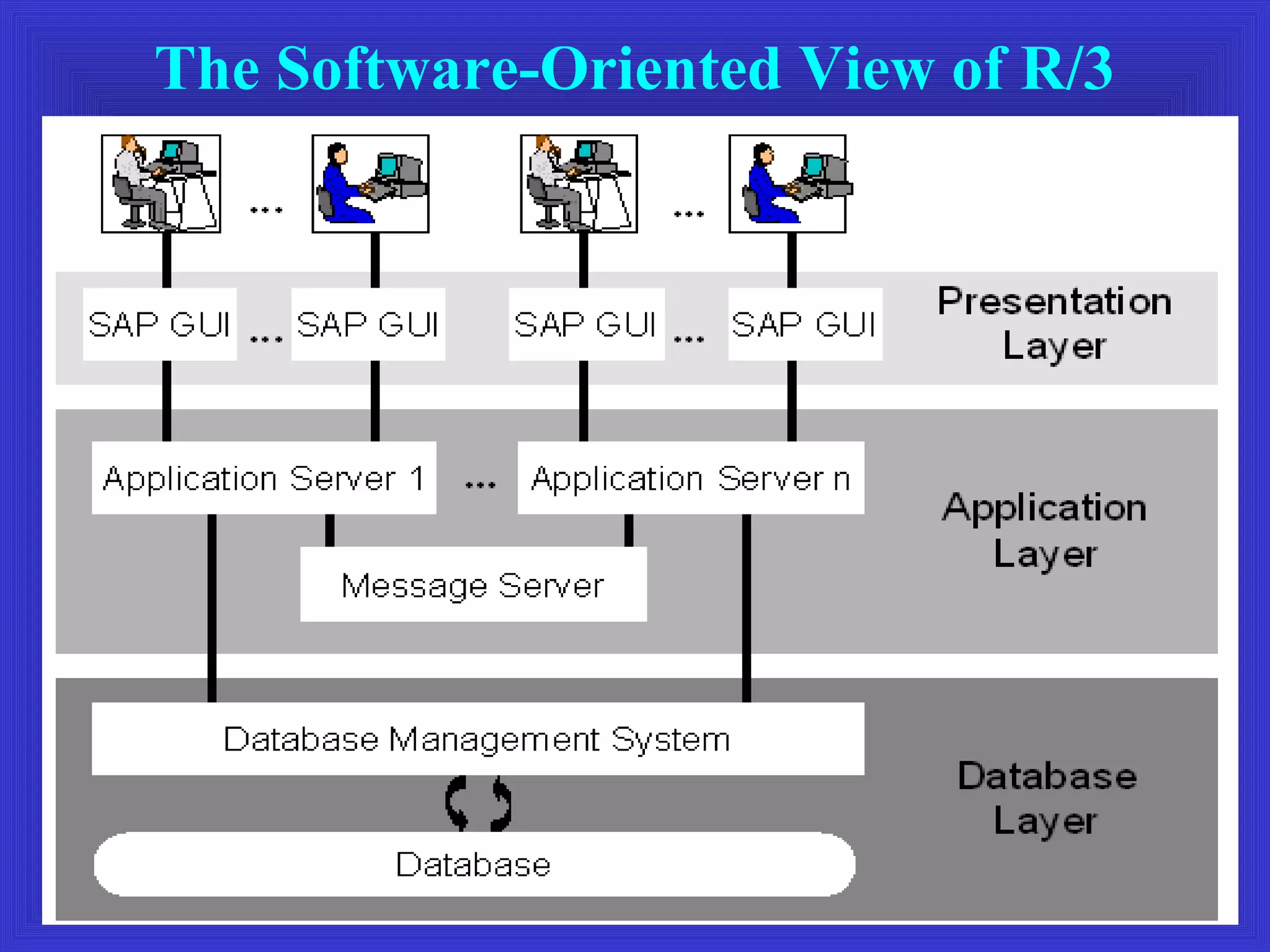
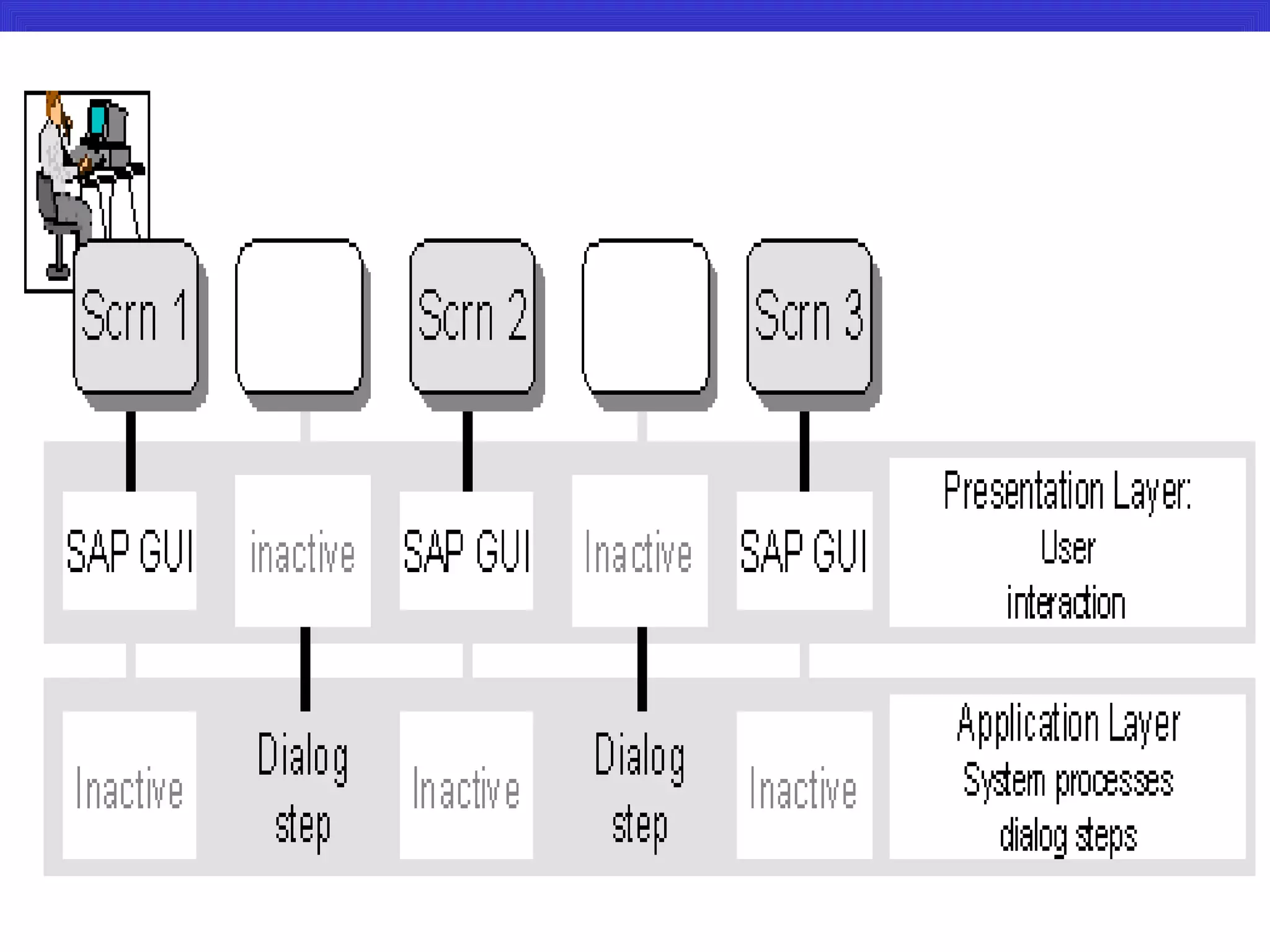
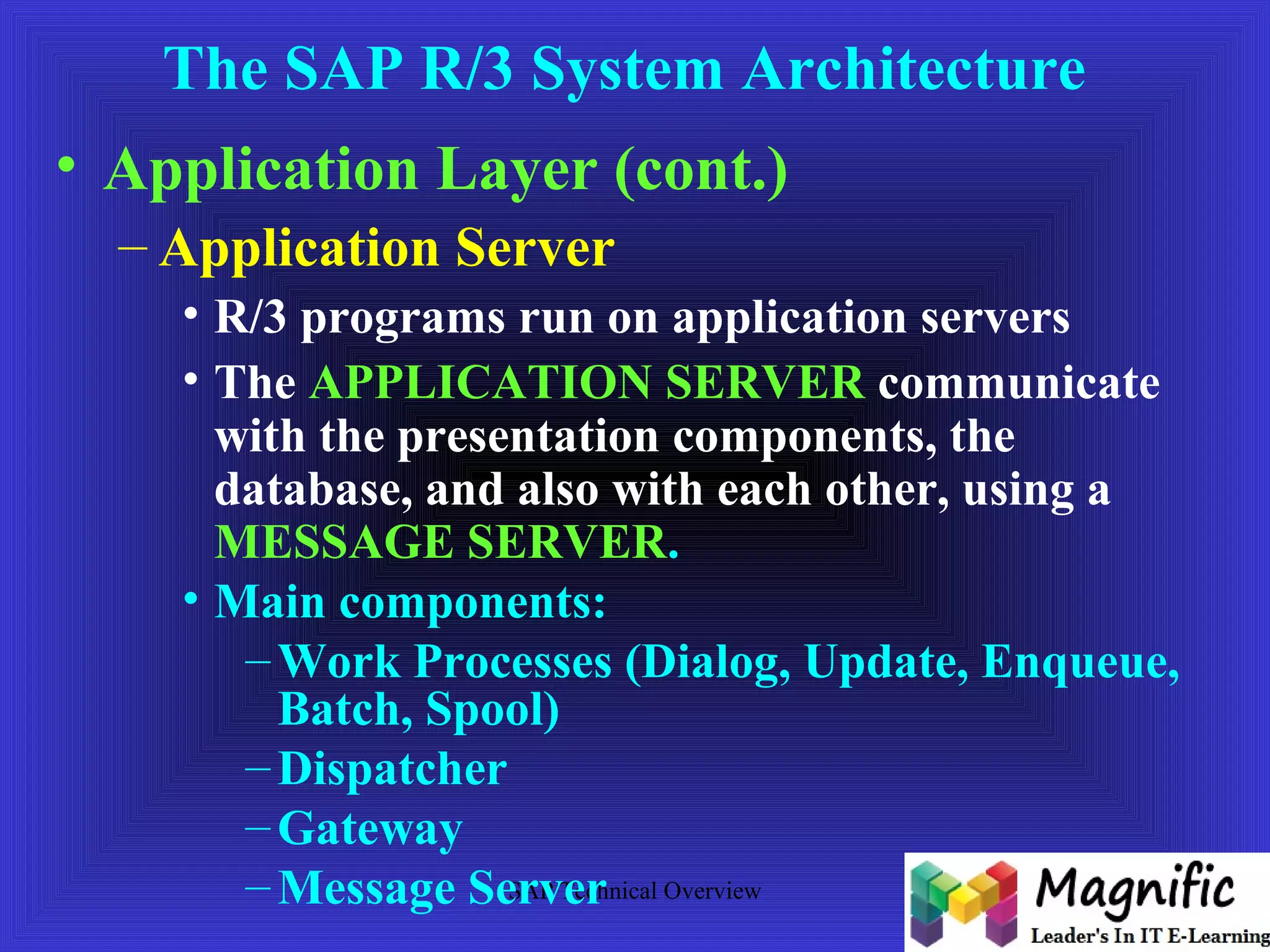
