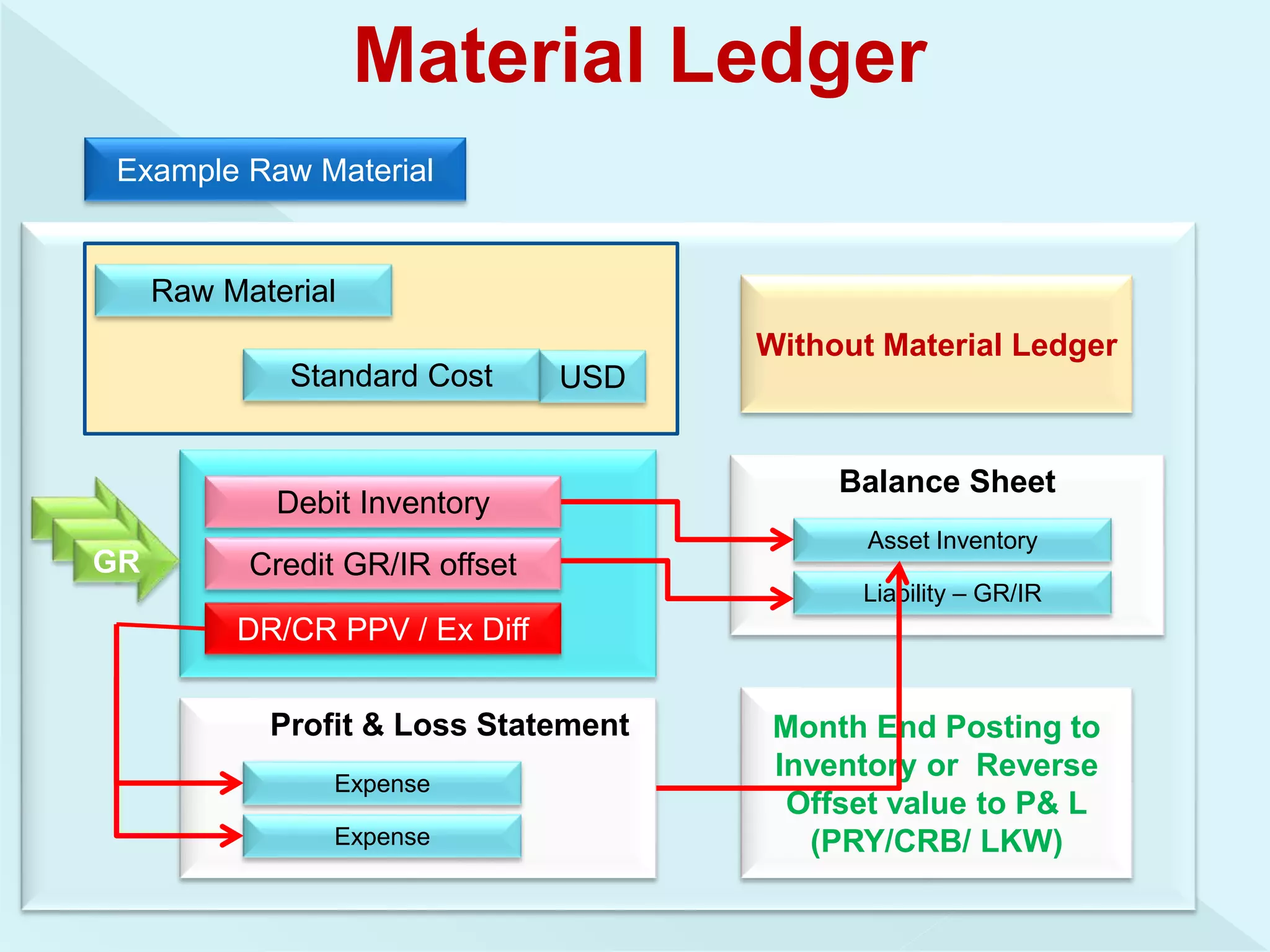
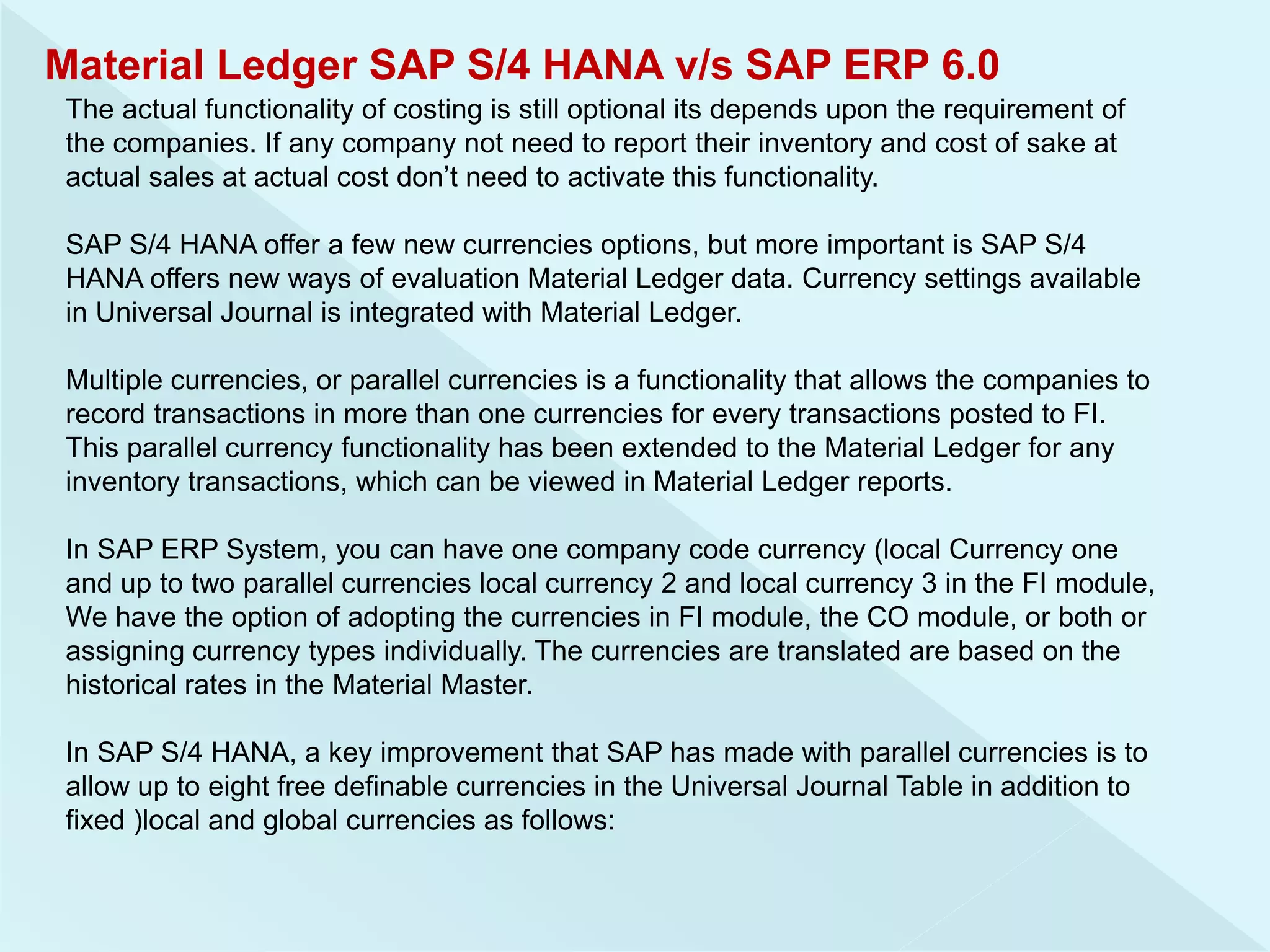
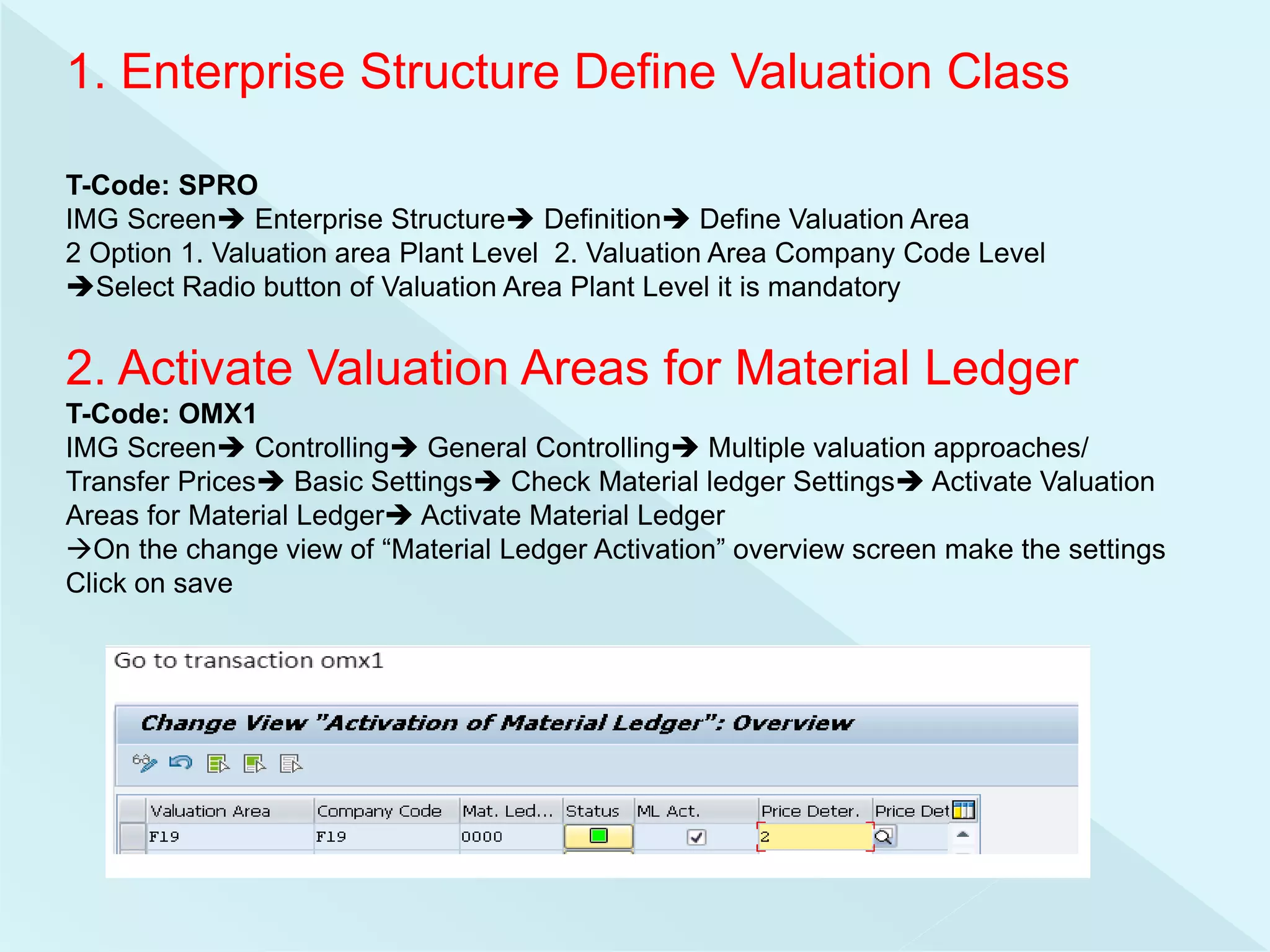
