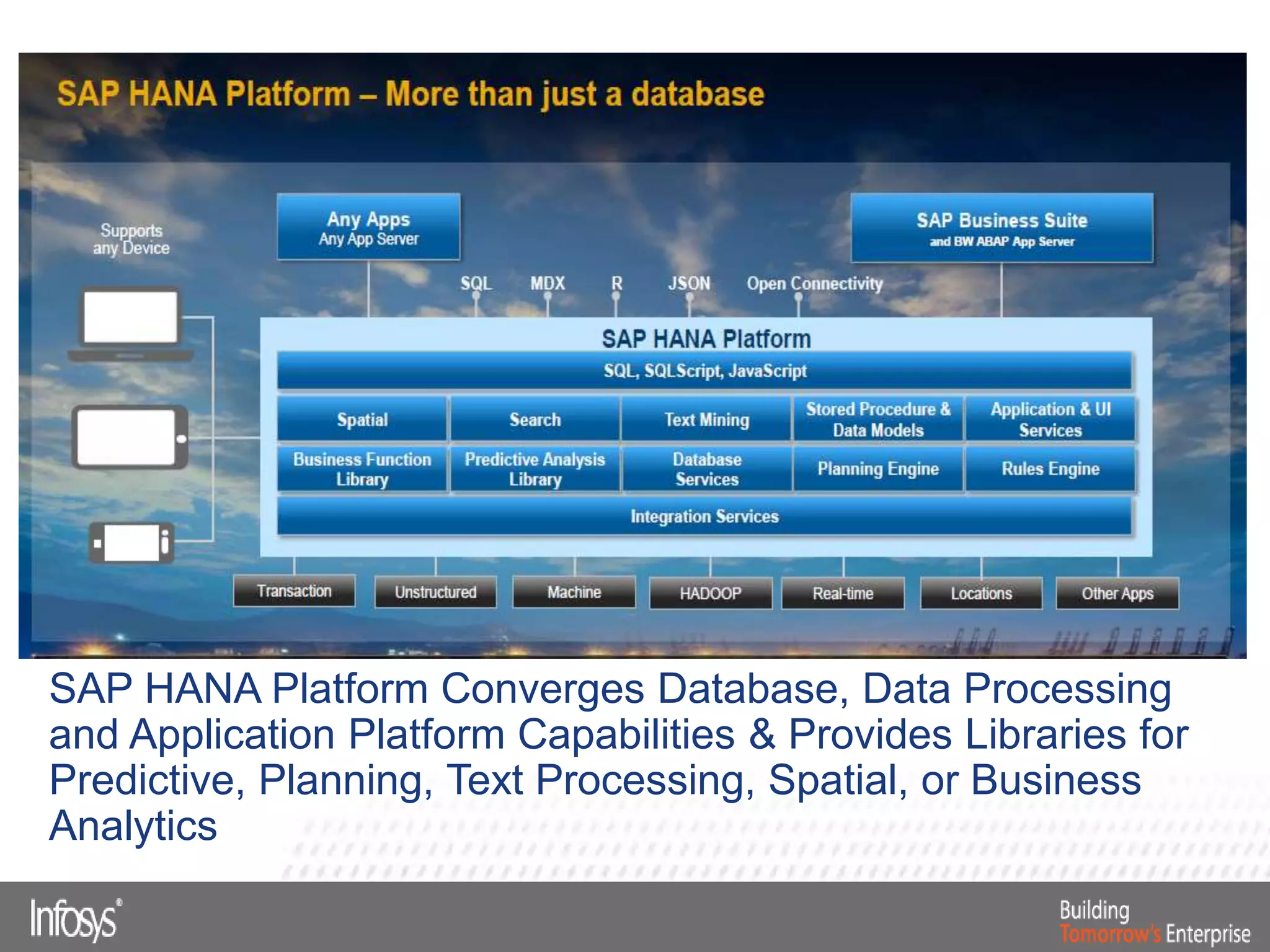
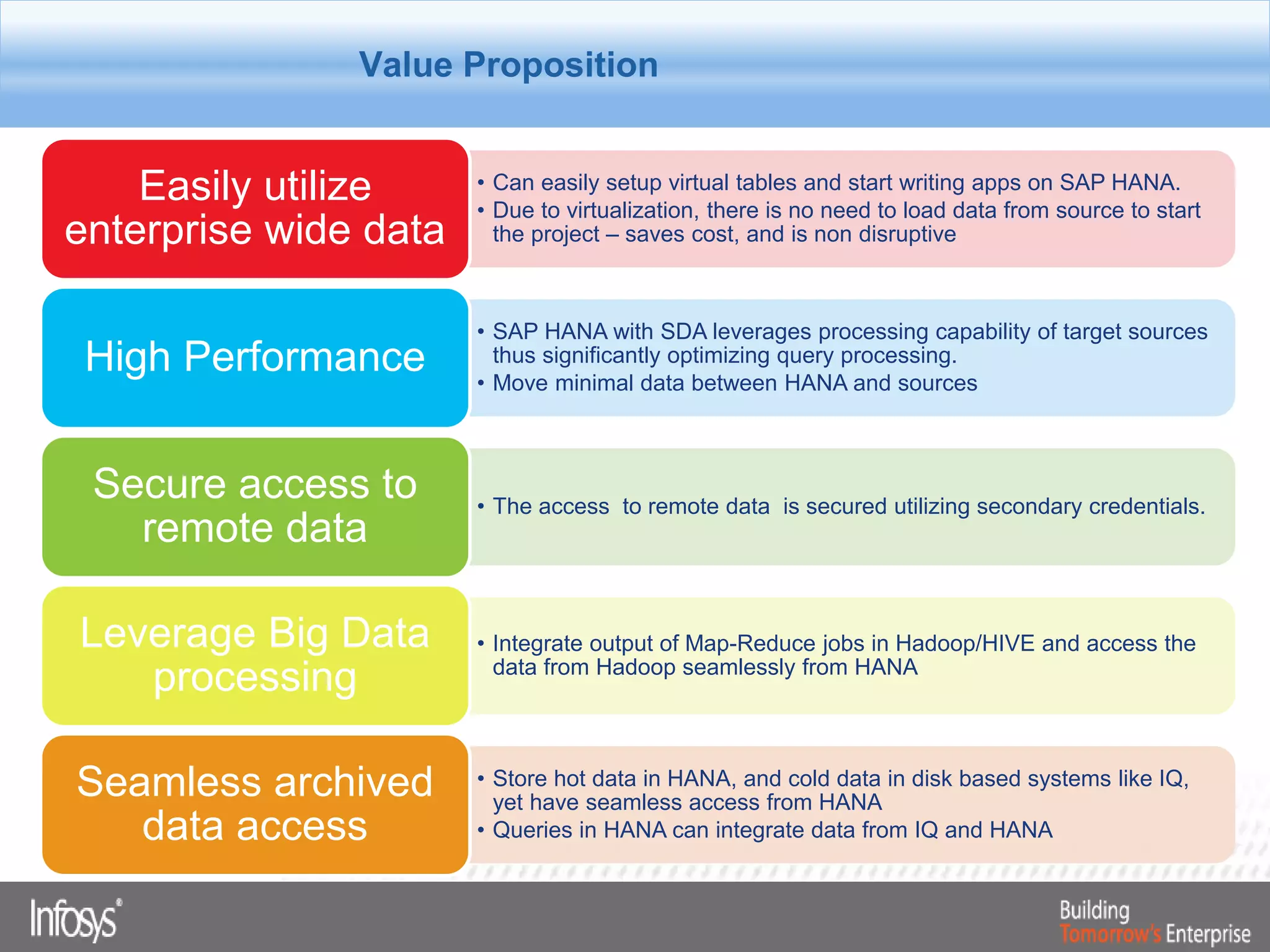
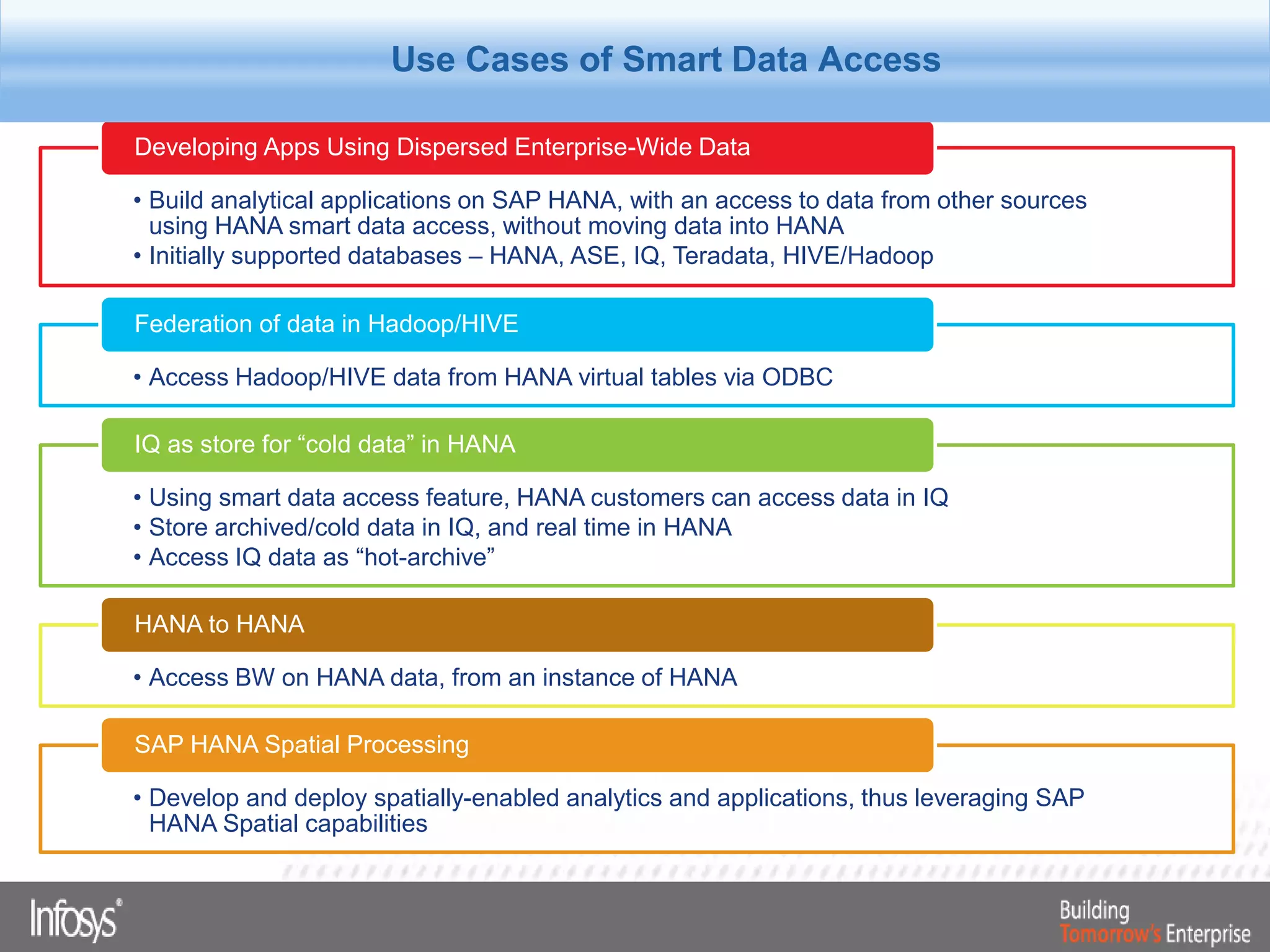
