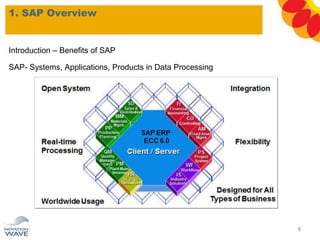
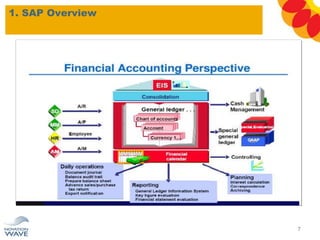
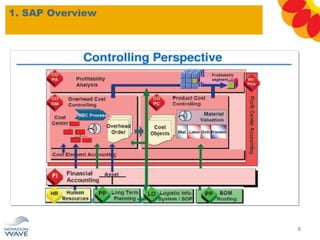
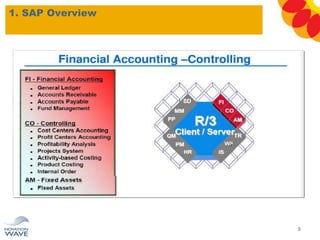
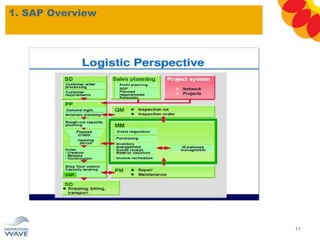
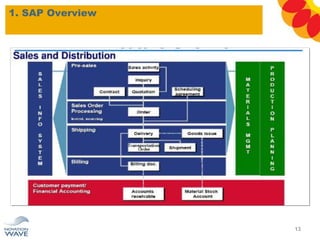
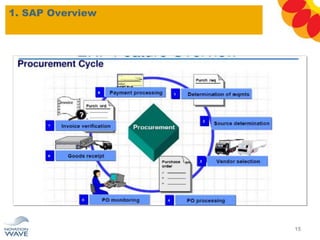
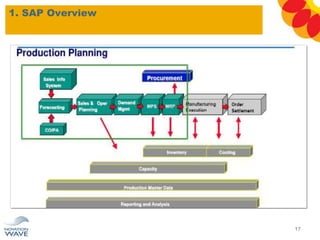
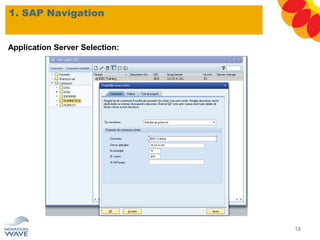
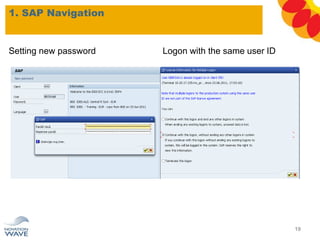
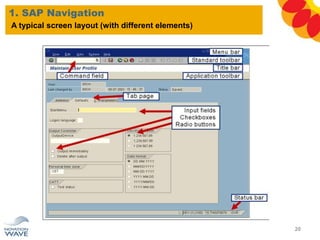
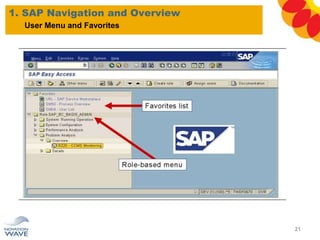
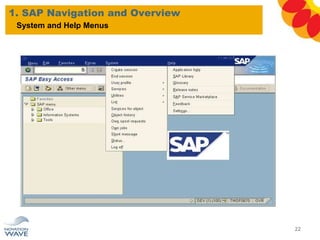
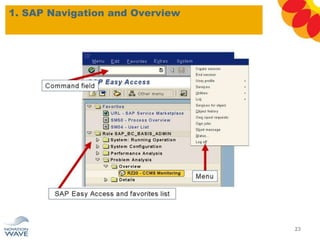
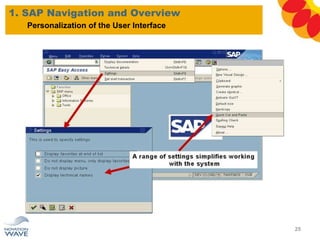
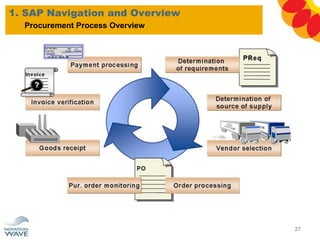
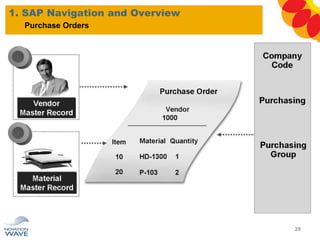
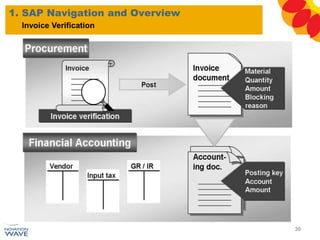
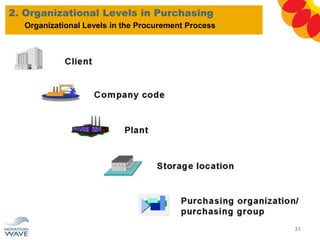
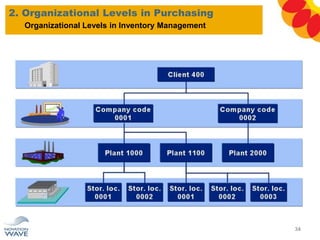
