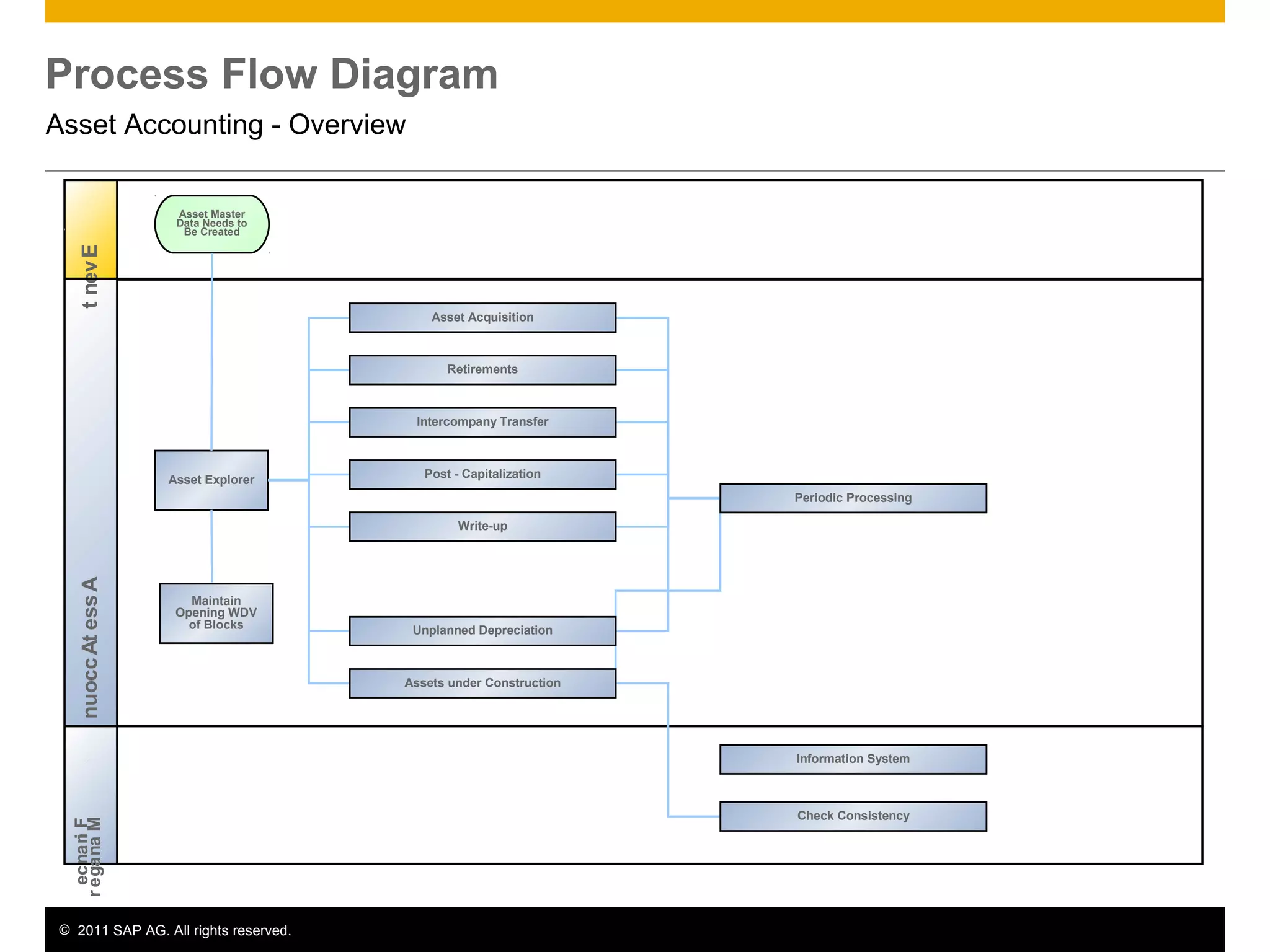
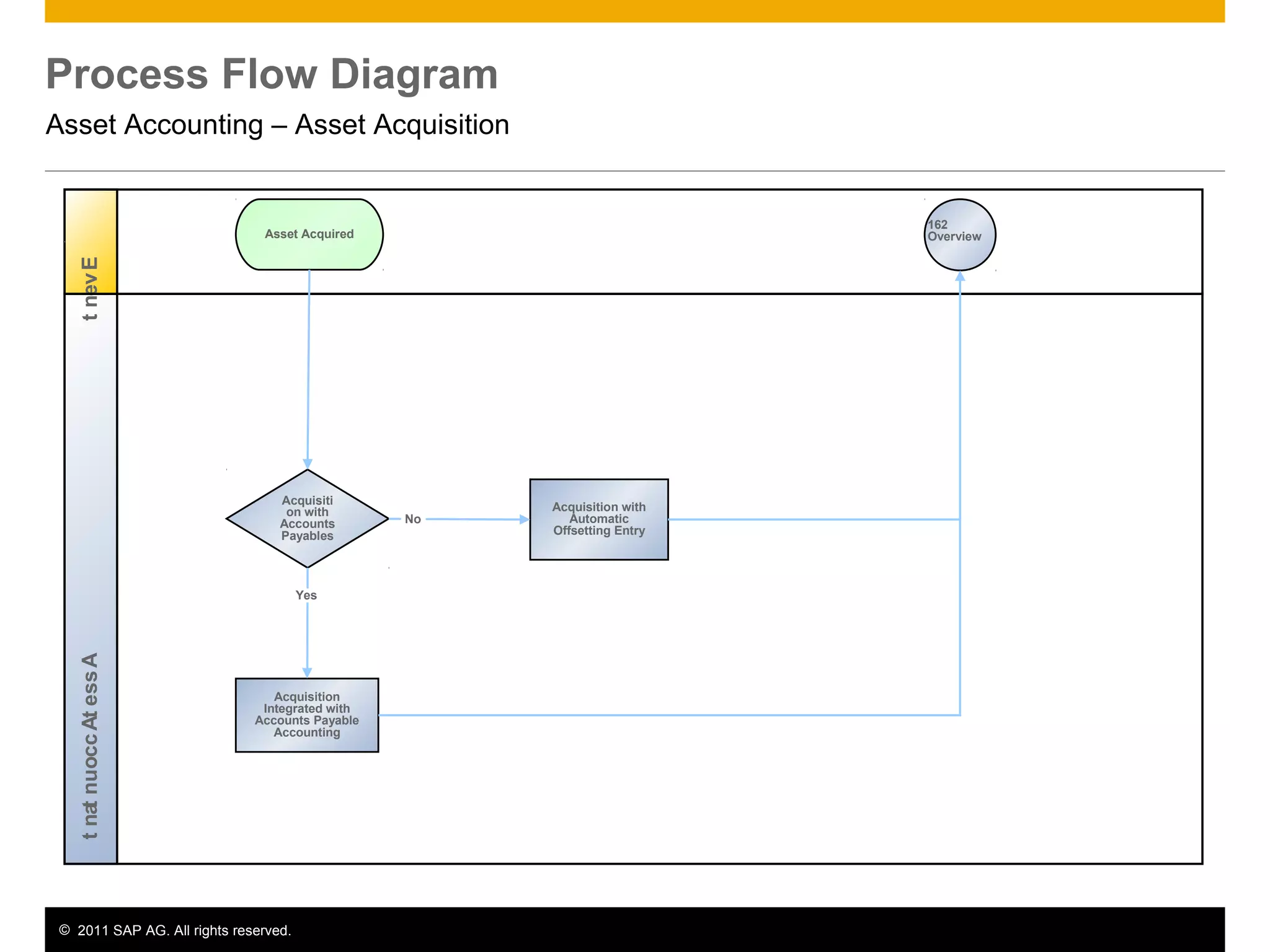
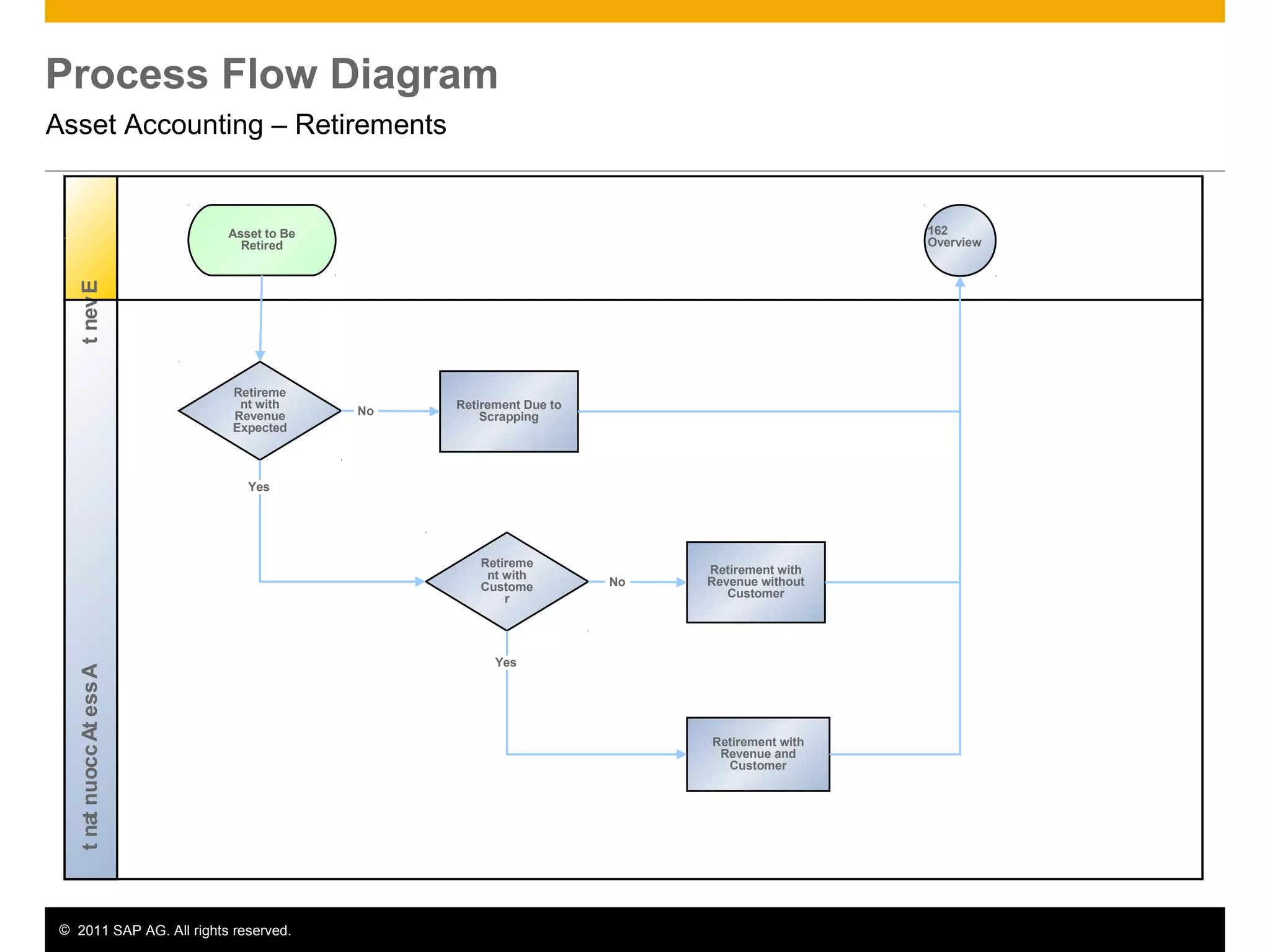