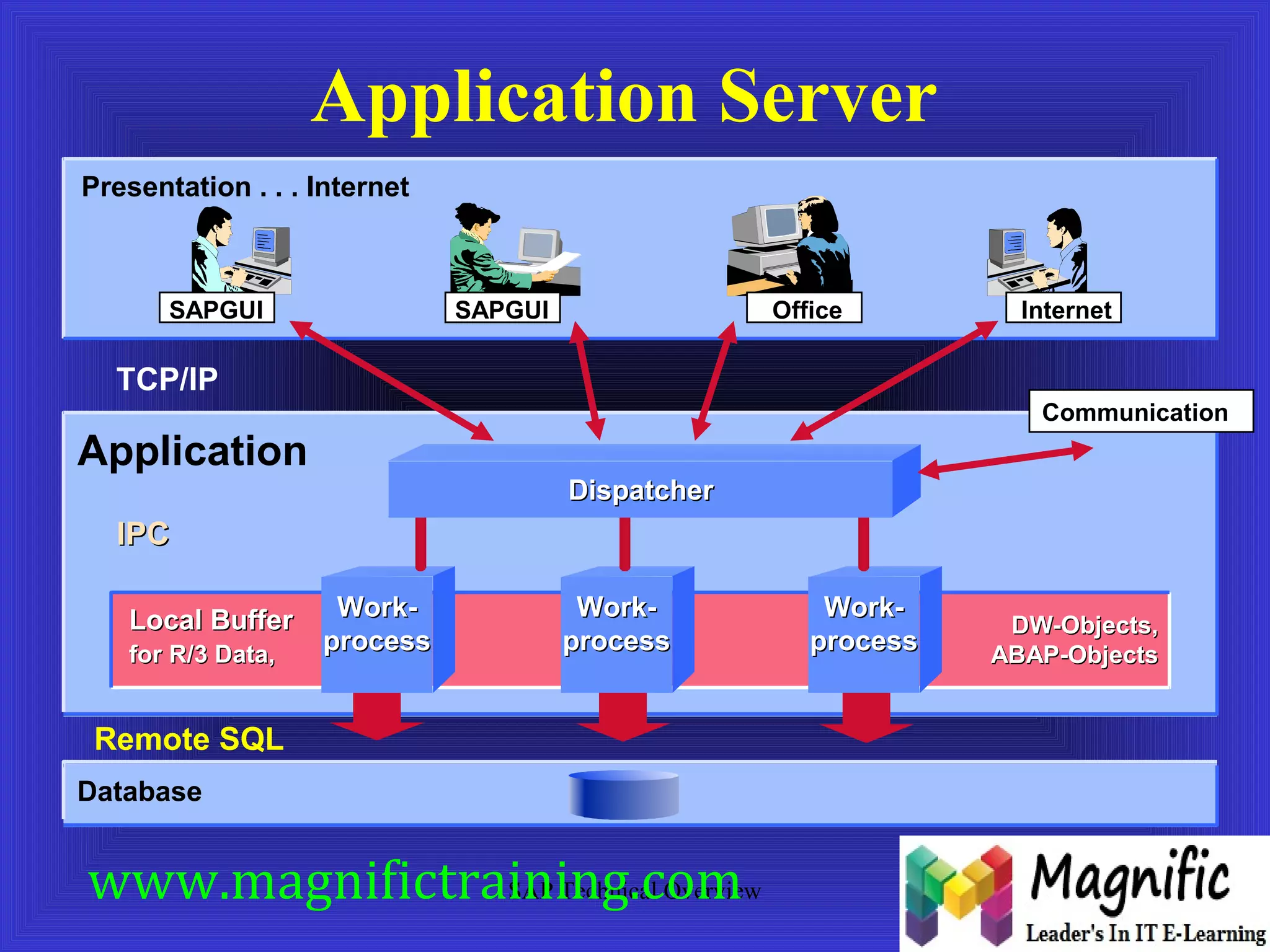
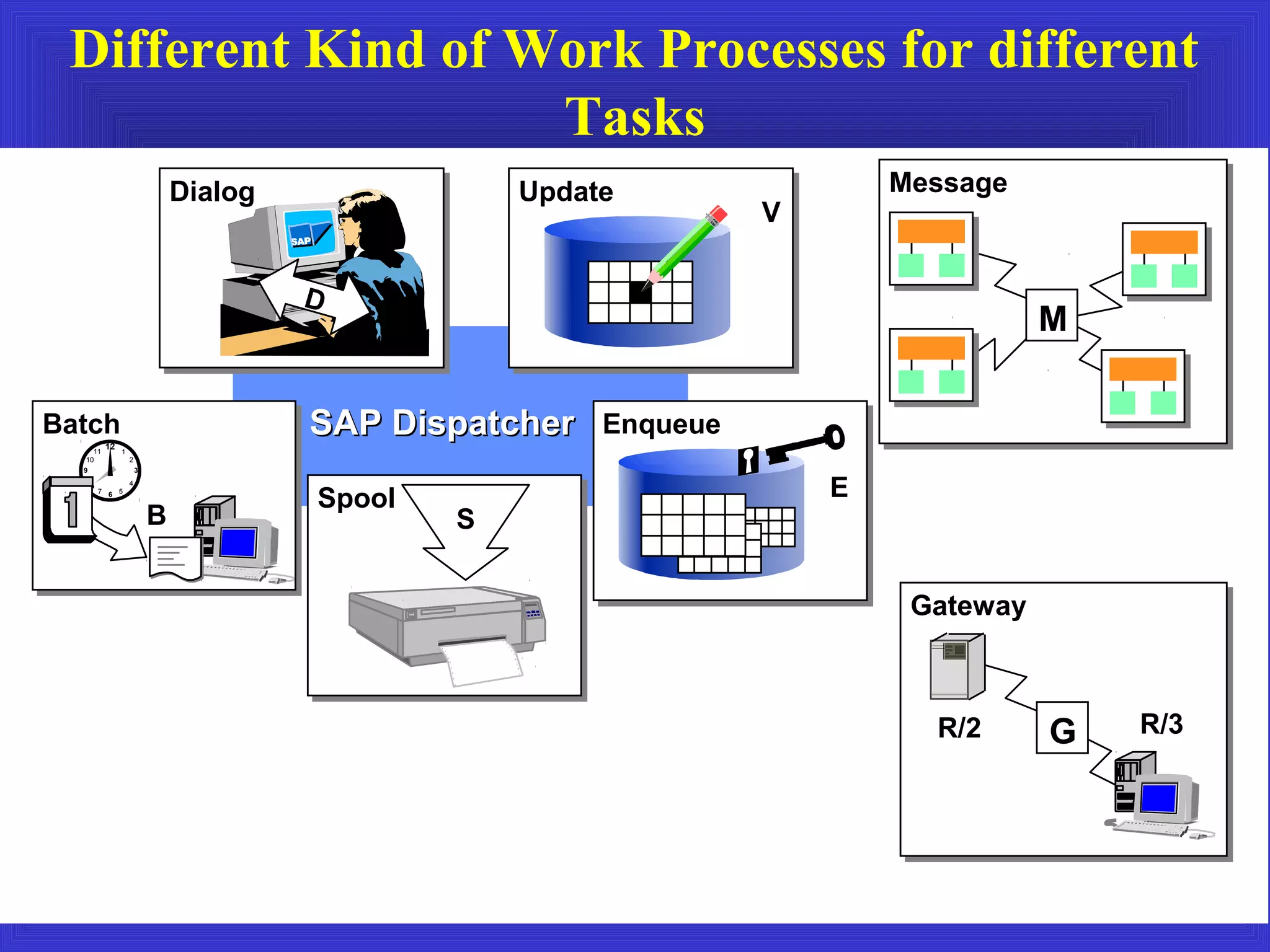
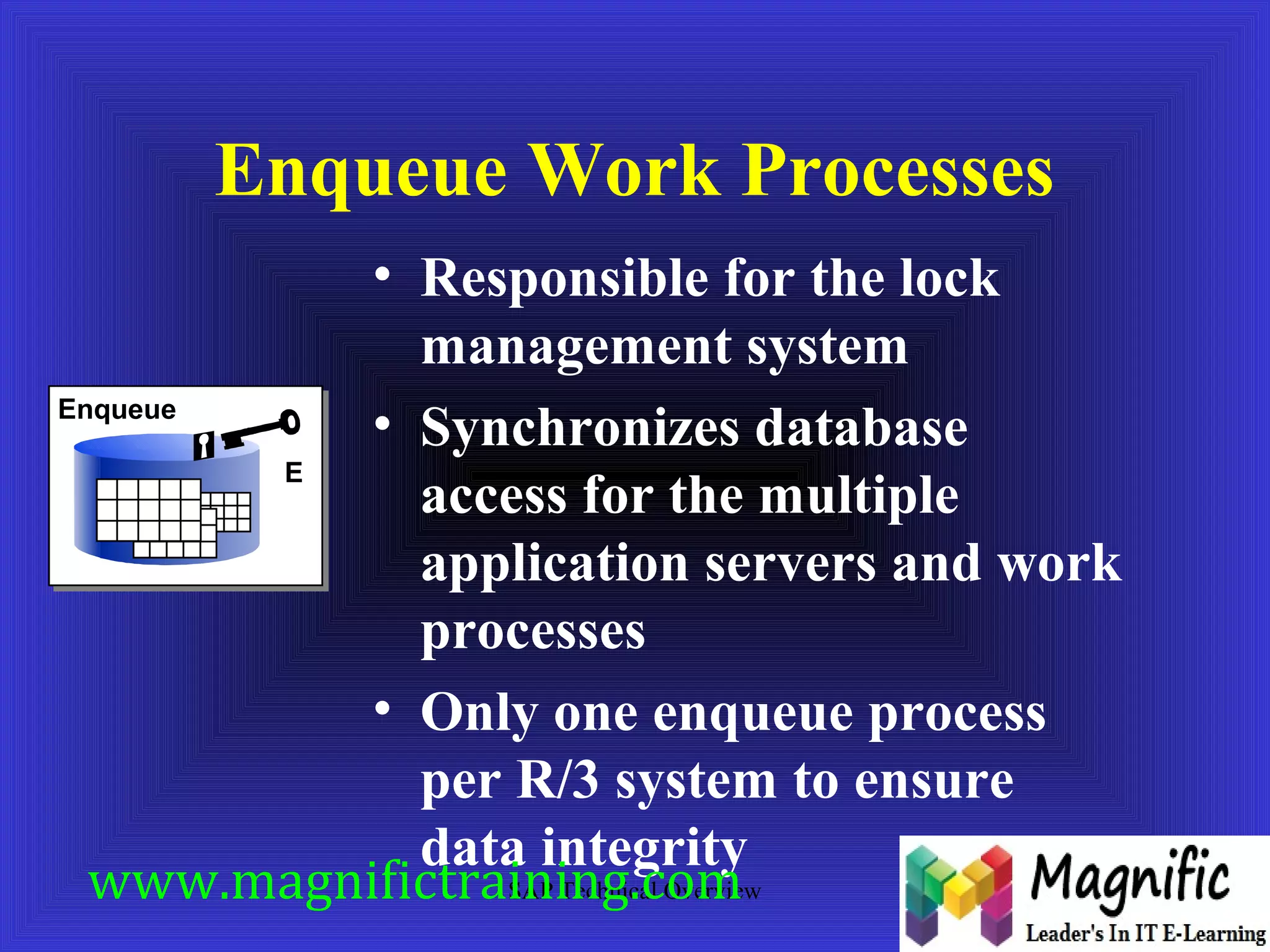
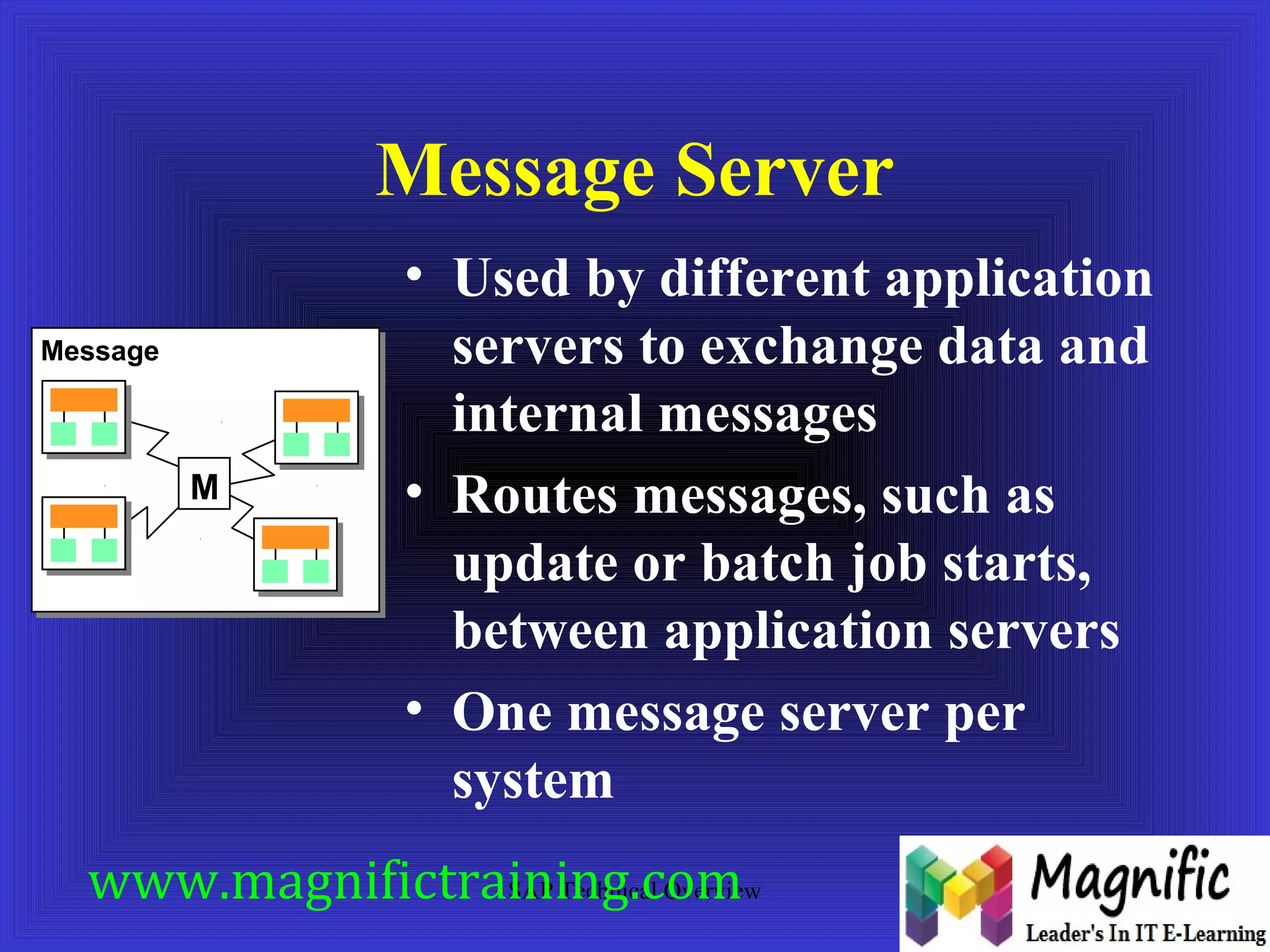