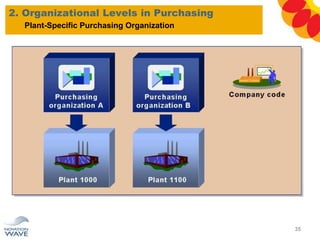
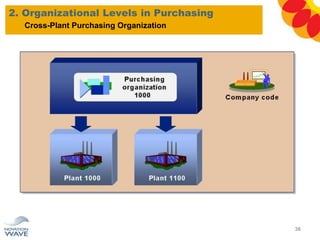
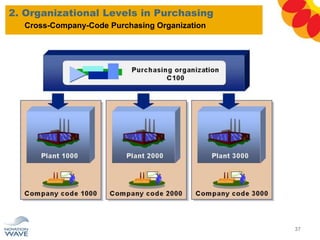
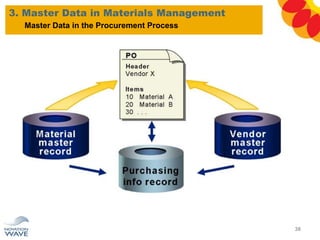
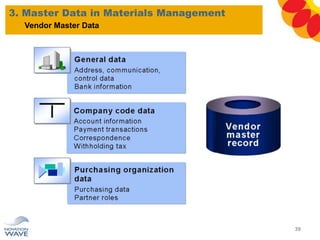
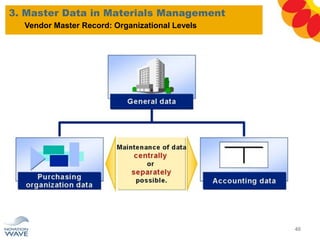
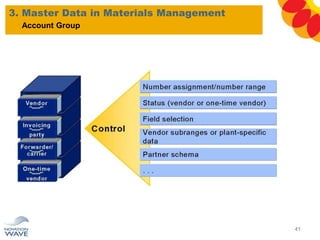
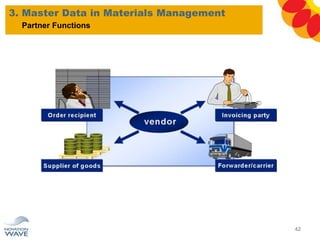
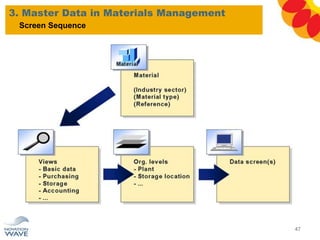
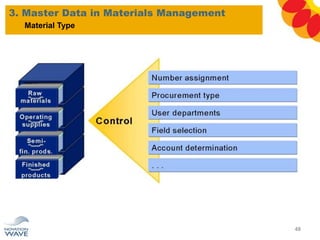
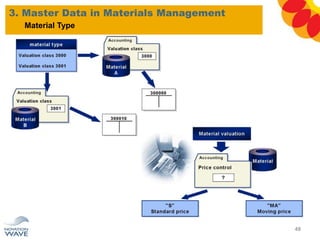
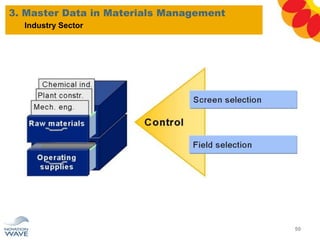
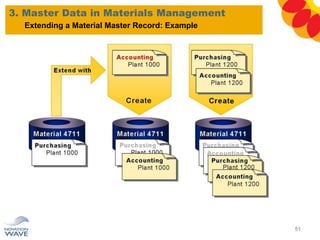
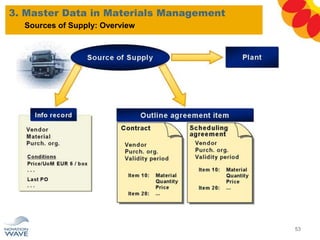
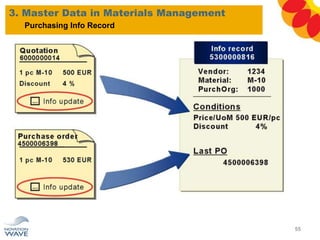
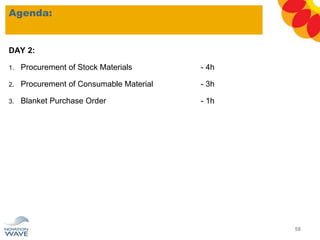
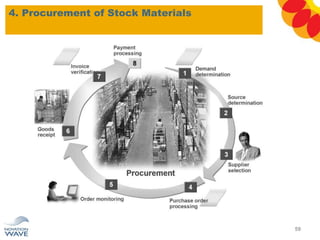
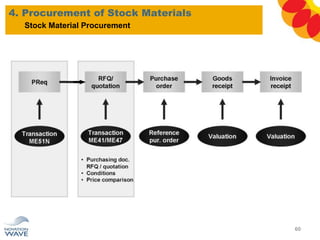
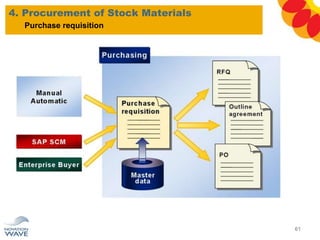
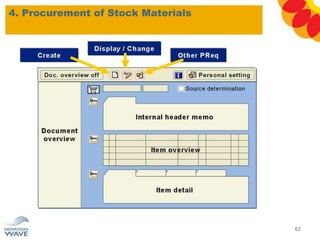