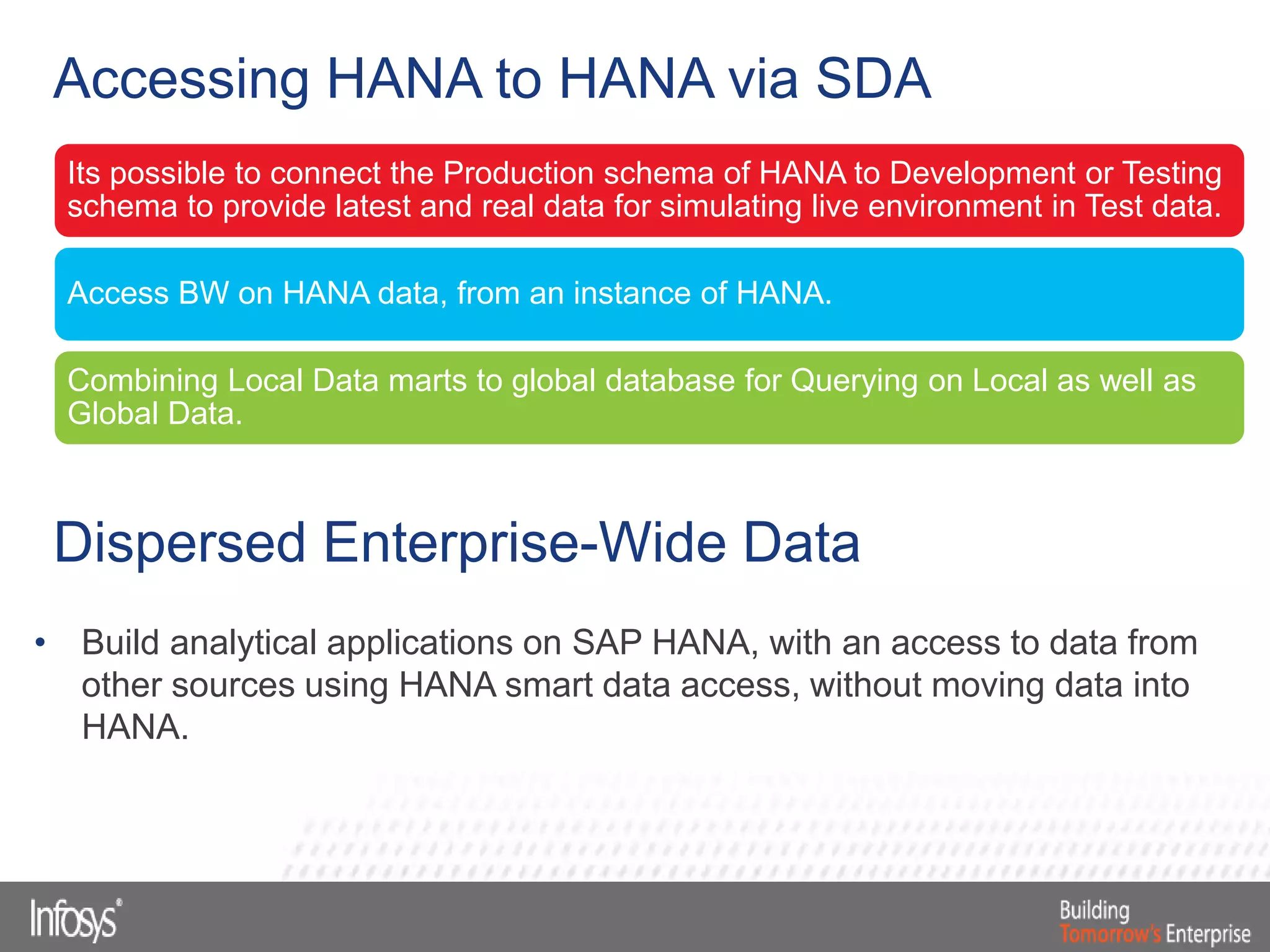
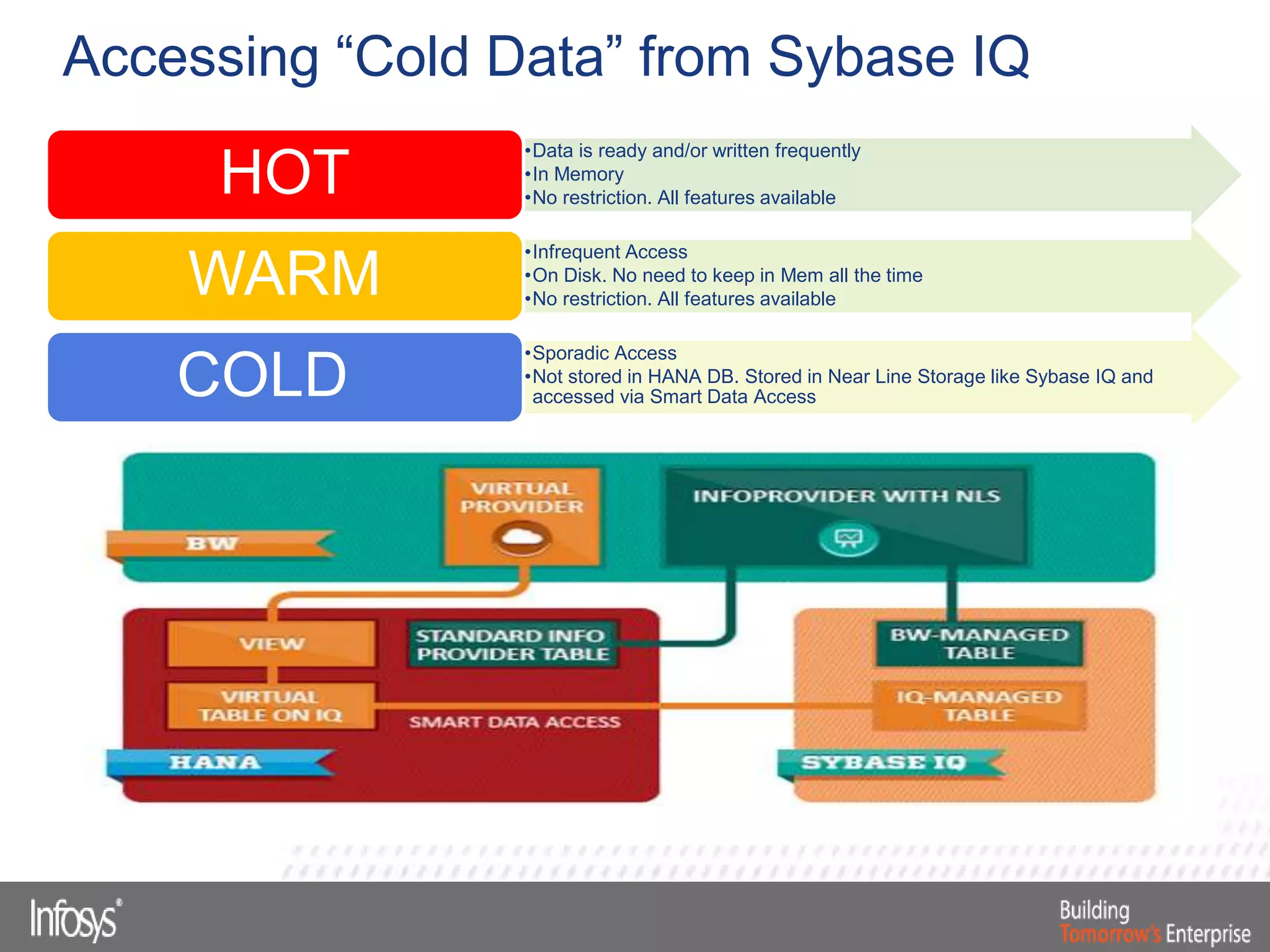
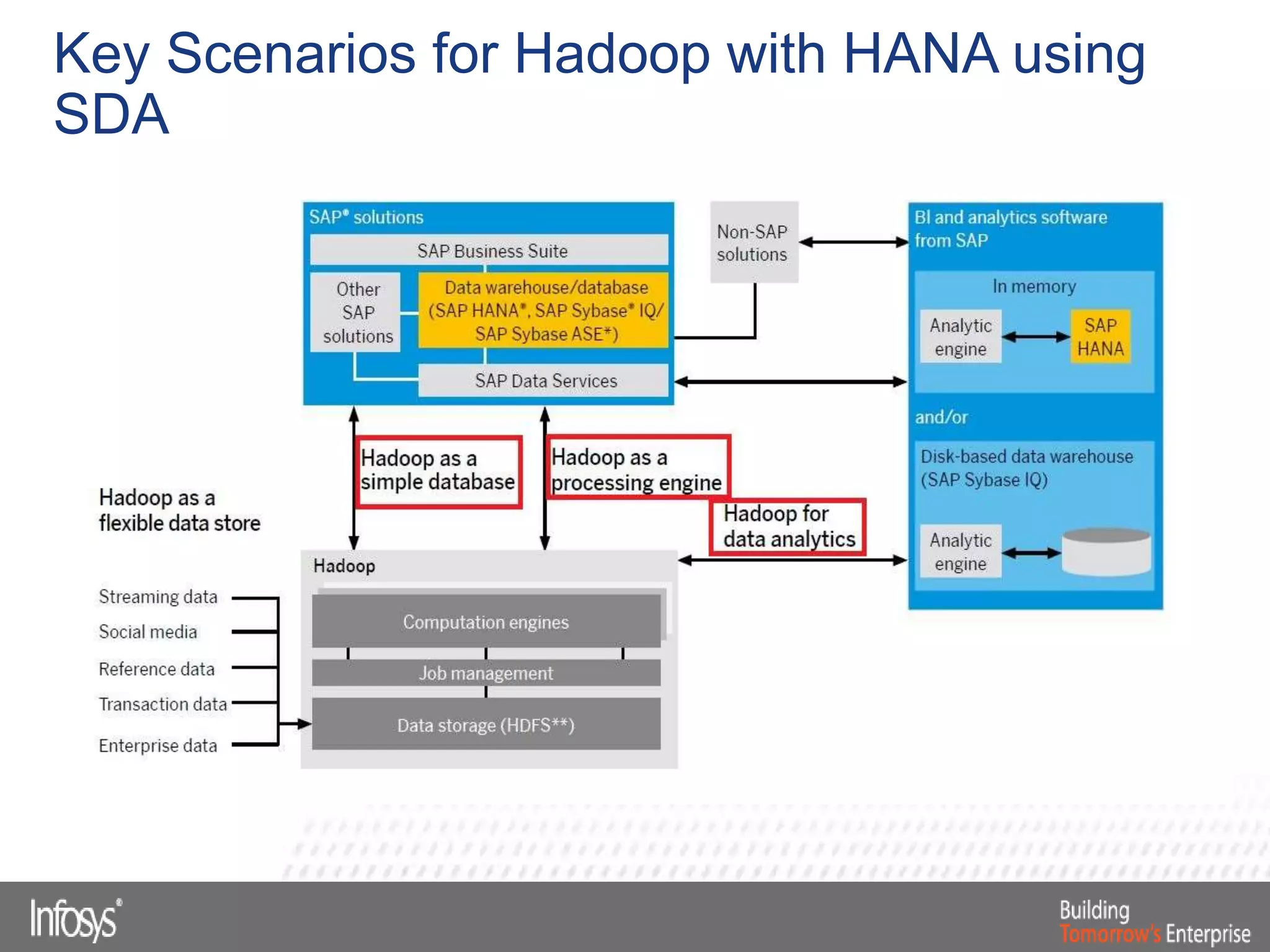
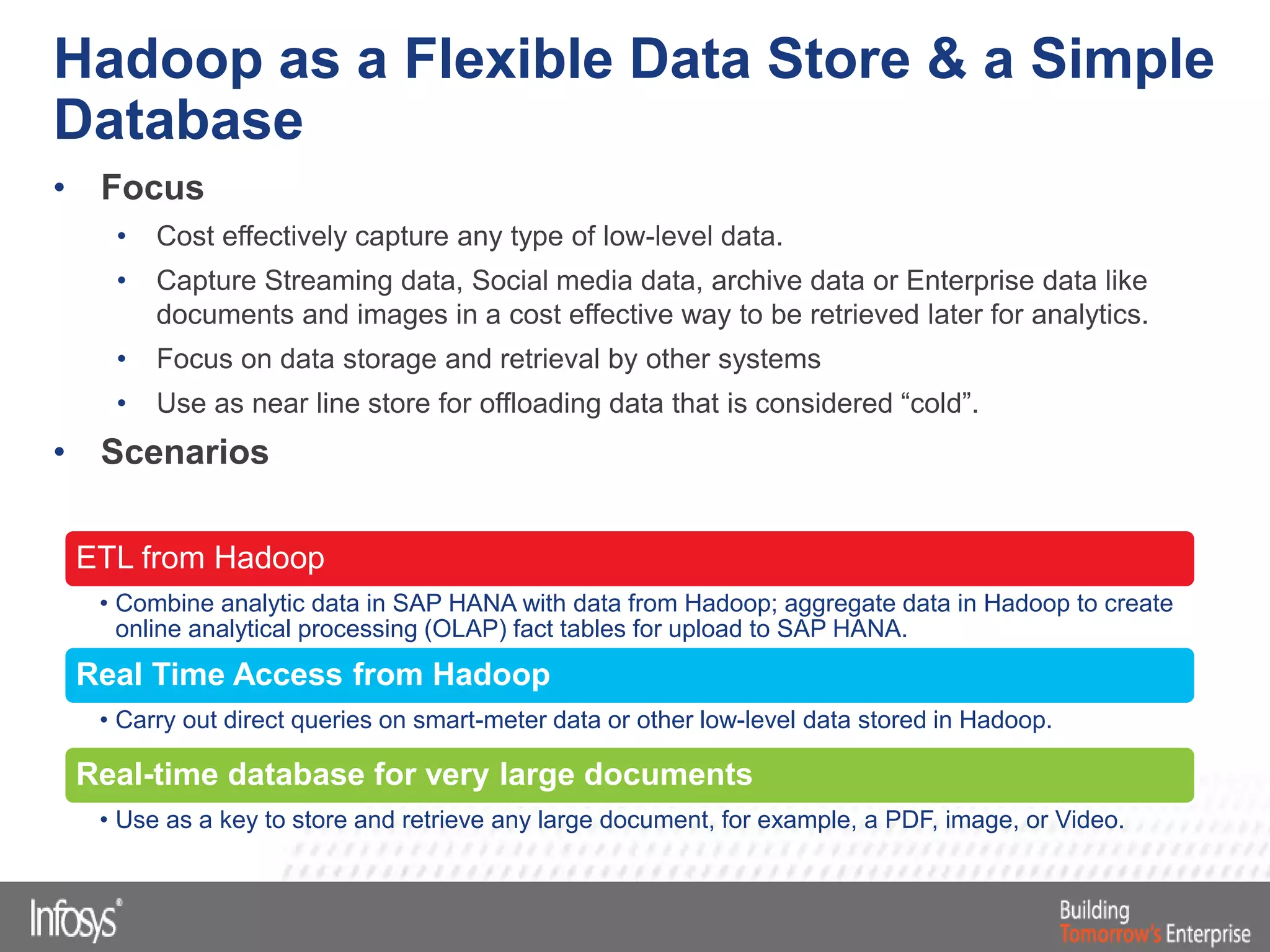
