This document provides an overview of SAP technical concepts including:
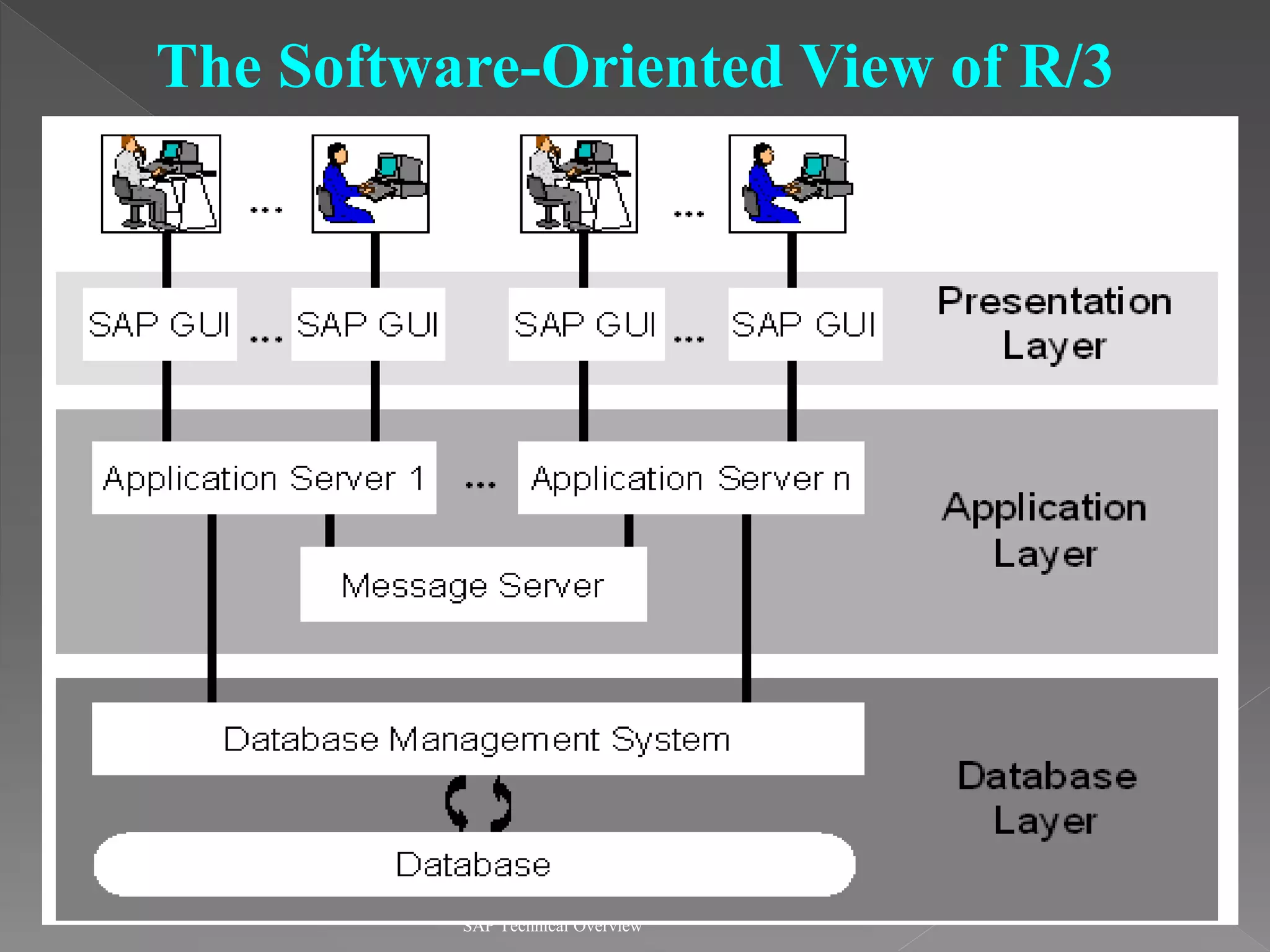
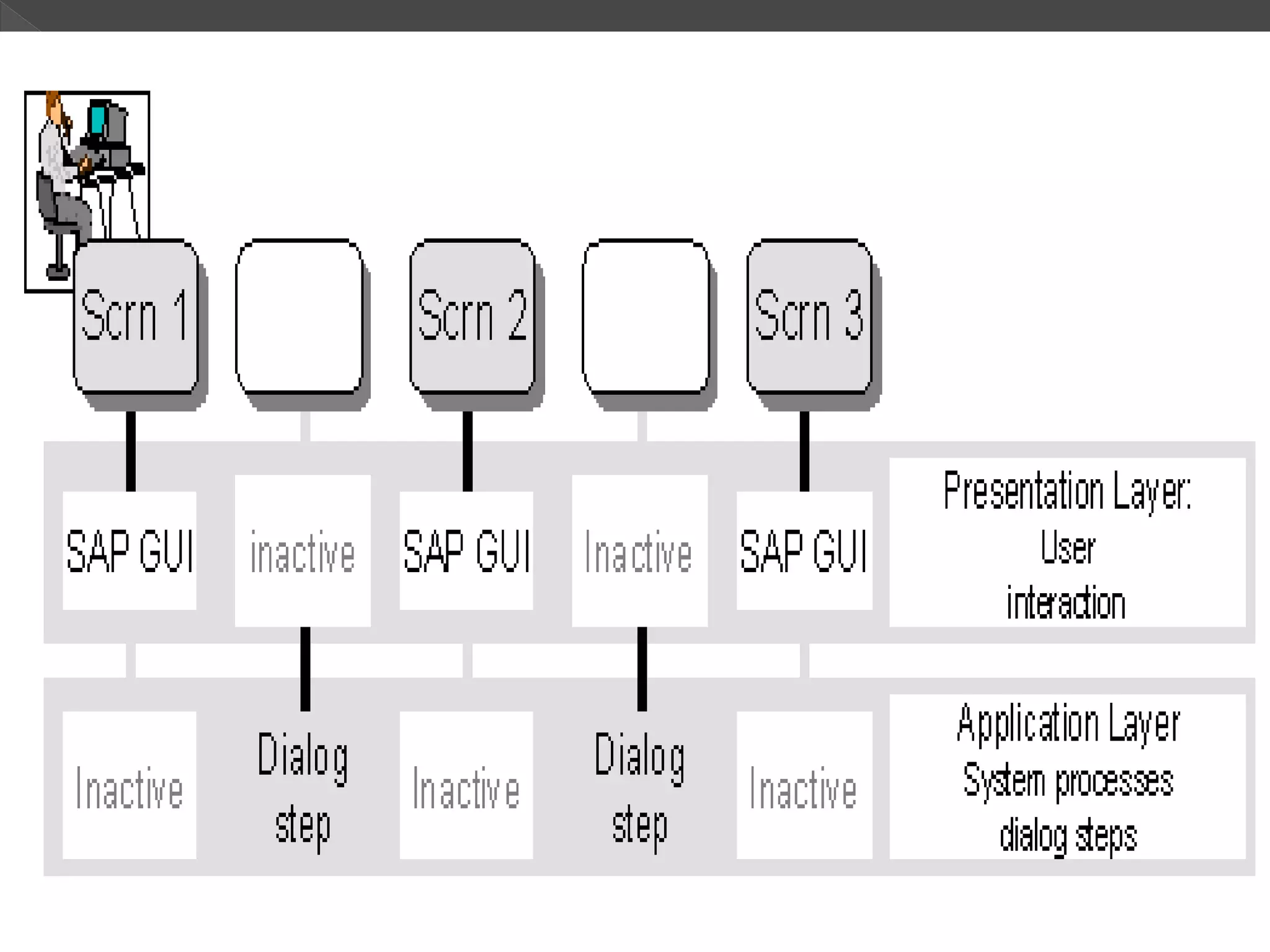
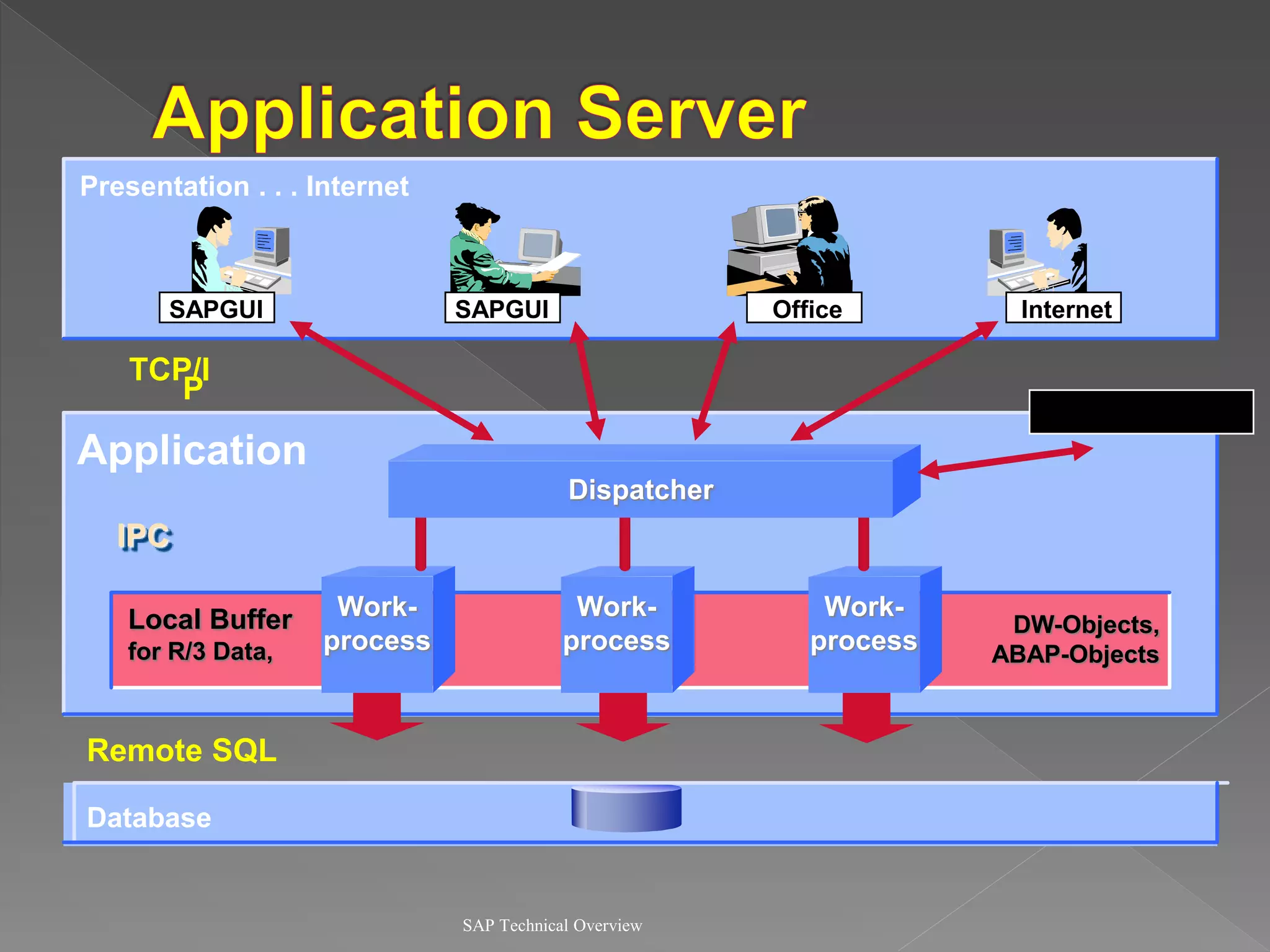