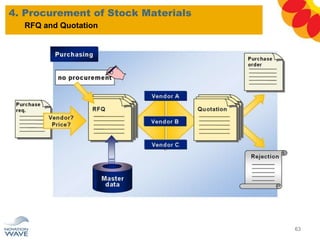
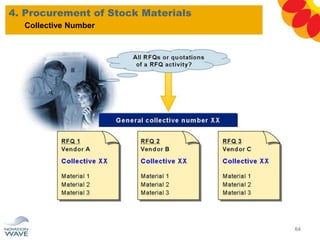
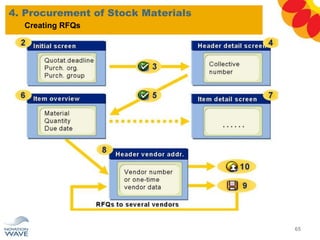
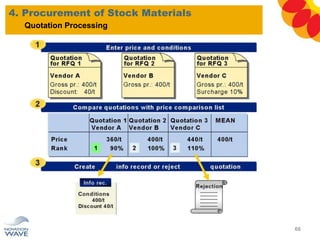
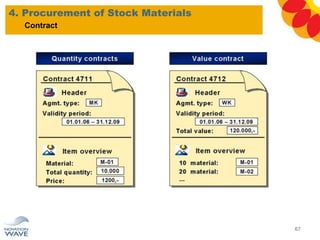
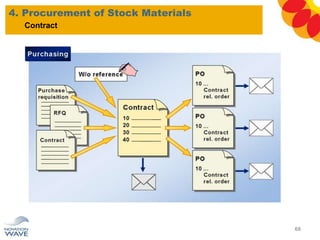
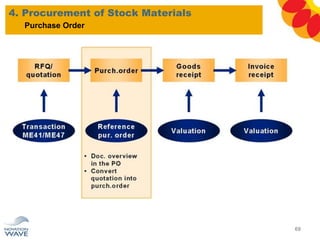
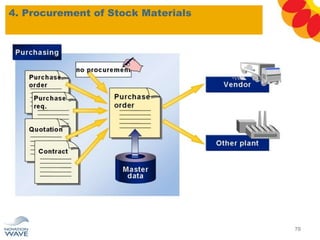
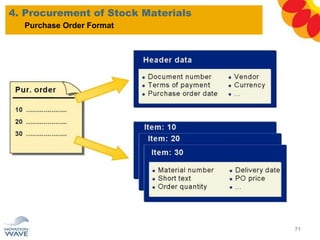
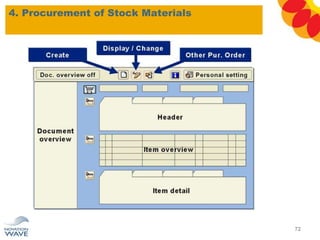
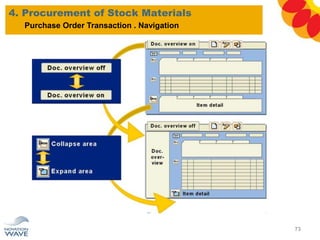
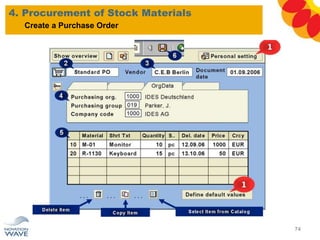
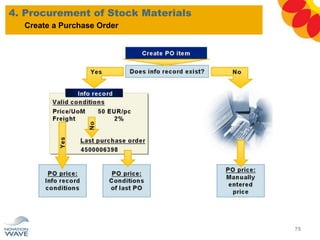
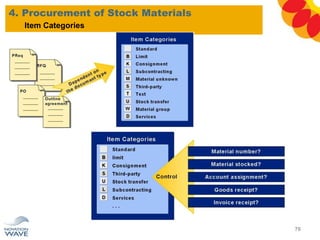
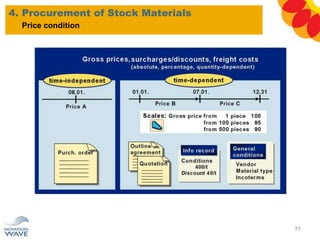
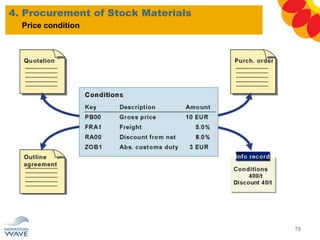
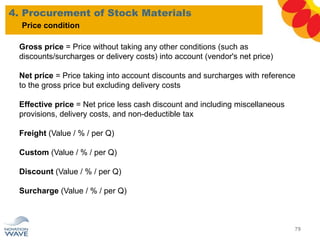
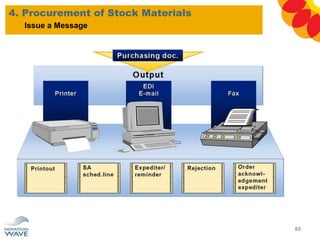
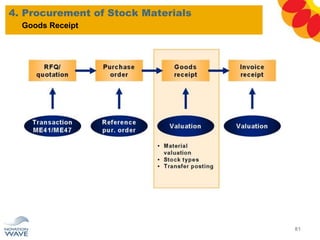