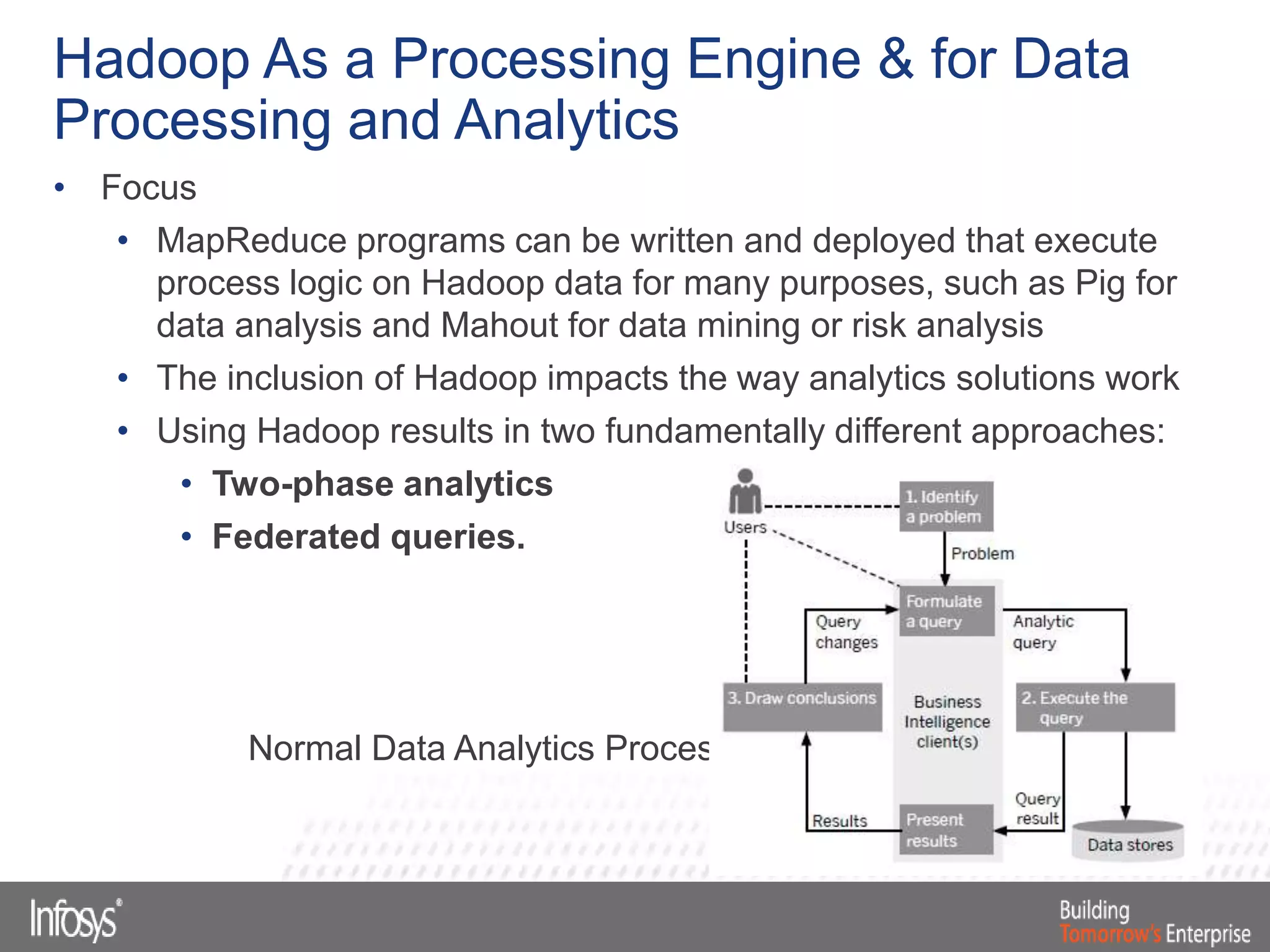
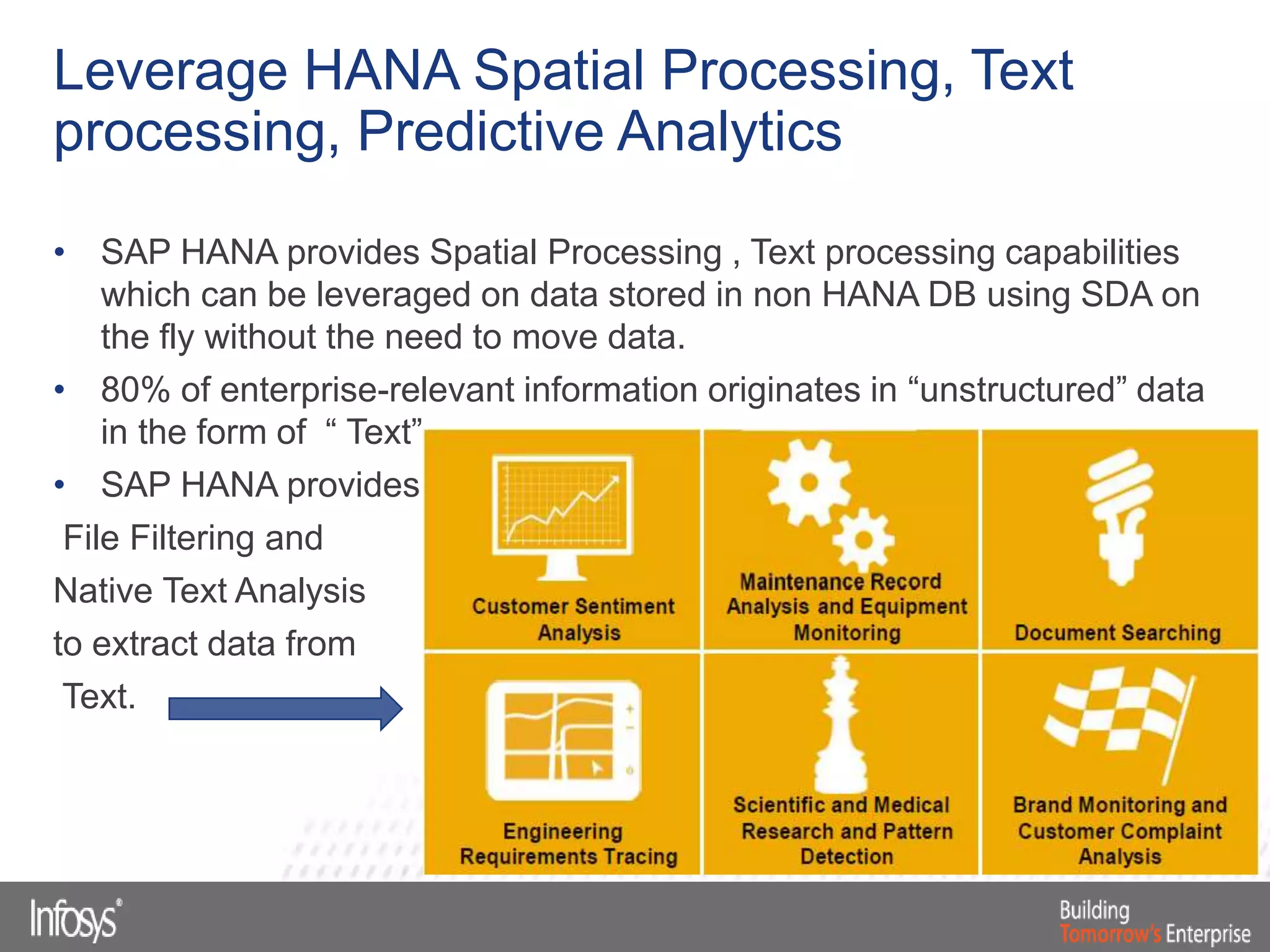
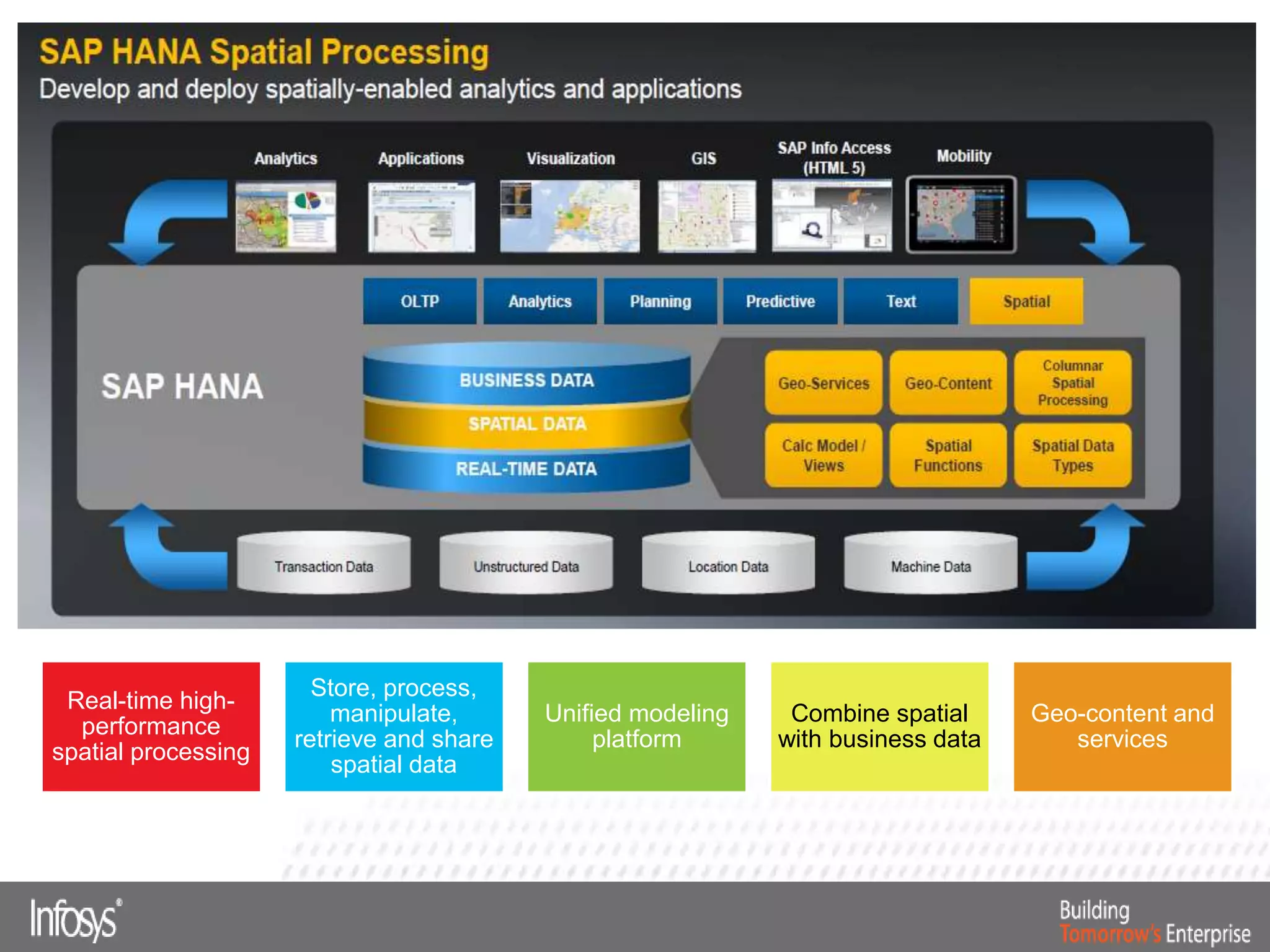