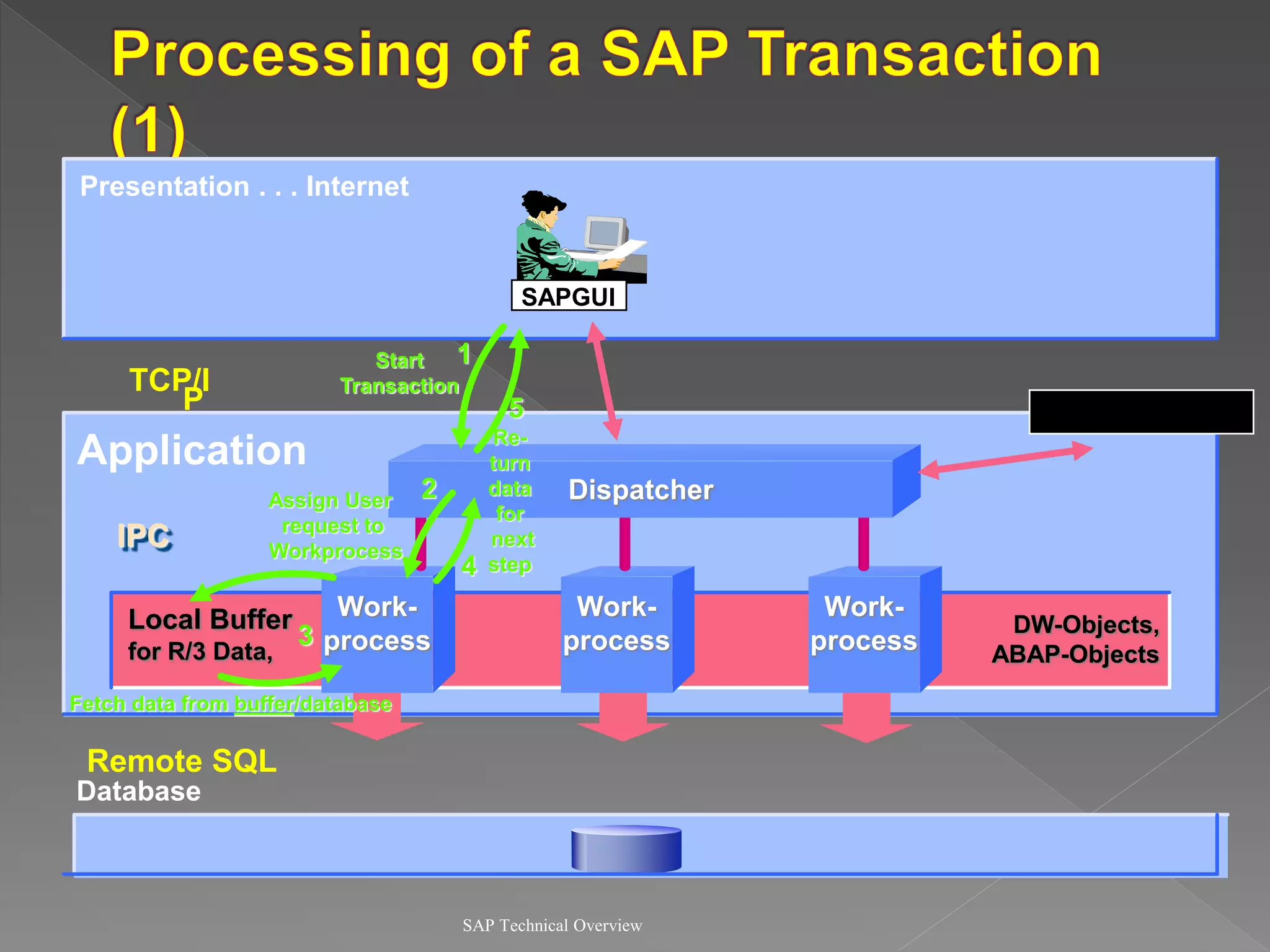
1) It describes the SAP R/3 system architecture with separate presentation and application layers and how transactions are handled.