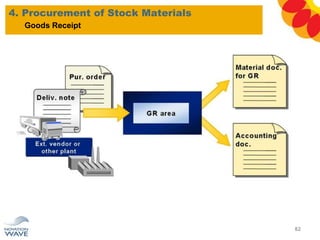
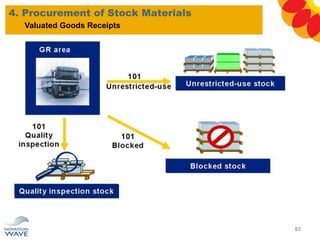
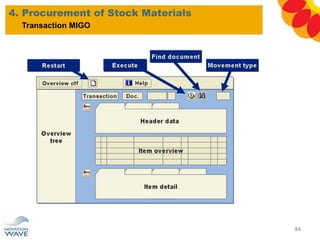
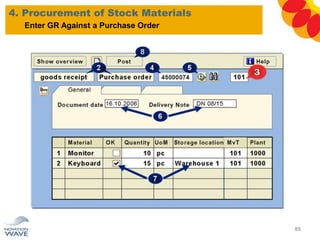
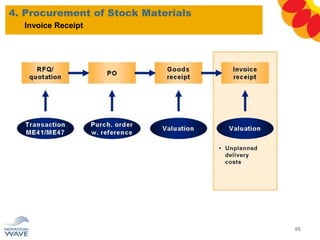
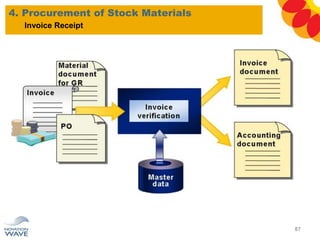
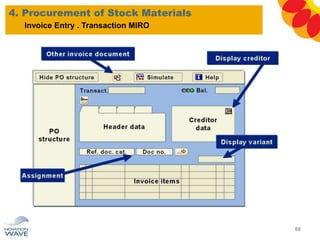
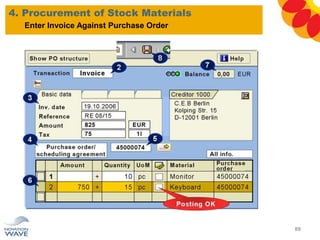
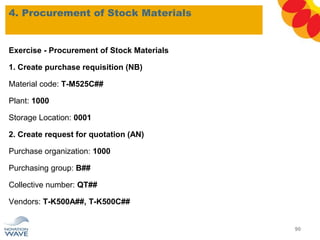
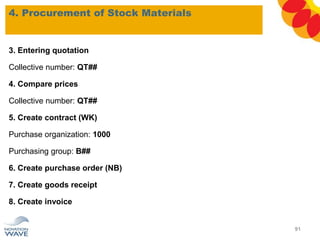
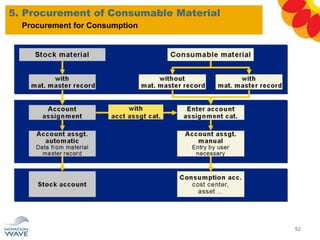
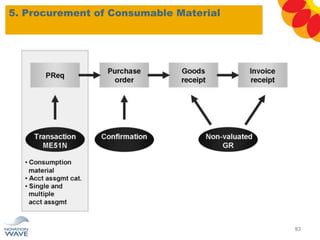
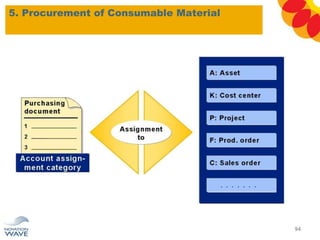
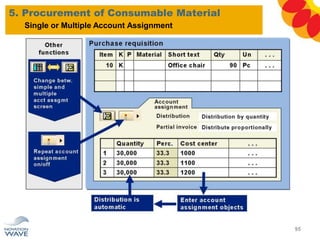
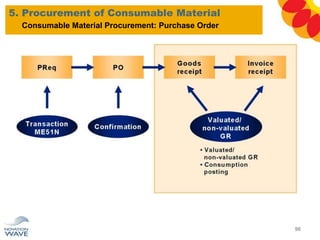
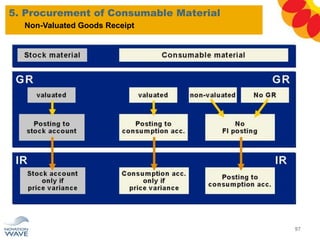
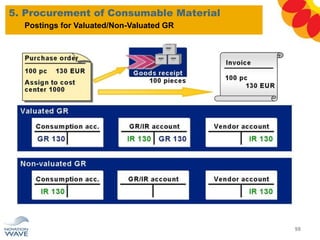
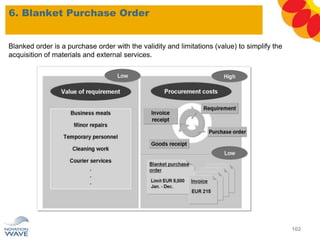
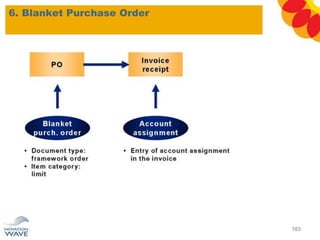
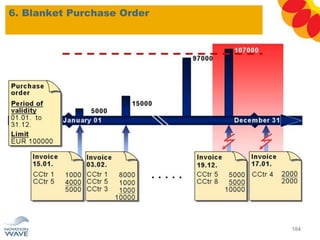