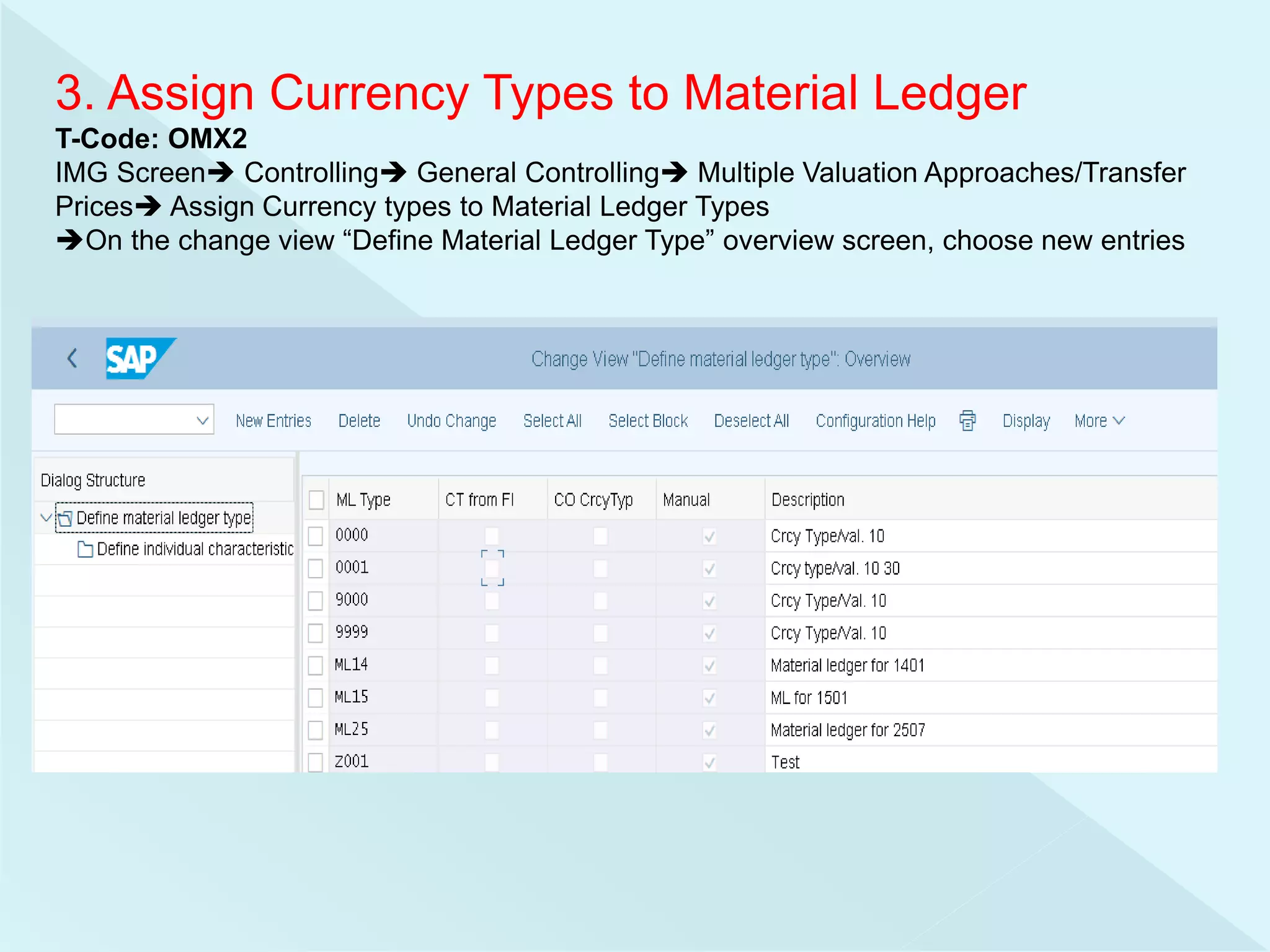
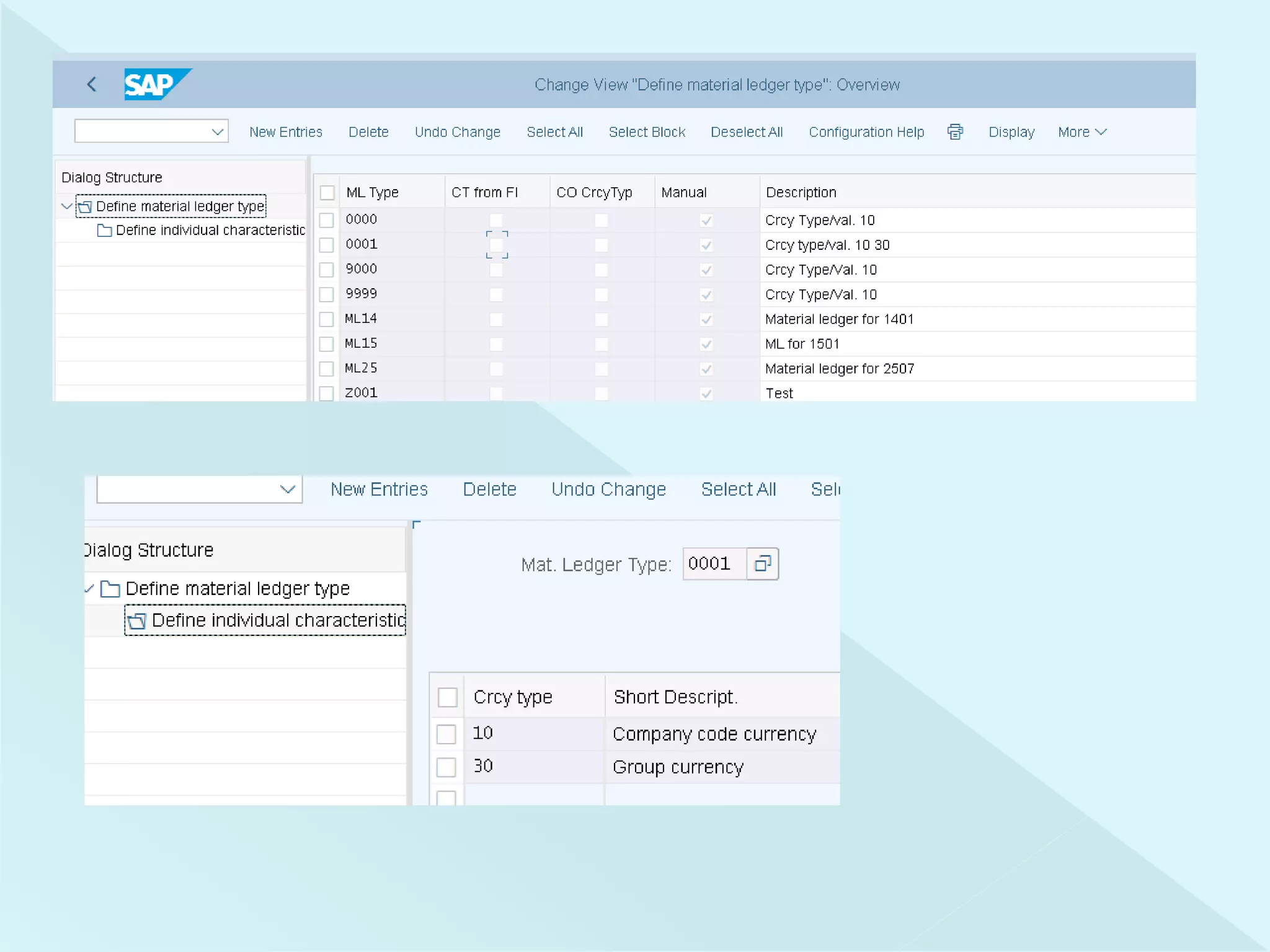