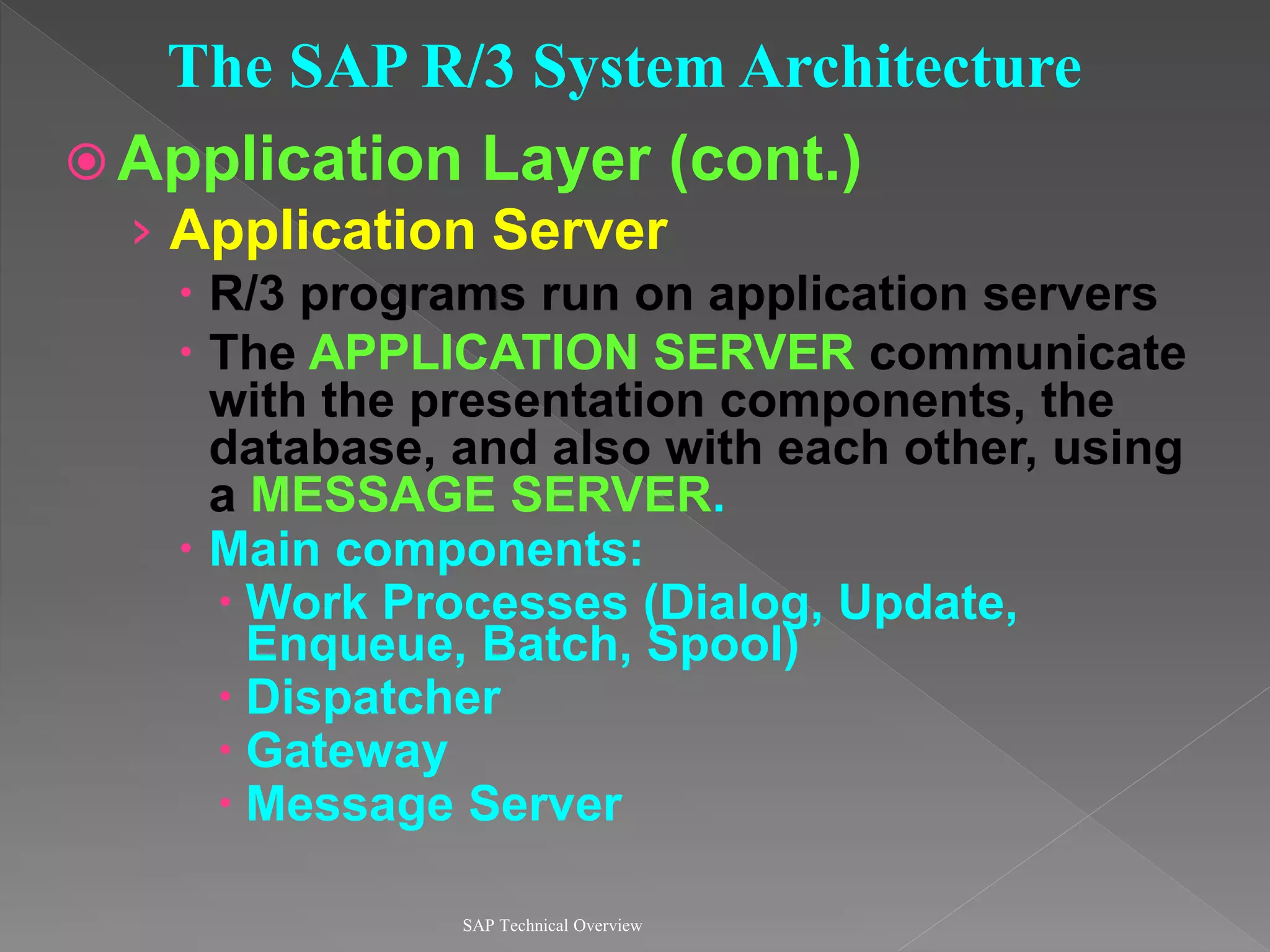