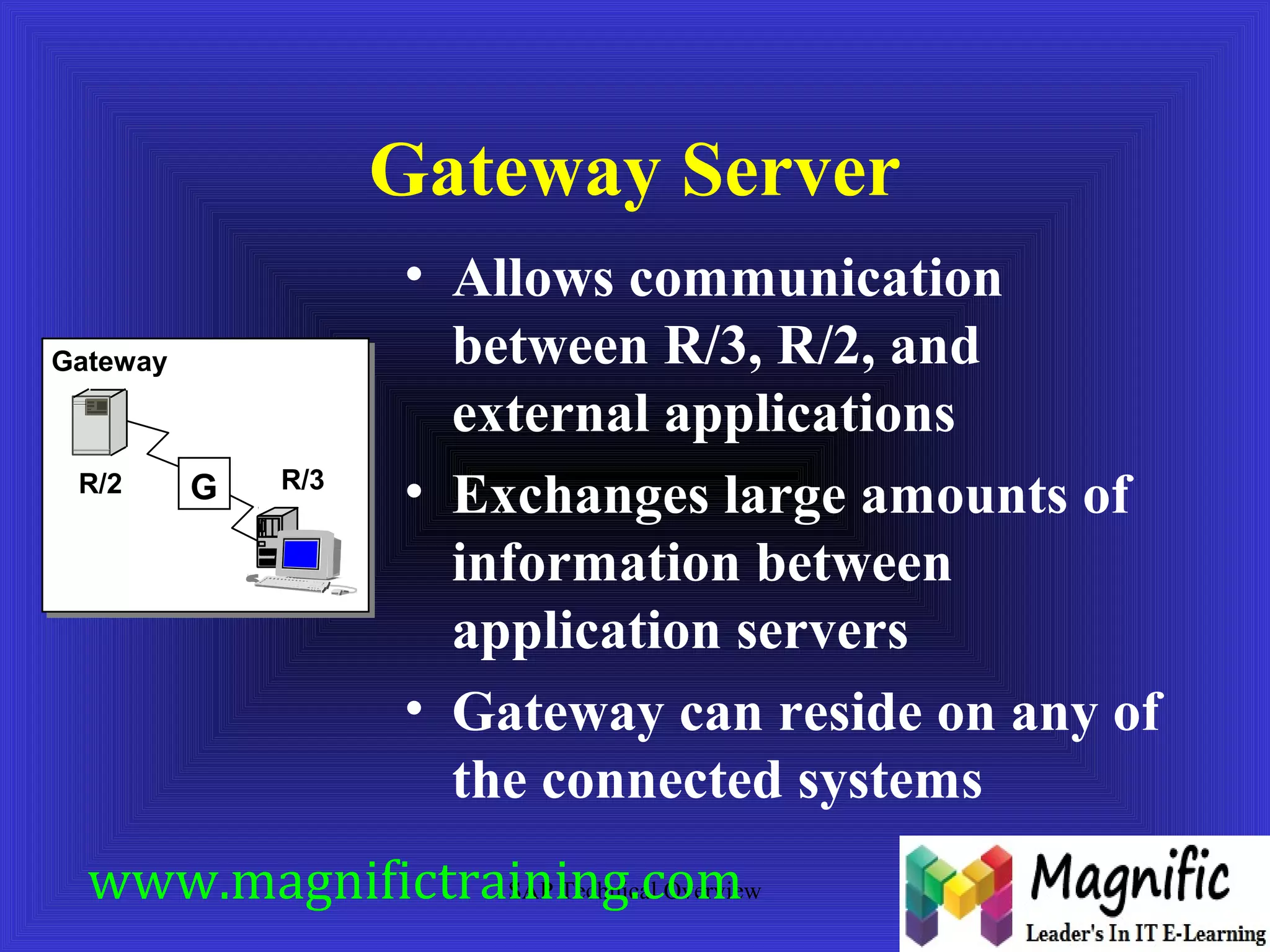
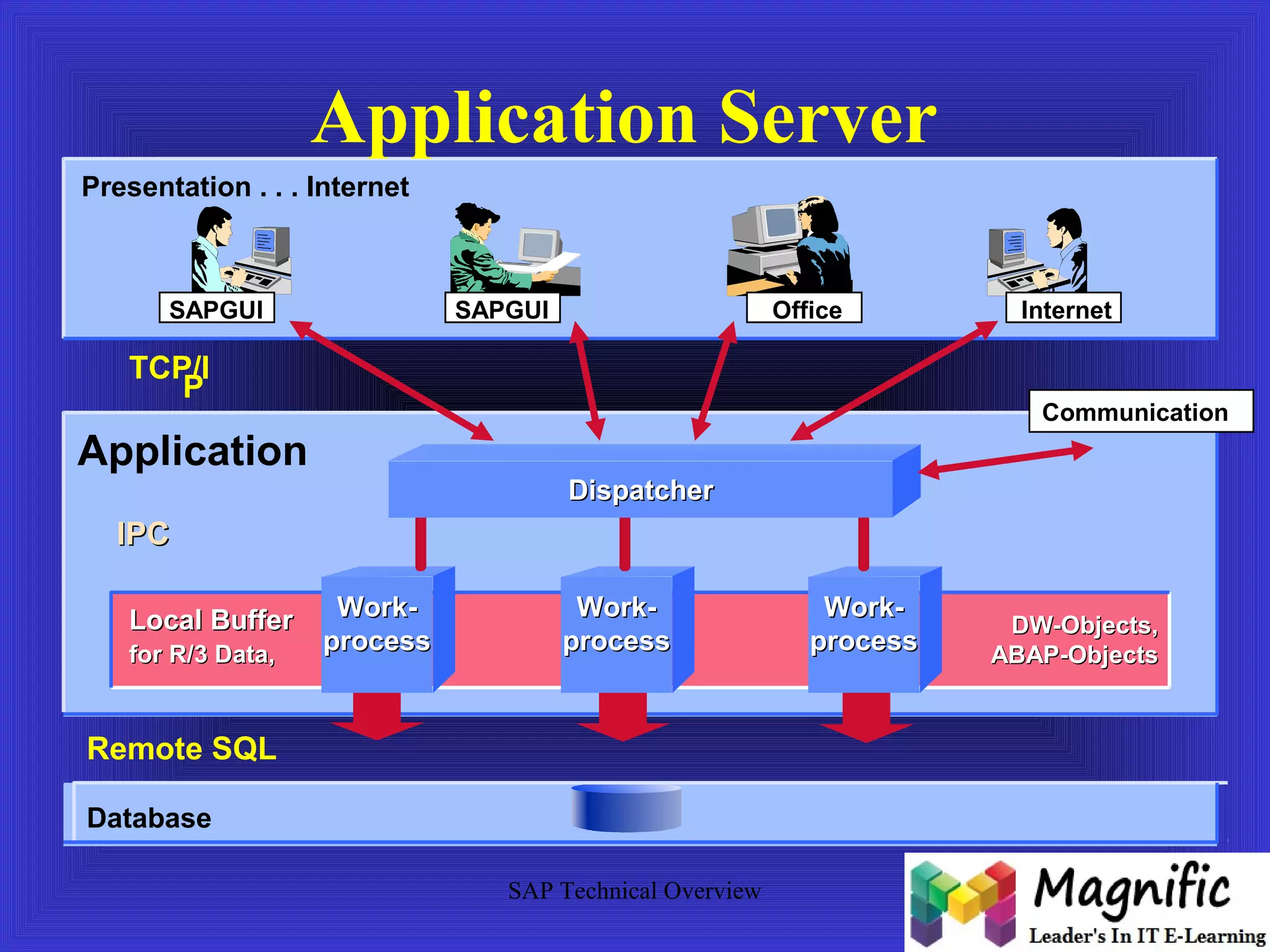
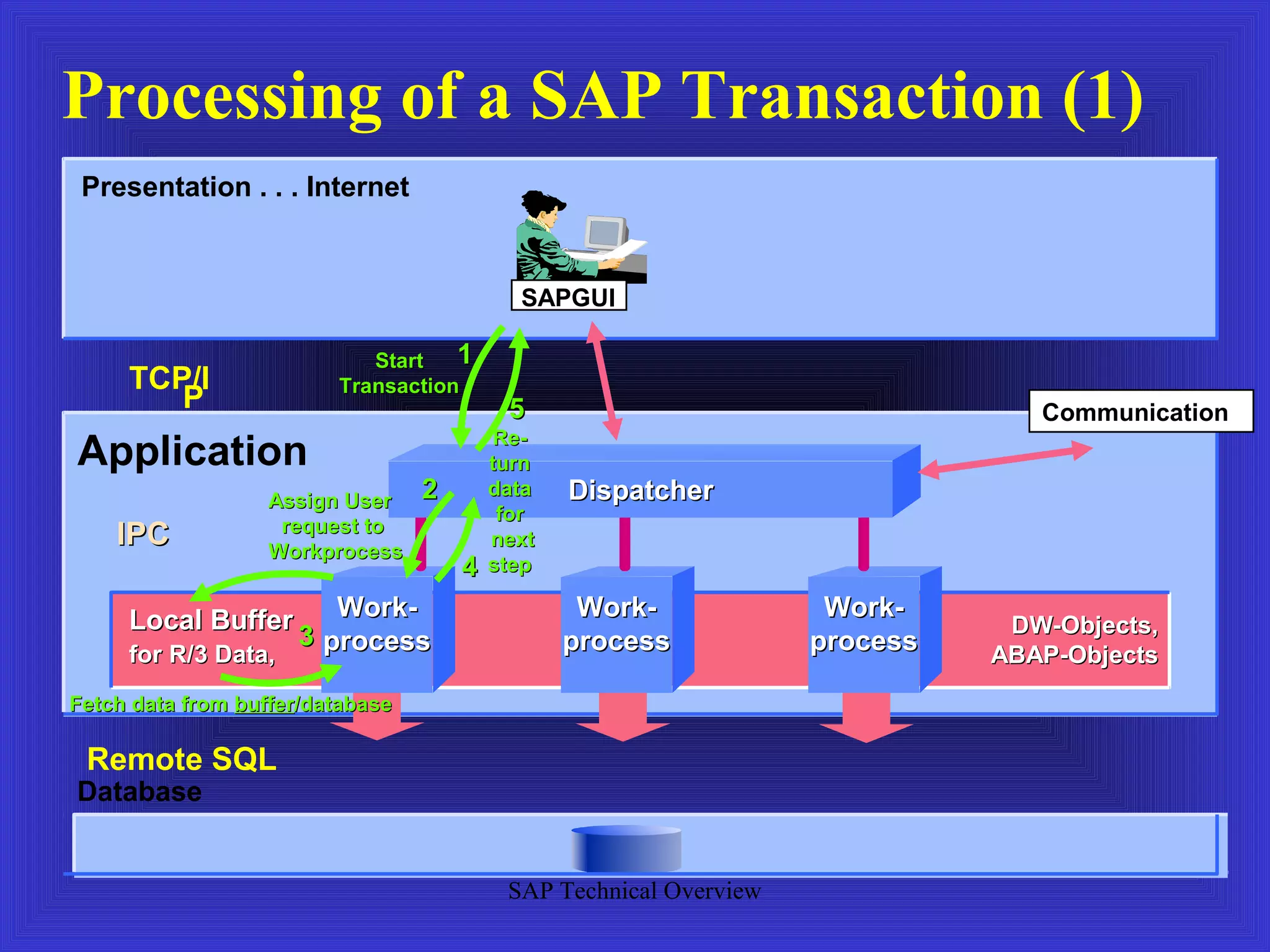