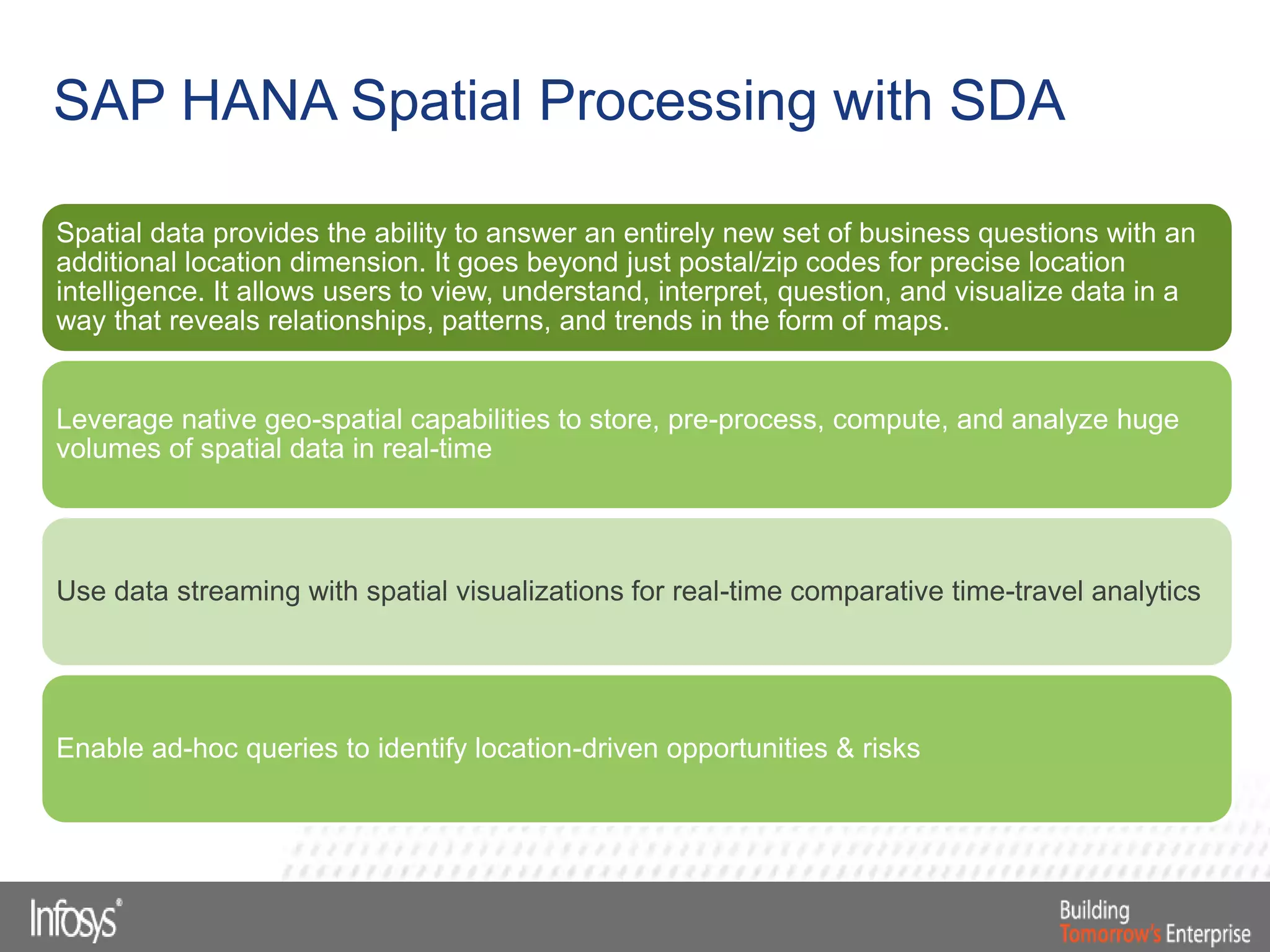
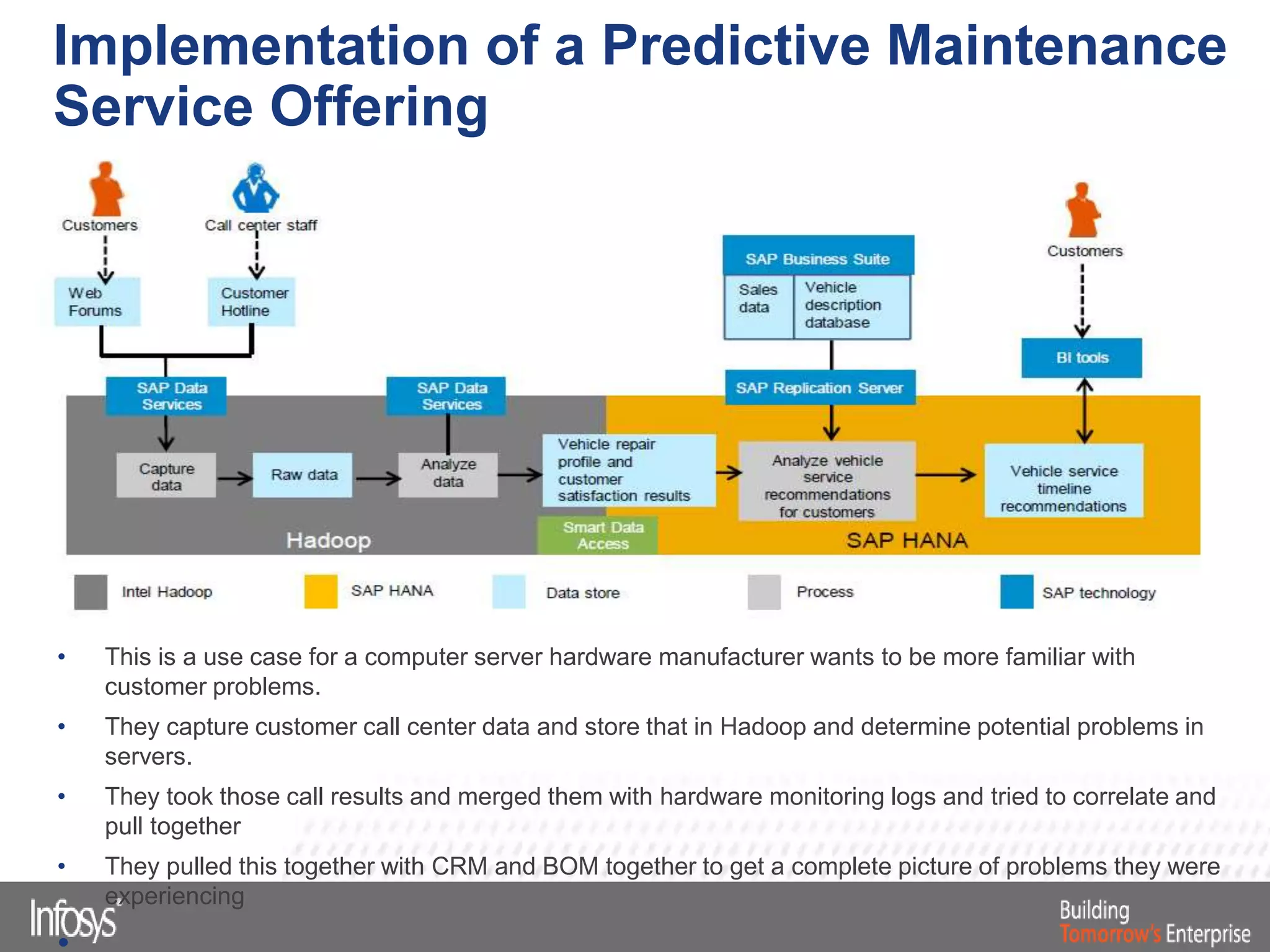
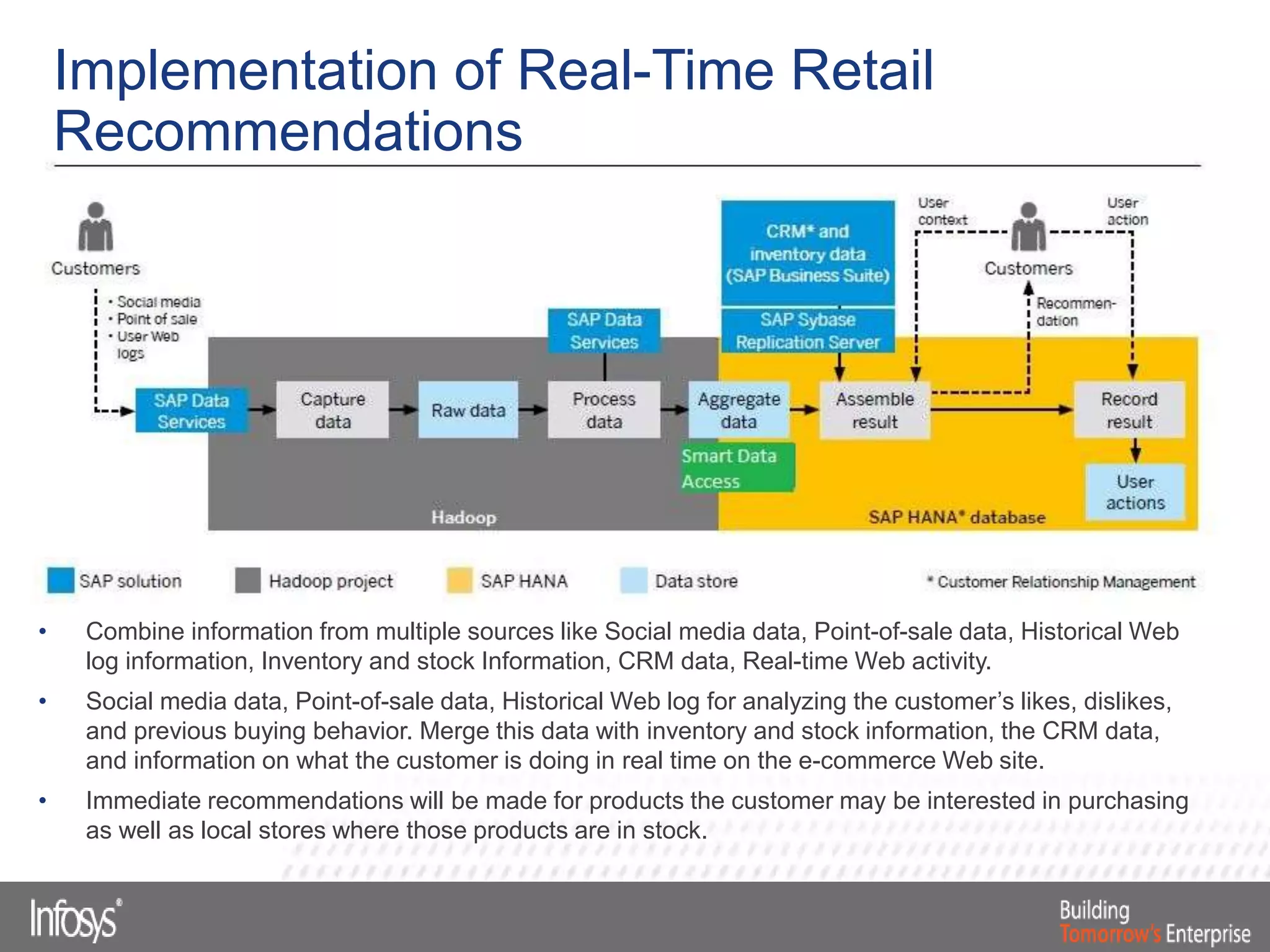