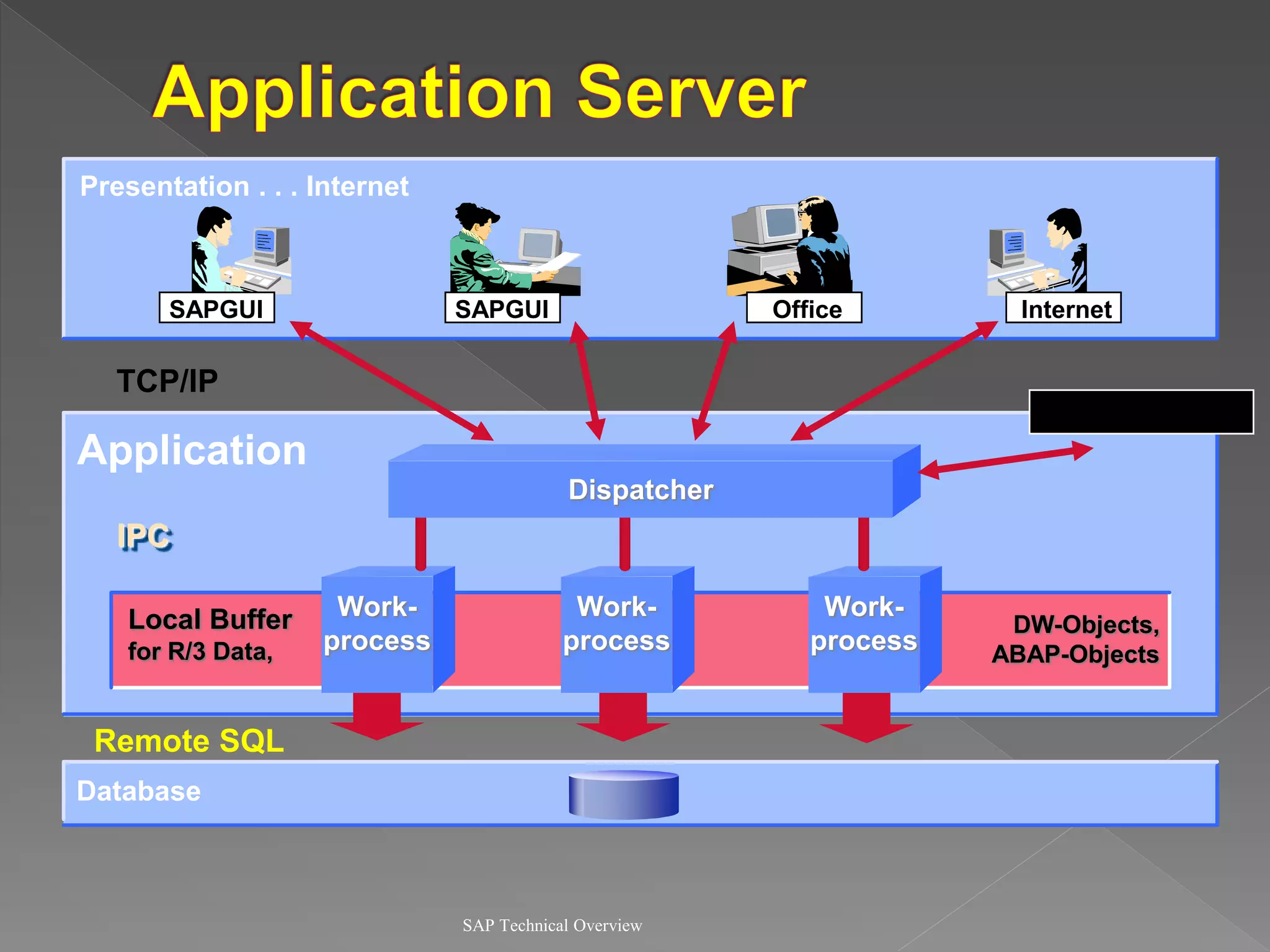