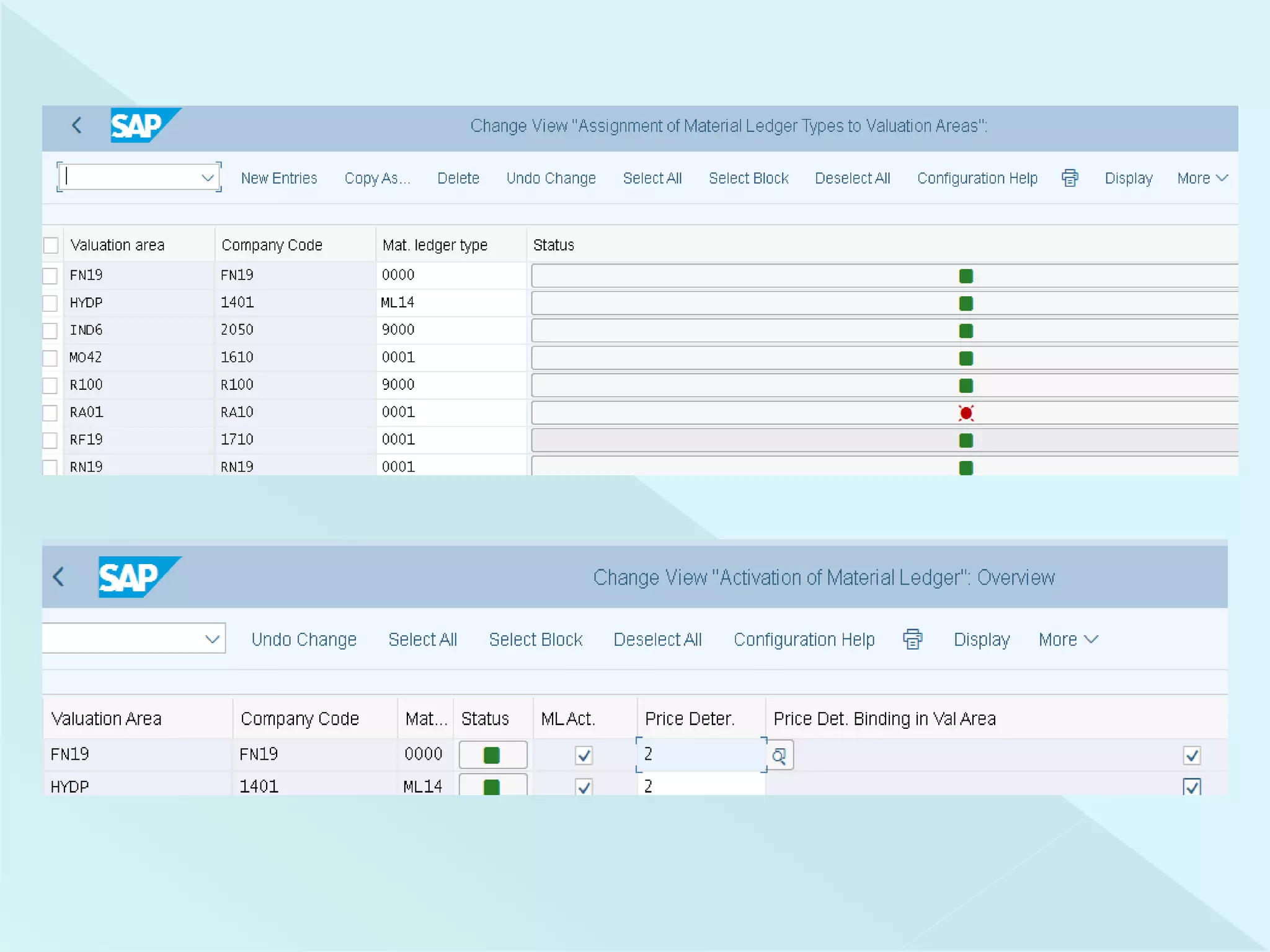
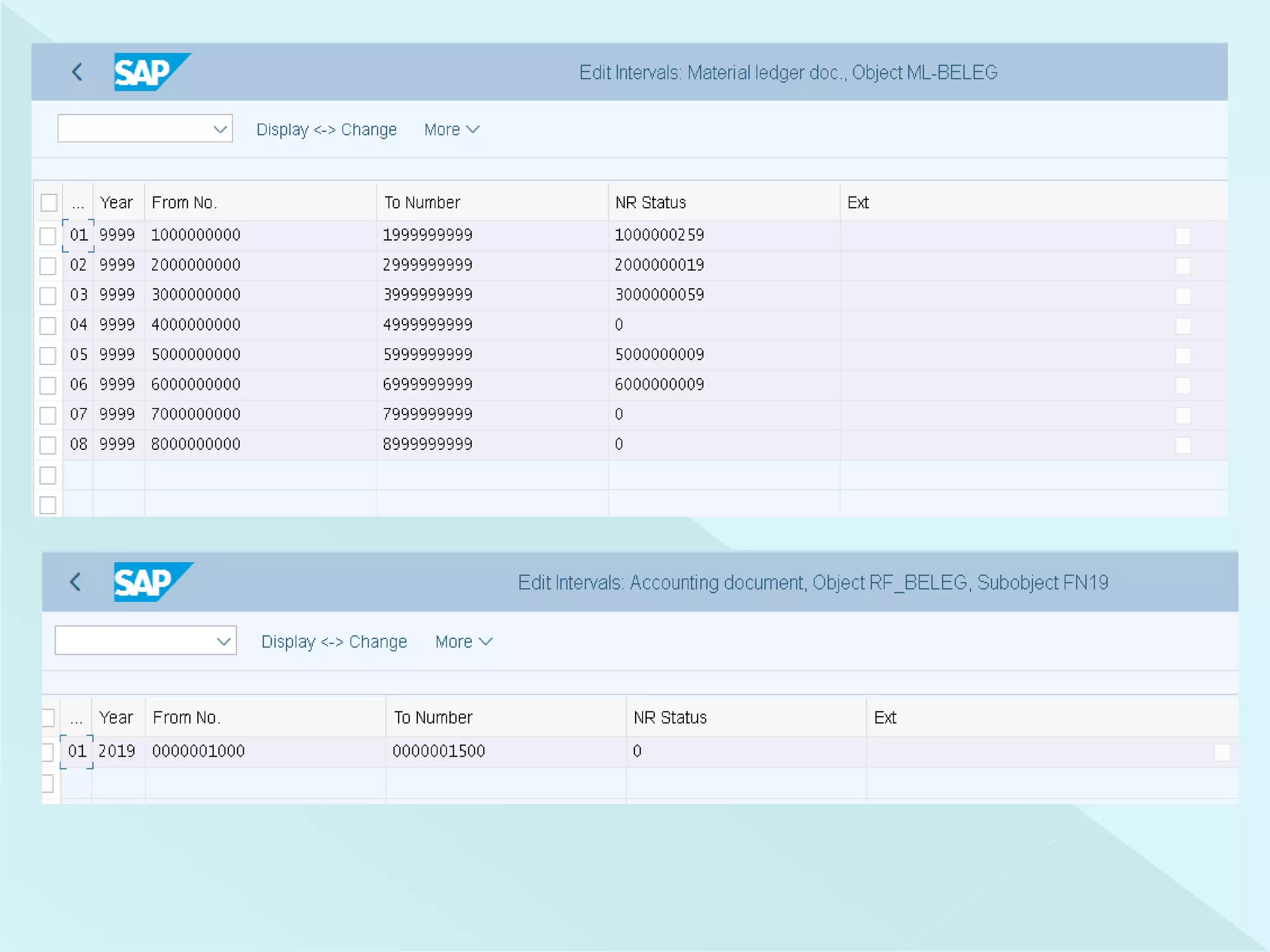
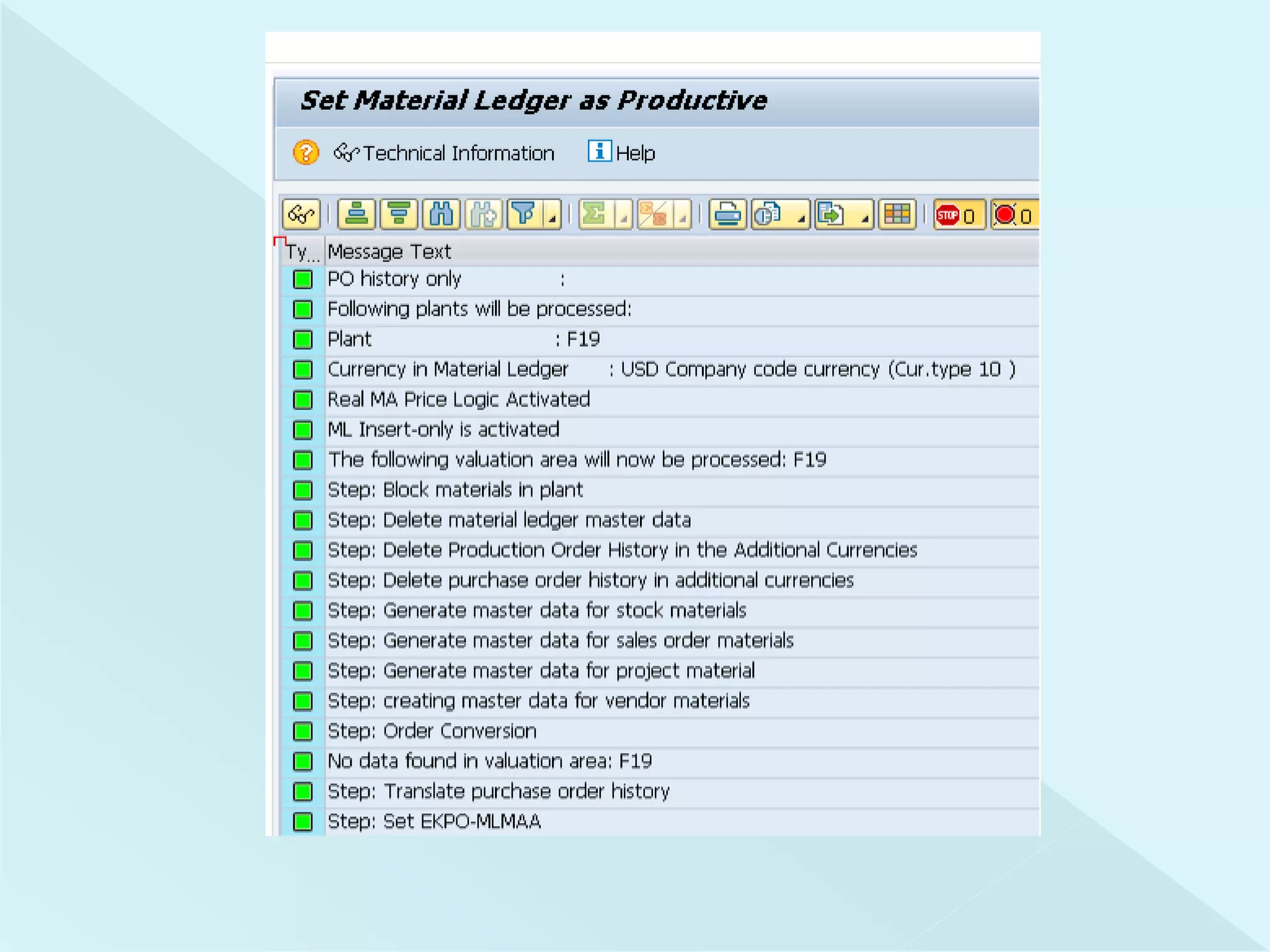
This document provides information about configuring and activating Material Ledger in SAP. It discusses the objectives of Material Ledger, the differences between Material Ledger in SAP S/4HANA versus SAP ERP, and the steps to activate Material Ledger which include assigning currency types, valuation areas, material update structures, and number ranges. It emphasizes that activating Material Ledger is mandatory in SAP S/4HANA to allow inventory valuation in multiple currencies at actual costs.