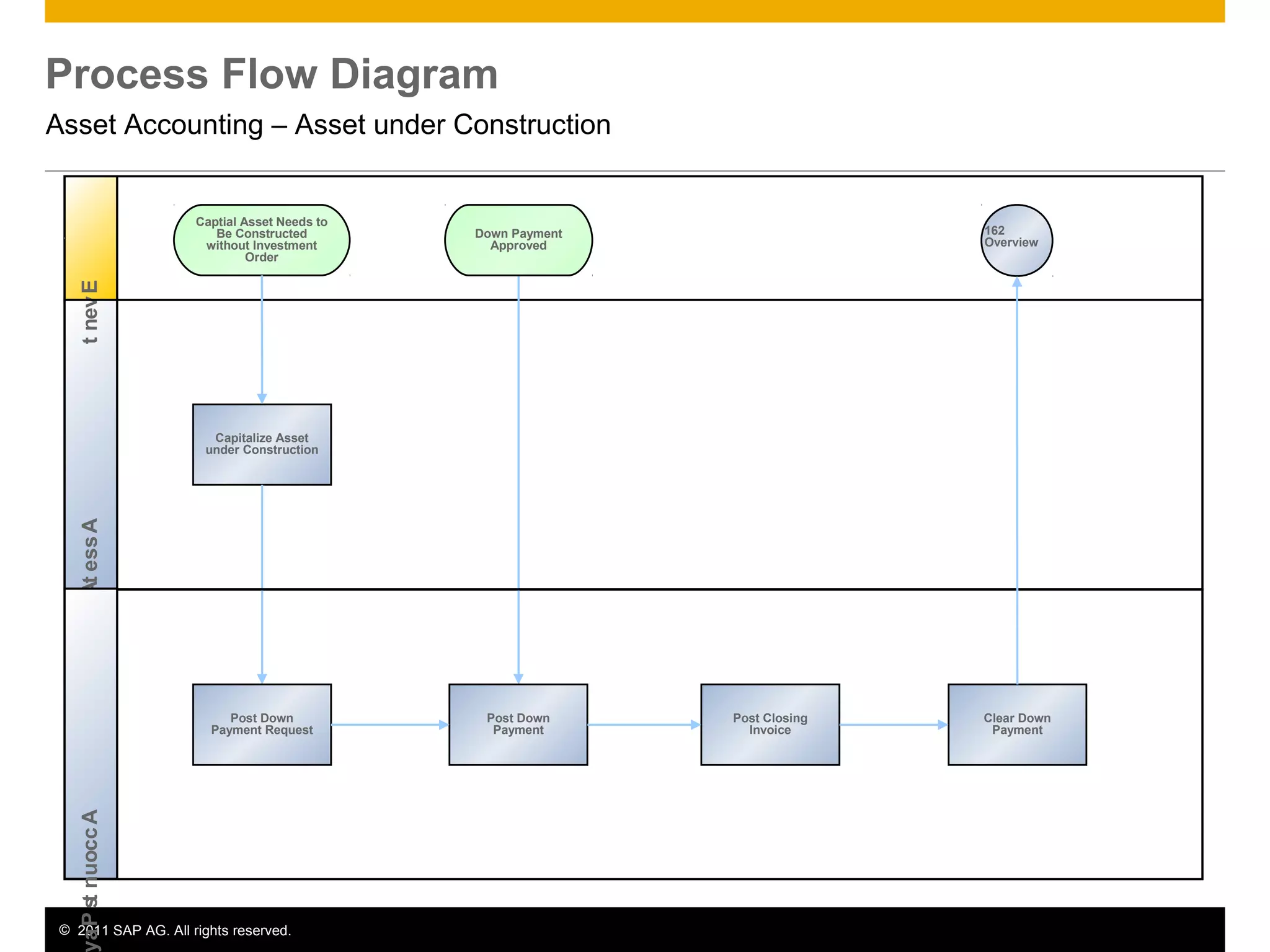
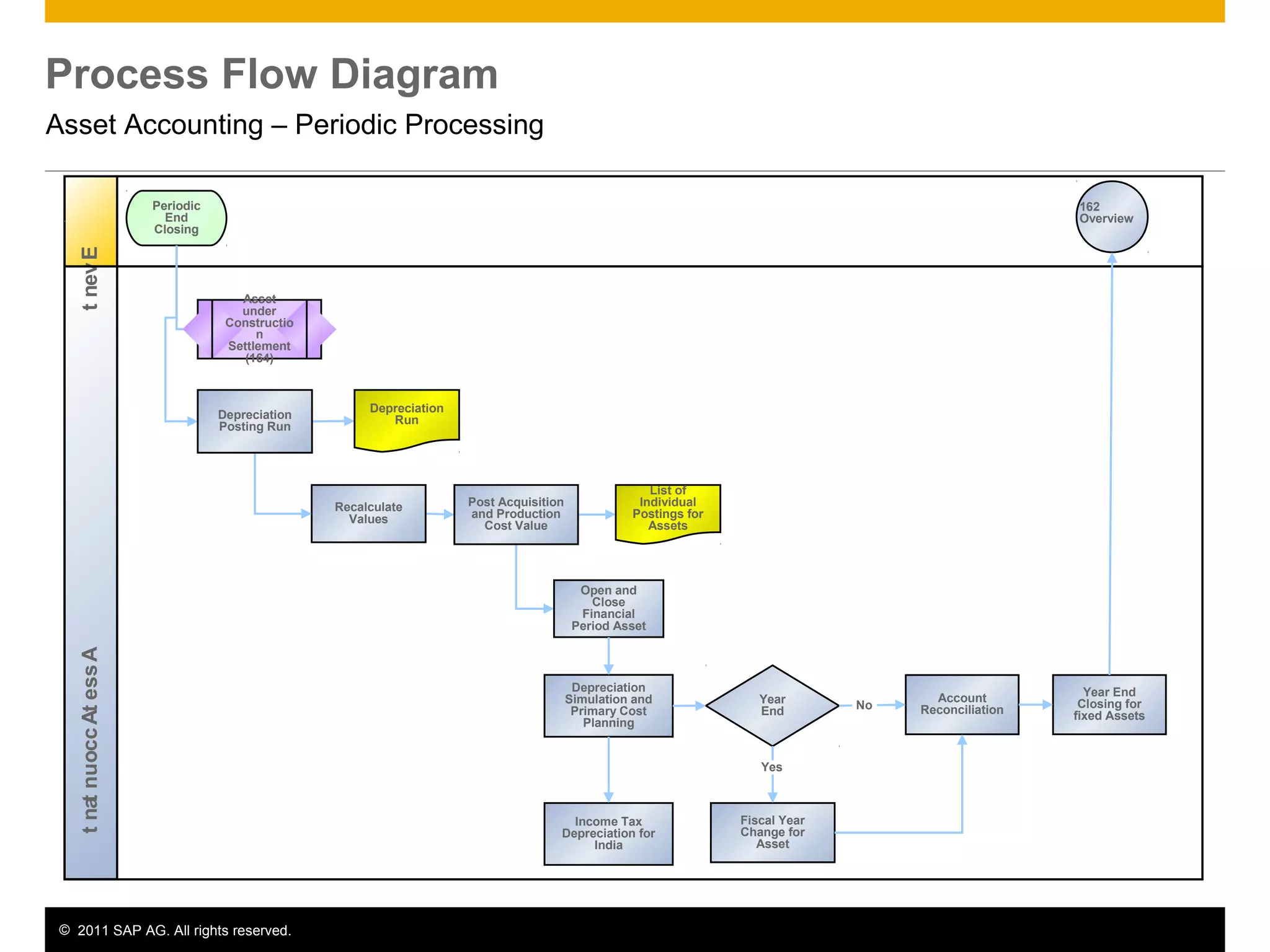
The document discusses asset accounting in SAP. It describes the purpose as managing fixed assets throughout their lifetime from acquisition to retirement. Key steps include acquisition, construction, depreciation calculation, and periodic processes like tax depreciation. Required applications are SAP ERP and roles include asset accountant, accounts payable accountant, and finance manager.