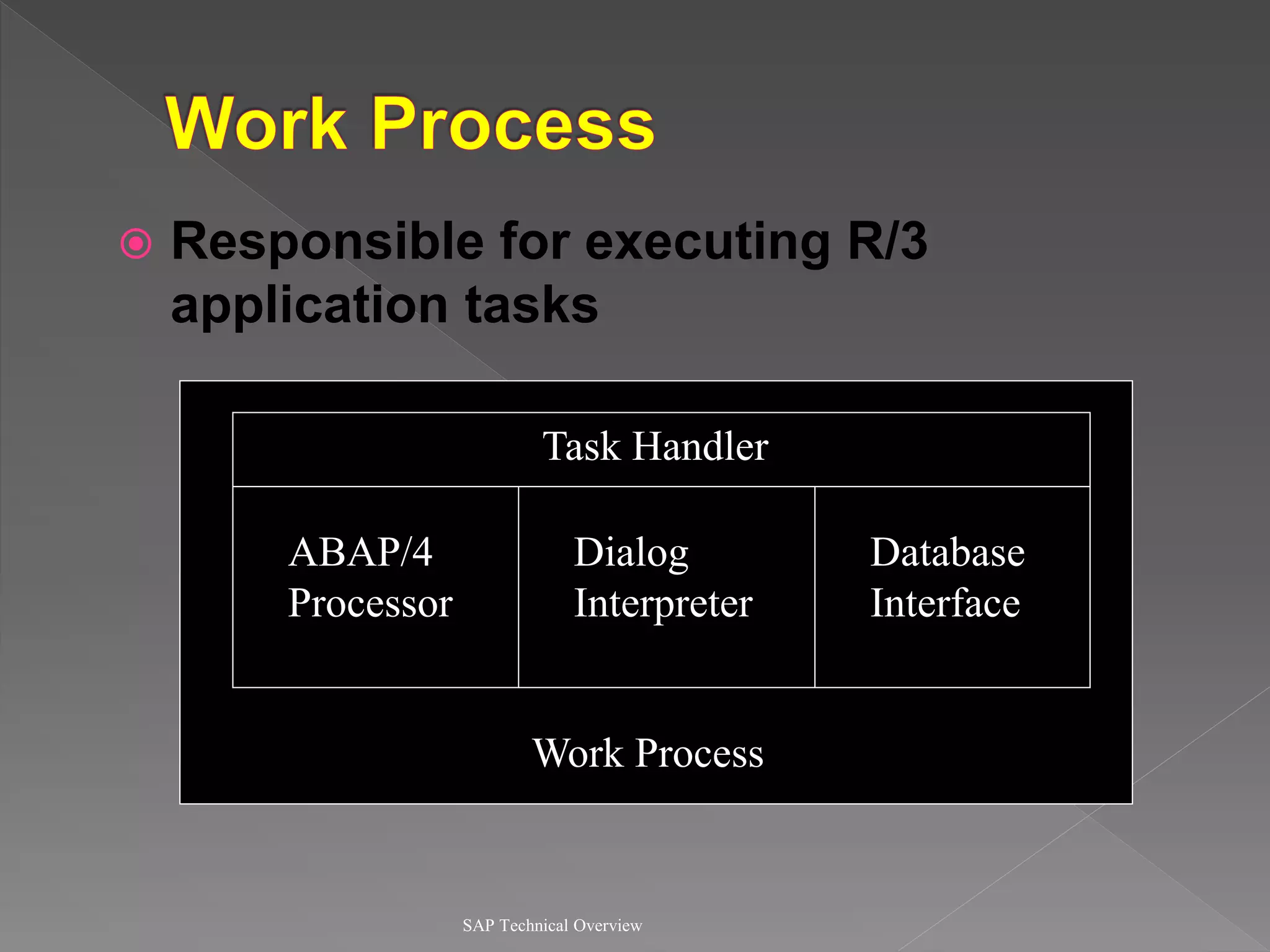