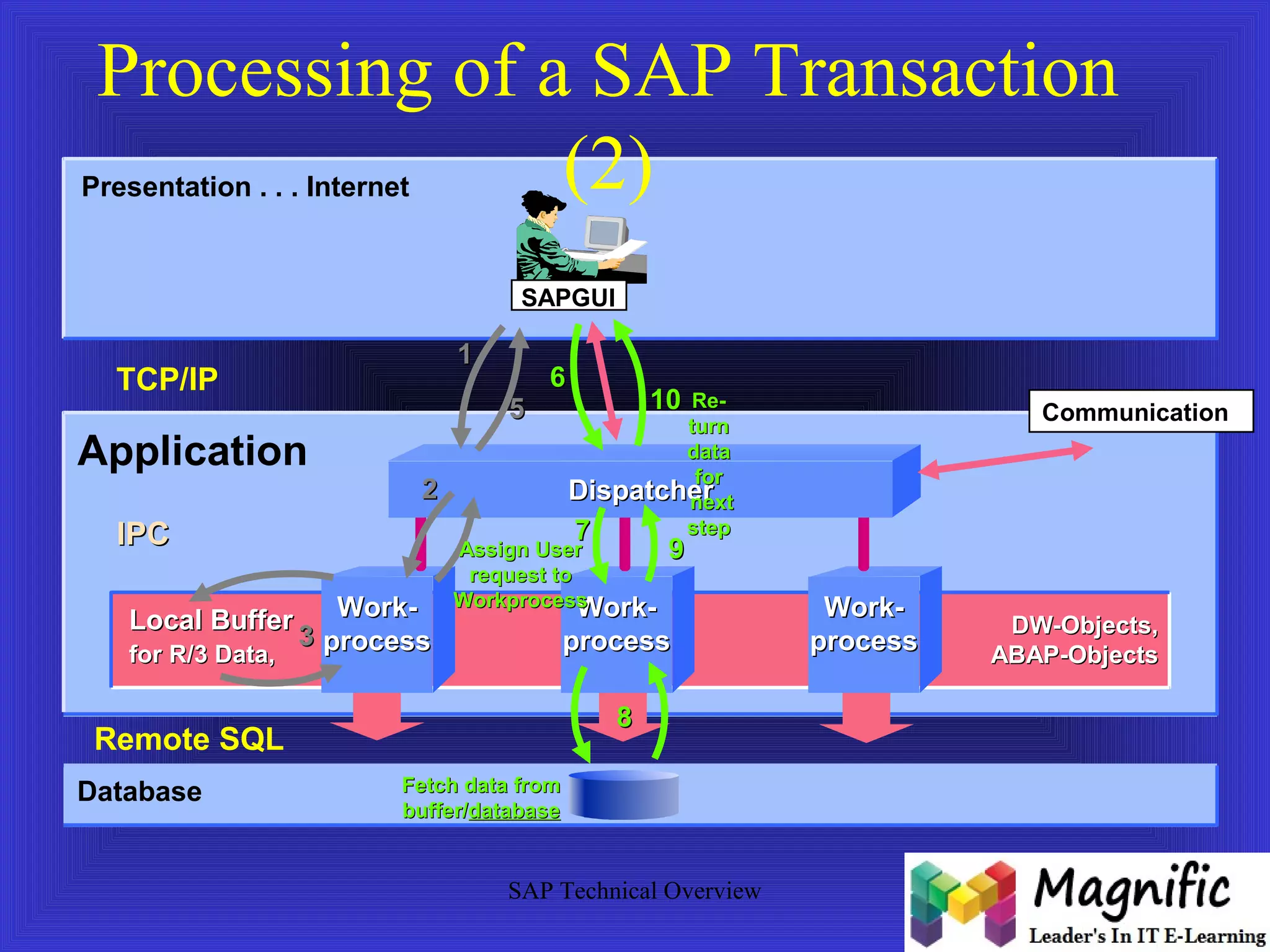
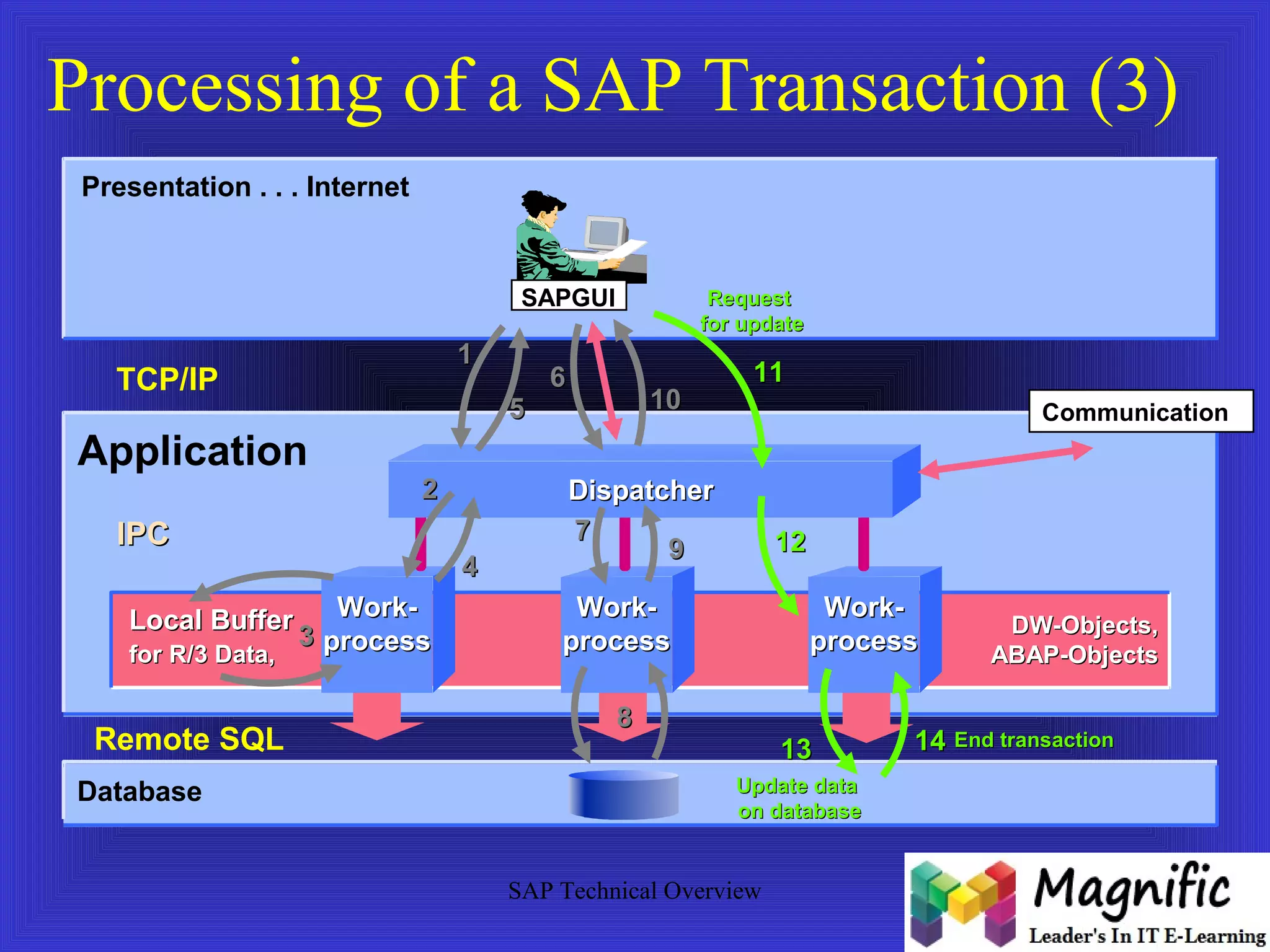
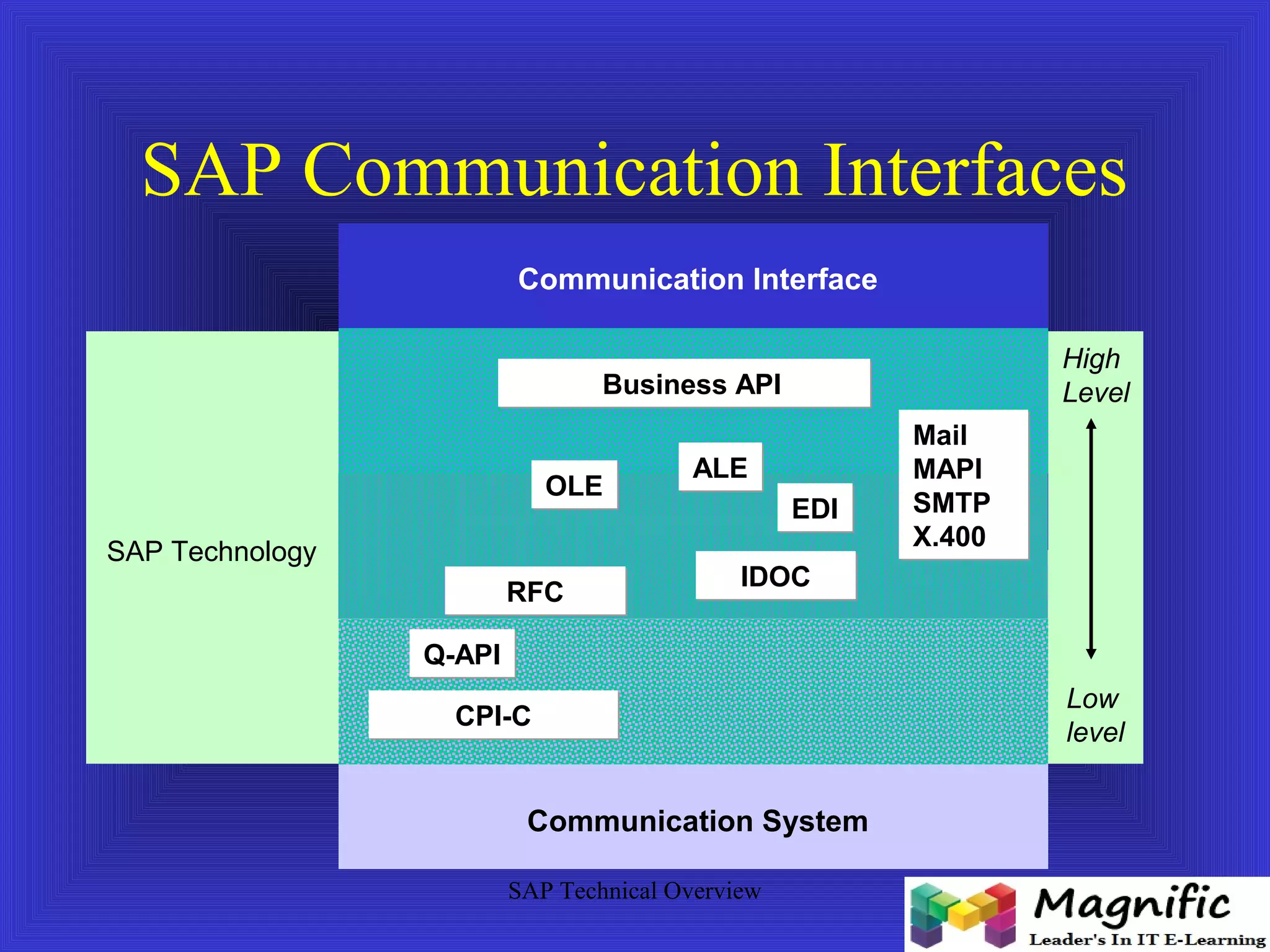
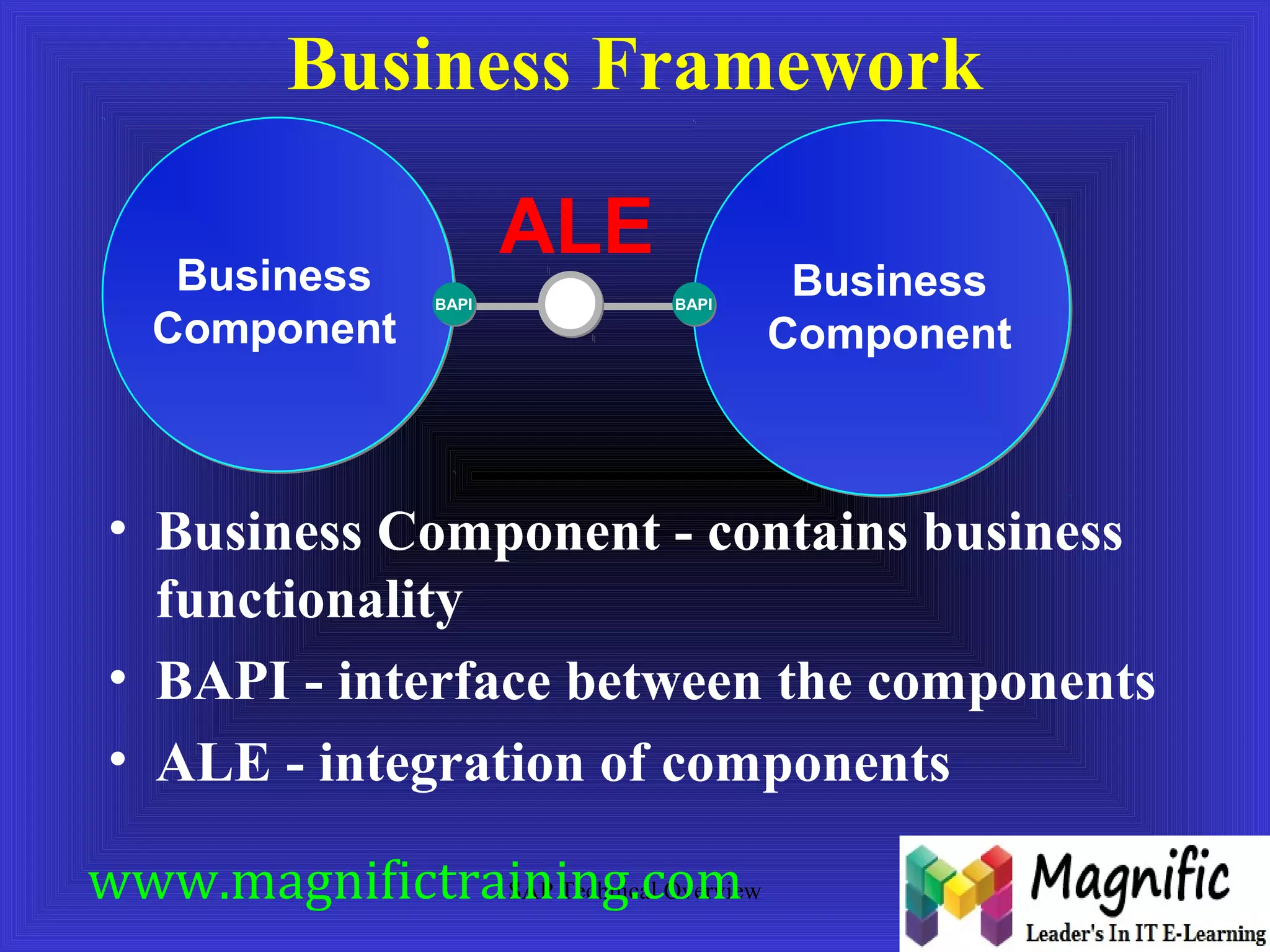