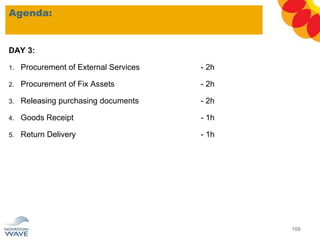
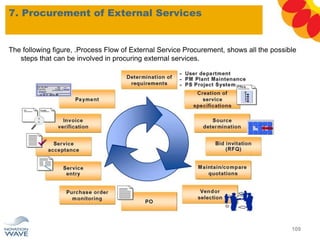
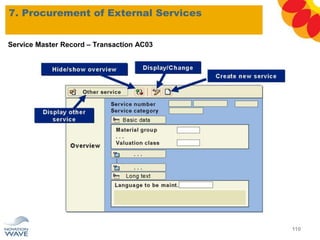
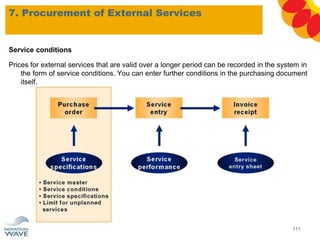
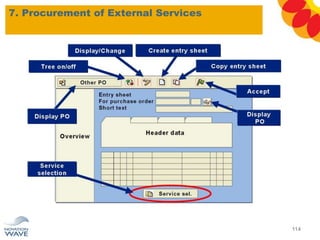
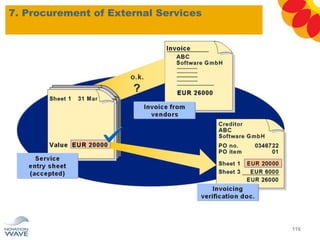
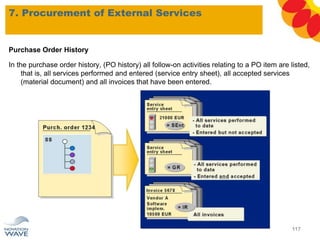
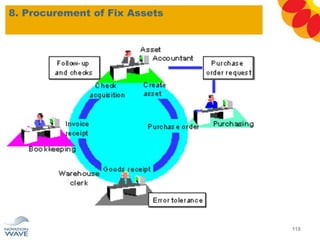
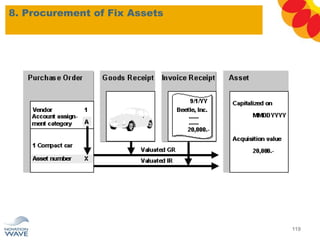
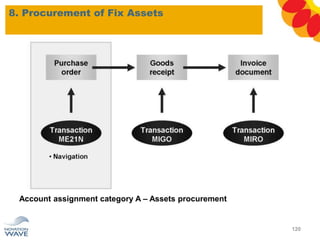
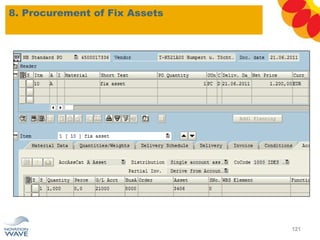
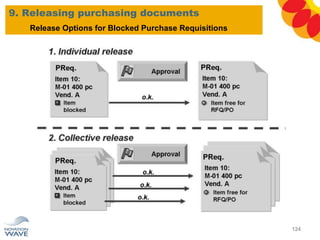
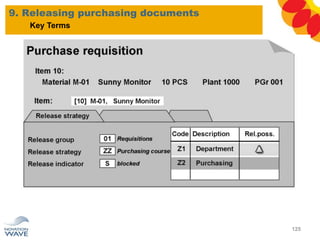
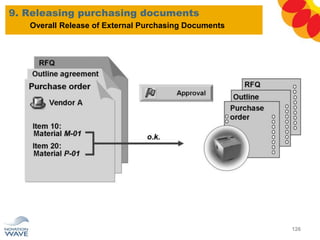
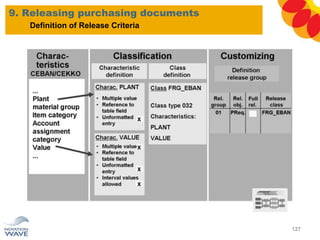
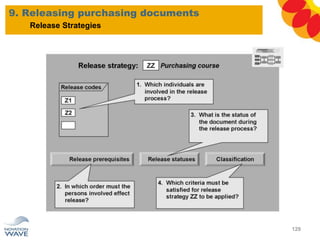
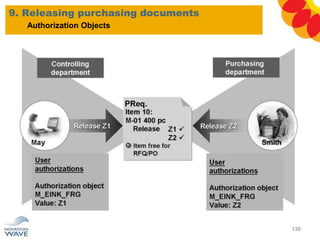
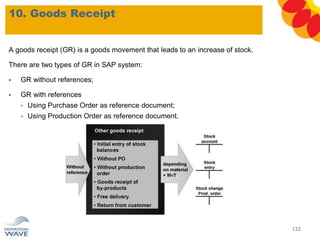
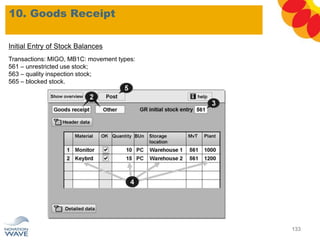
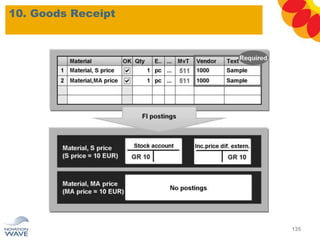