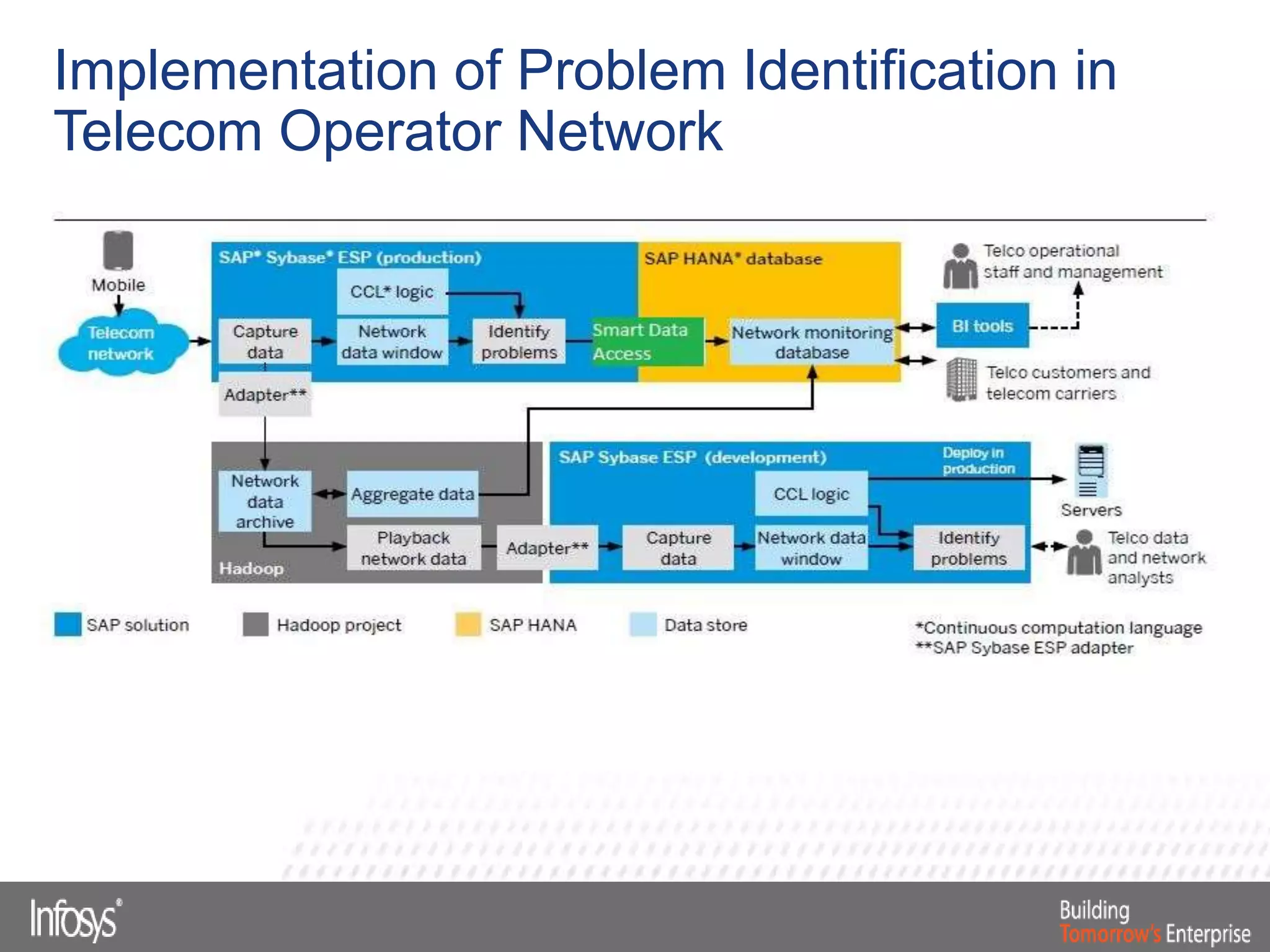
This document discusses Smart Data Access (SDA) in SAP HANA. SDA allows virtual access to remote data sources without moving the data into HANA. It discusses use cases like accessing HANA and Sybase IQ data, using Hadoop for flexible data storage and processing, and leveraging HANA capabilities like spatial processing and analytics. Example implementations described are predictive maintenance using various data sources, real-time retail recommendations, and problem identification in telecom networks.