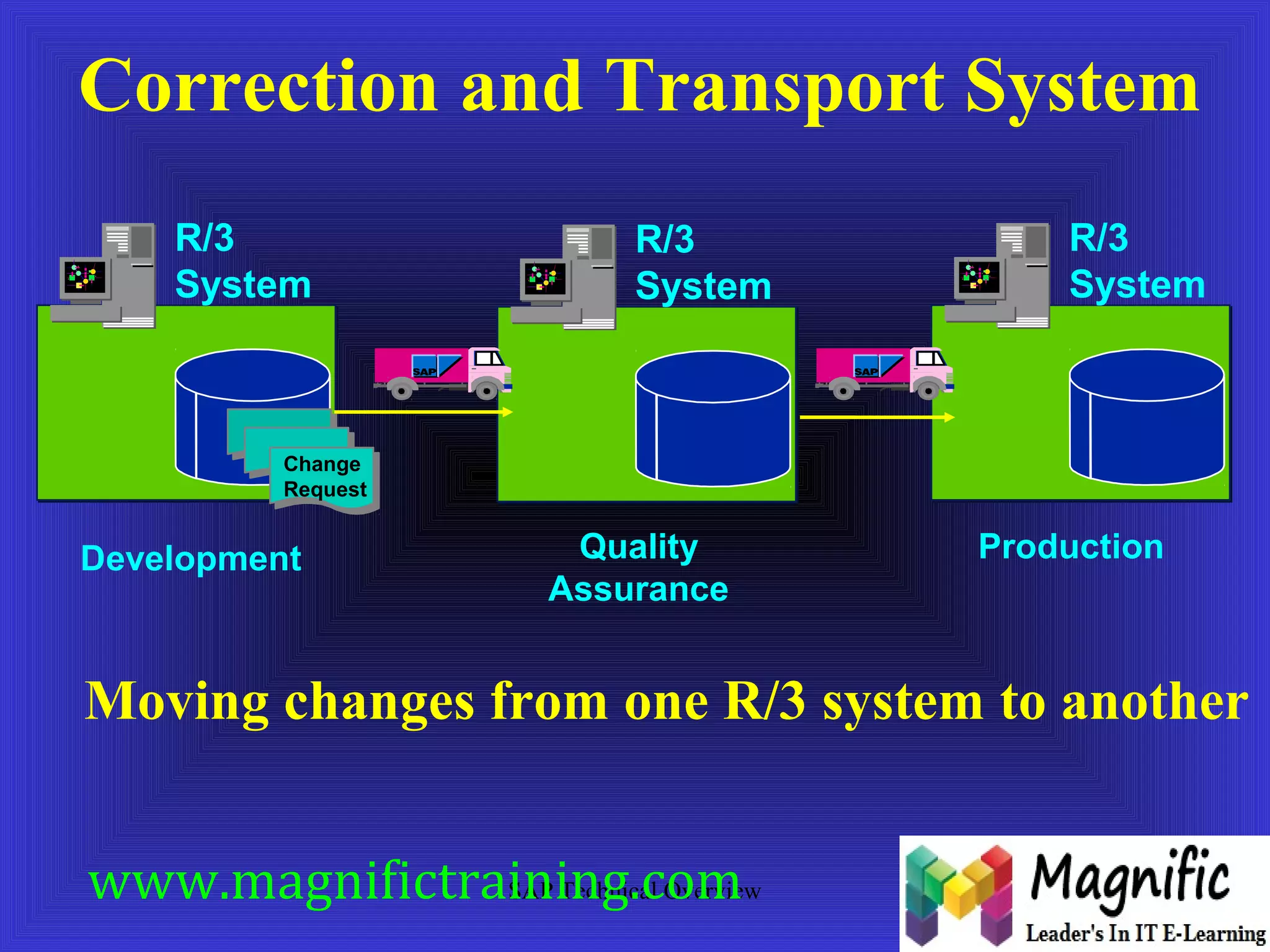
The document provides an overview of an SAP Basis online training session, covering learning objectives such as user administration, transaction processing, and SAP system architecture. It details the various work processes within the SAP R/3 system including dialog, background, and update processes, as well as essential functions such as user management, client maintenance, and performance tuning. Additionally, it mentions the support and resources available post-training, alongside contact information for further inquiries.