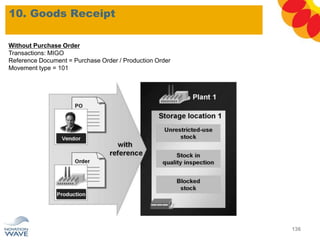
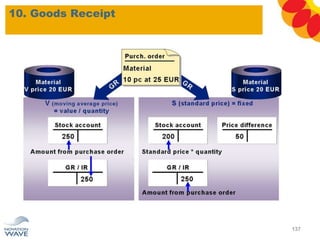
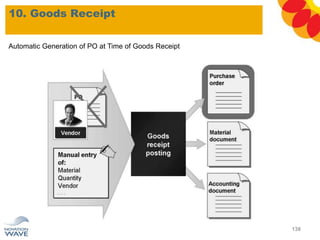
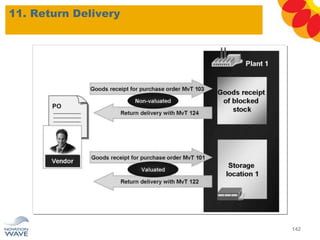
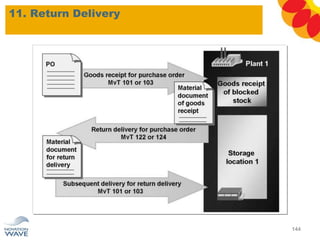
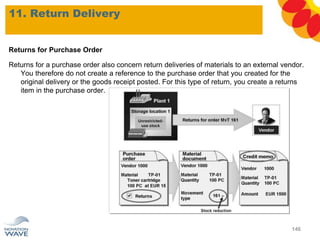
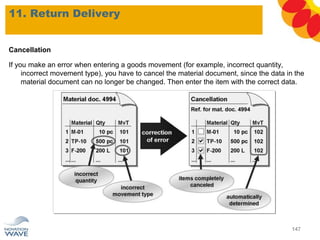
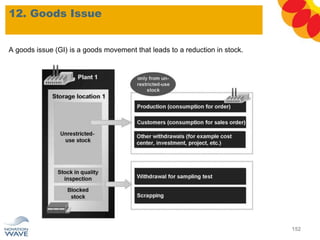
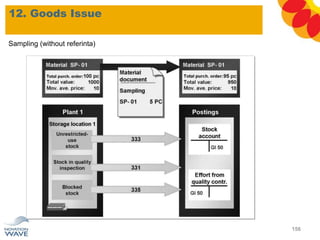
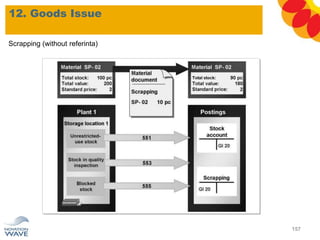
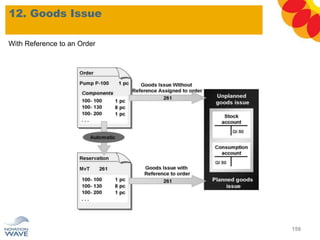
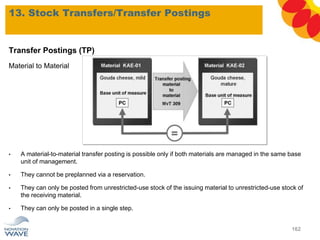
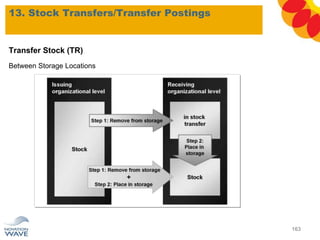
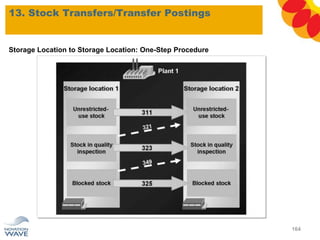
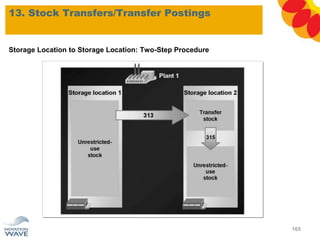
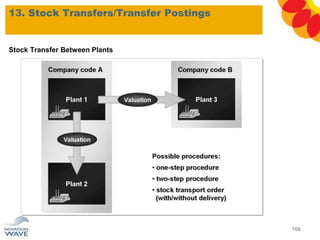
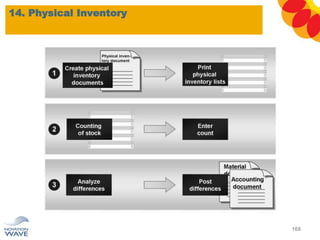
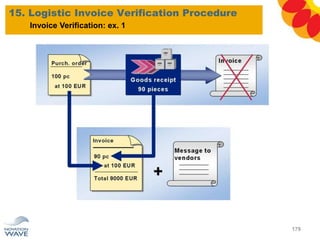
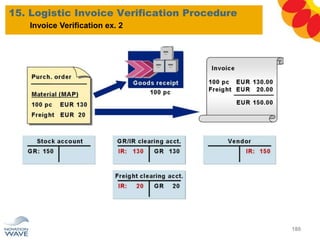
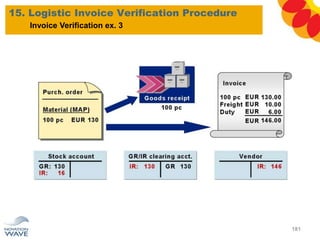
