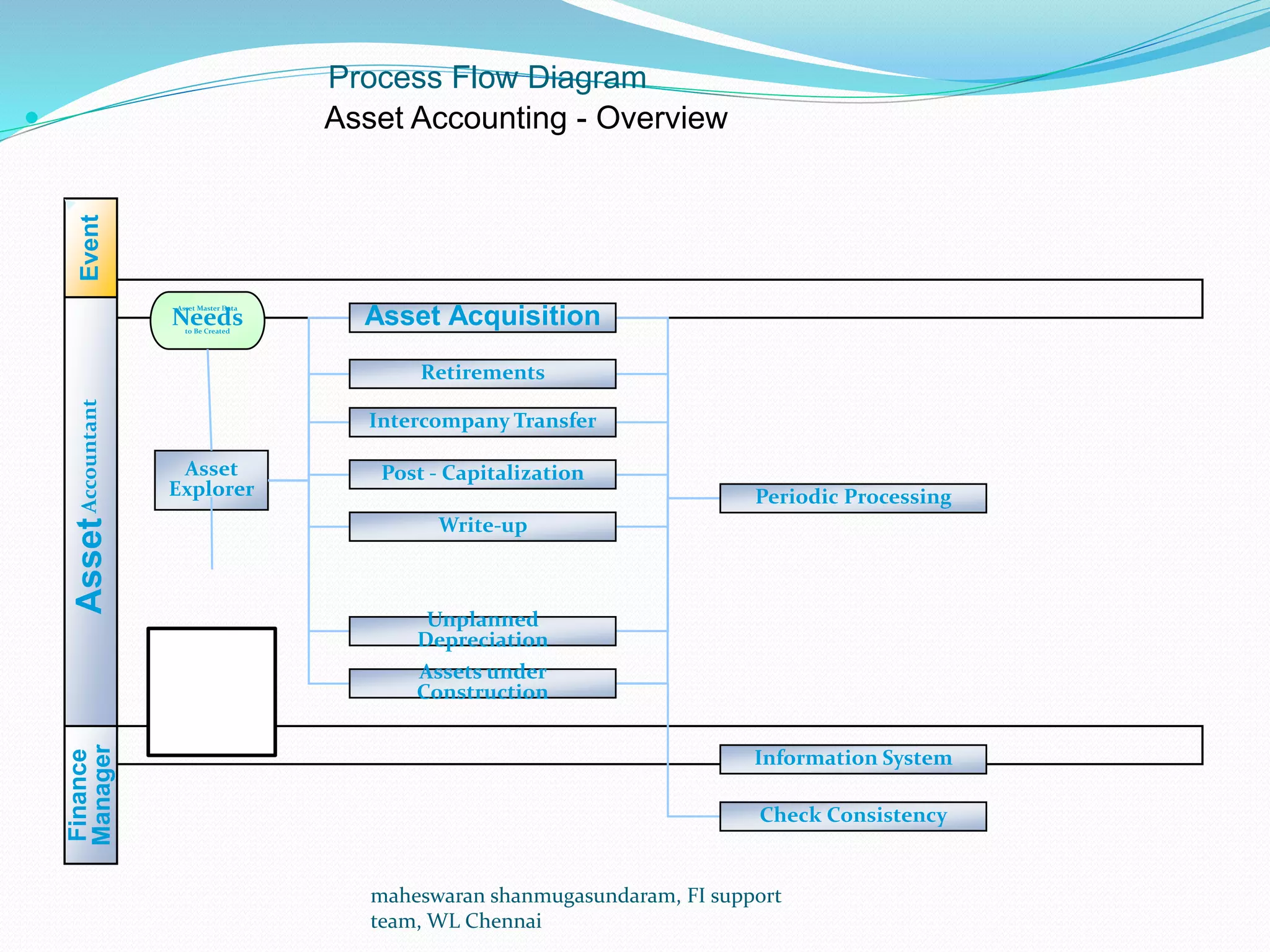
The document discusses Asset Accounting (FI-AA) in SAP, which manages fixed assets in the SAP system. It manages assets from acquisition through retirement, calculates depreciation and interest, and allows for depreciation forecasting. Key process steps include acquisition, retirement, sale, capitalization, write-ups, depreciation posting runs, and taxation calculations. Required applications include SAP ERP and roles such as Asset Accountant.