1. There are two main types of IDocs: outbound and inbound. Inbound IDocs are received from external systems by SAP through middleware like SAP PI or SOA.
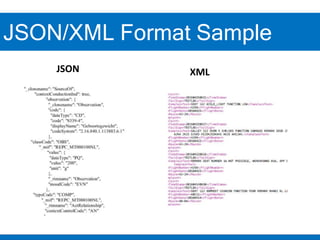
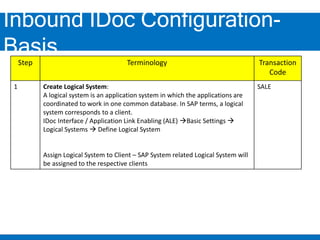
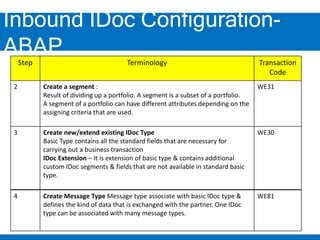
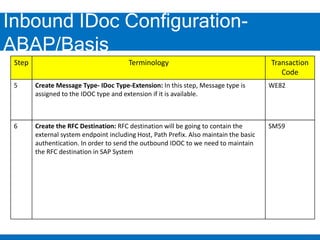
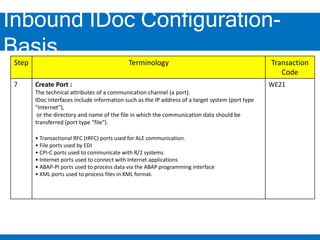
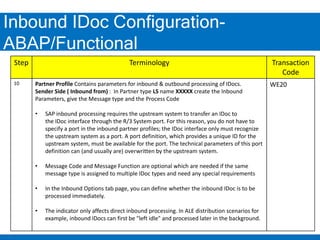
2. Configuring inbound IDocs involves creating logical systems, IDoc types, message types, RFC destinations, ports, and process codes. Partner profiles must also be created to define inbound processing parameters.
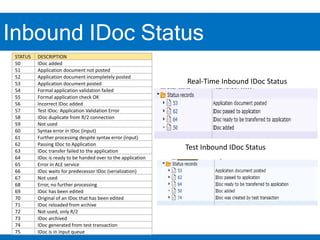
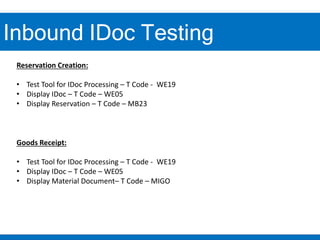
3. Testing inbound IDocs can involve using transaction codes to display IDocs, reservation documents, or materials documents to validate successful inbound processing.