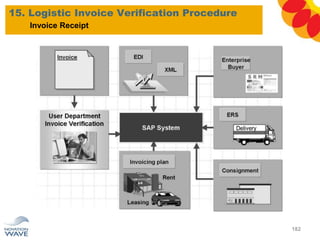
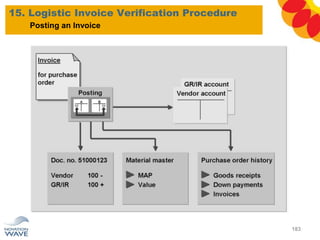
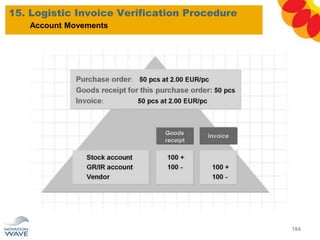
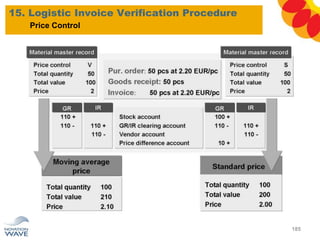
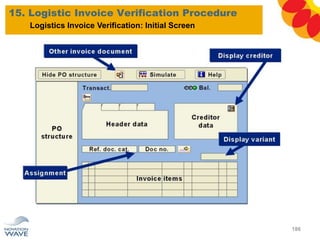
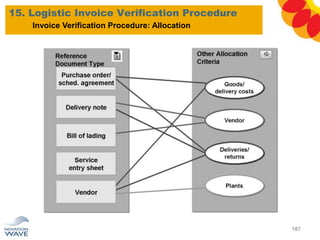
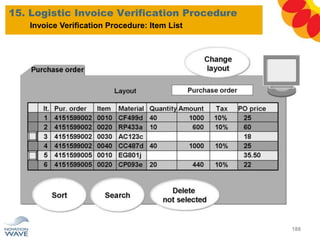
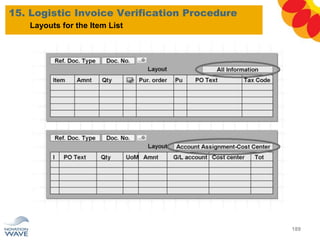
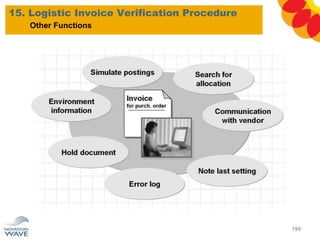
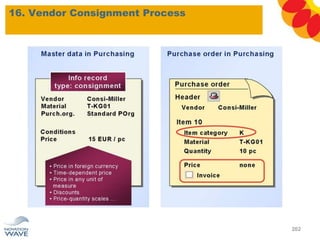
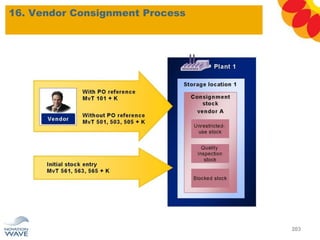
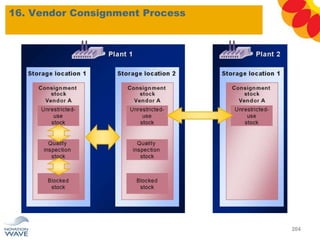
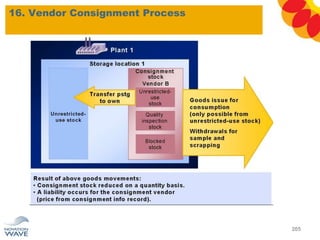
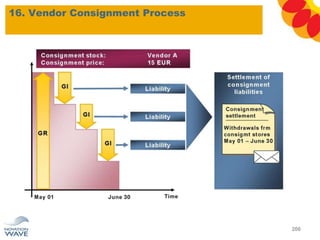
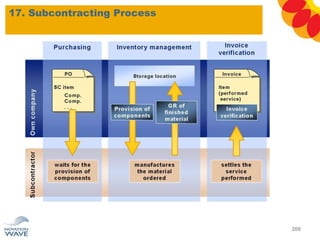
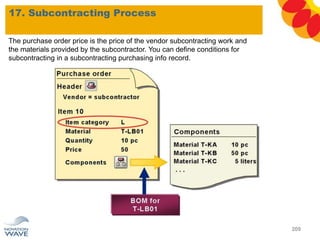
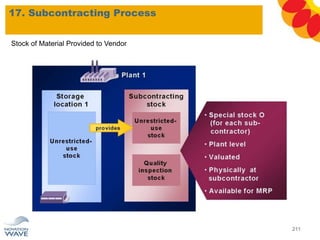
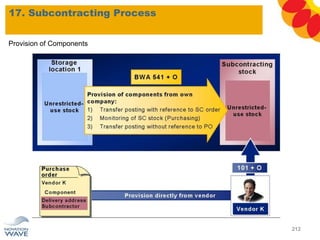
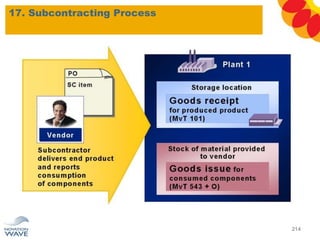
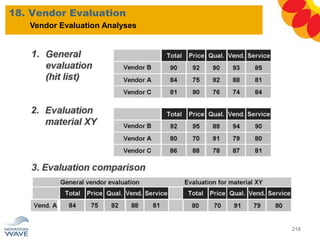
