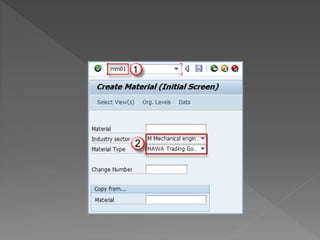
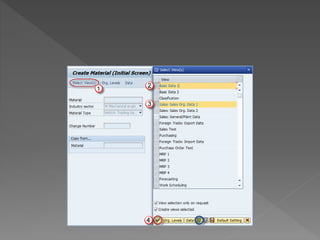
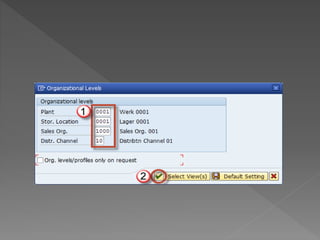
The document outlines the SAP Material Management (MM) module, which is integral to the logistics area of an organization, managing procurement, inventory, and material planning. It describes the importance of master data, detailing both material and vendor master information, as well as the processes involved in creating and managing material records. Additionally, it provides instructions on how to use transactions such as MM01 and MM17 for material creation and mass changes, alongside a call to action for training services.