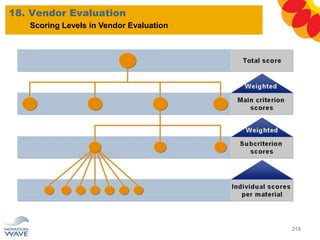
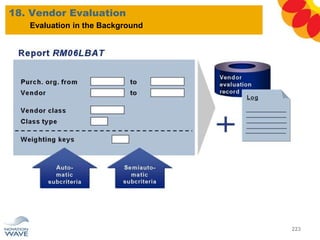
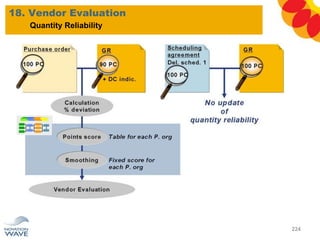
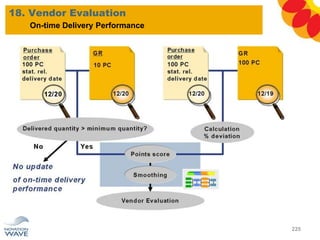
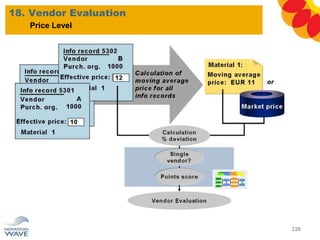
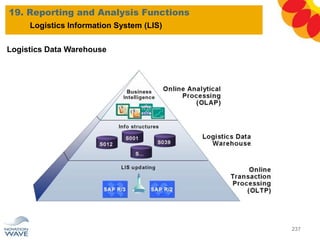
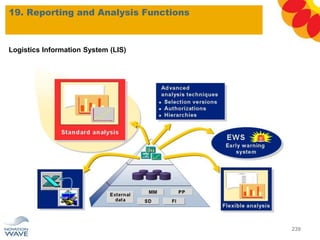
The document outlines a comprehensive training agenda for materials management, including SAP navigation, procurement processes for stock, consumable materials, and external services, as well as vendor evaluation and invoicing procedures. It covers key organizational structures, master data maintenance, and different purchasing types such as blanket orders and fixed assets. The agenda is structured over three days, detailing various exercises and key concepts necessary for effective materials management in SAP.