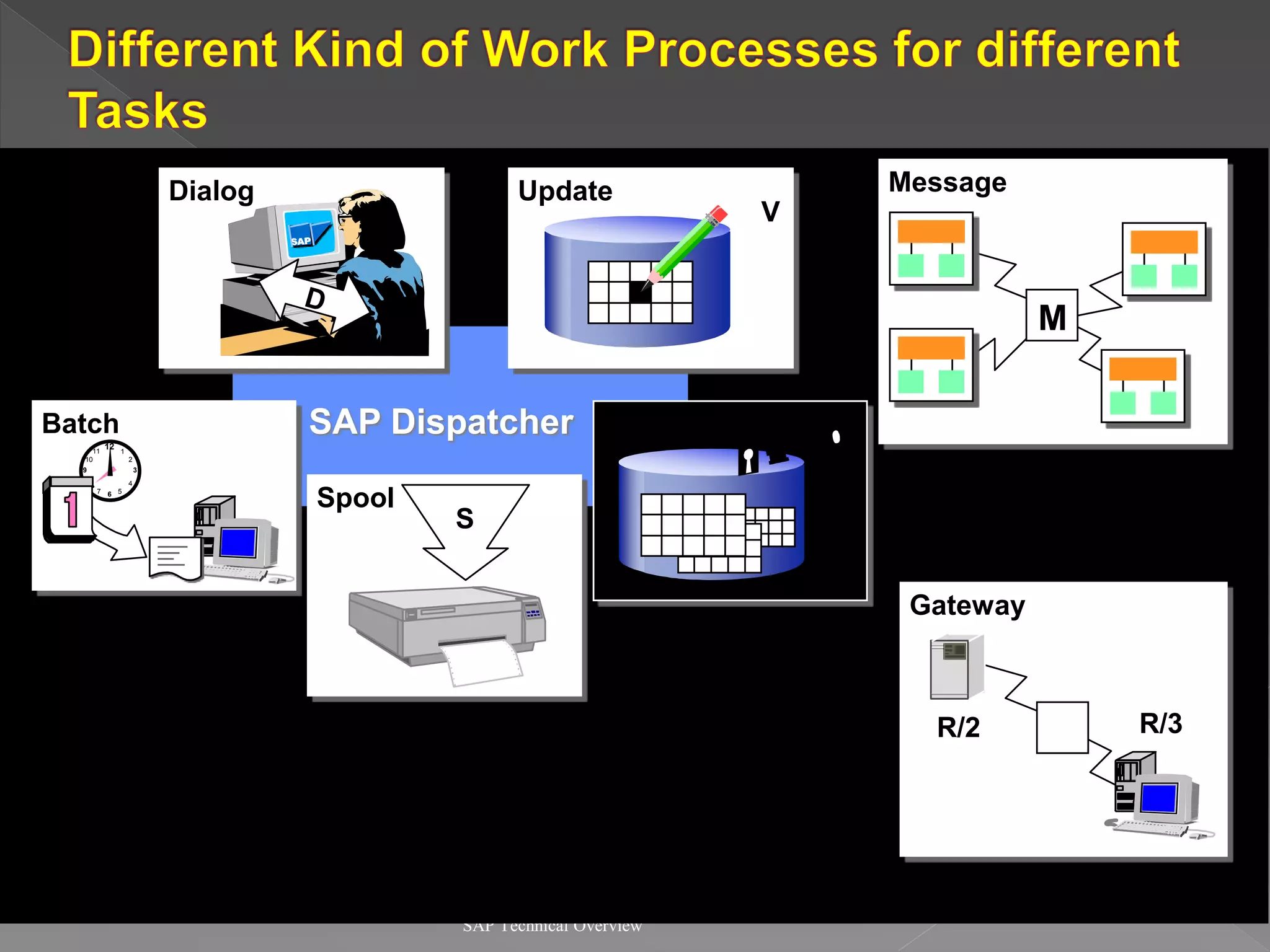
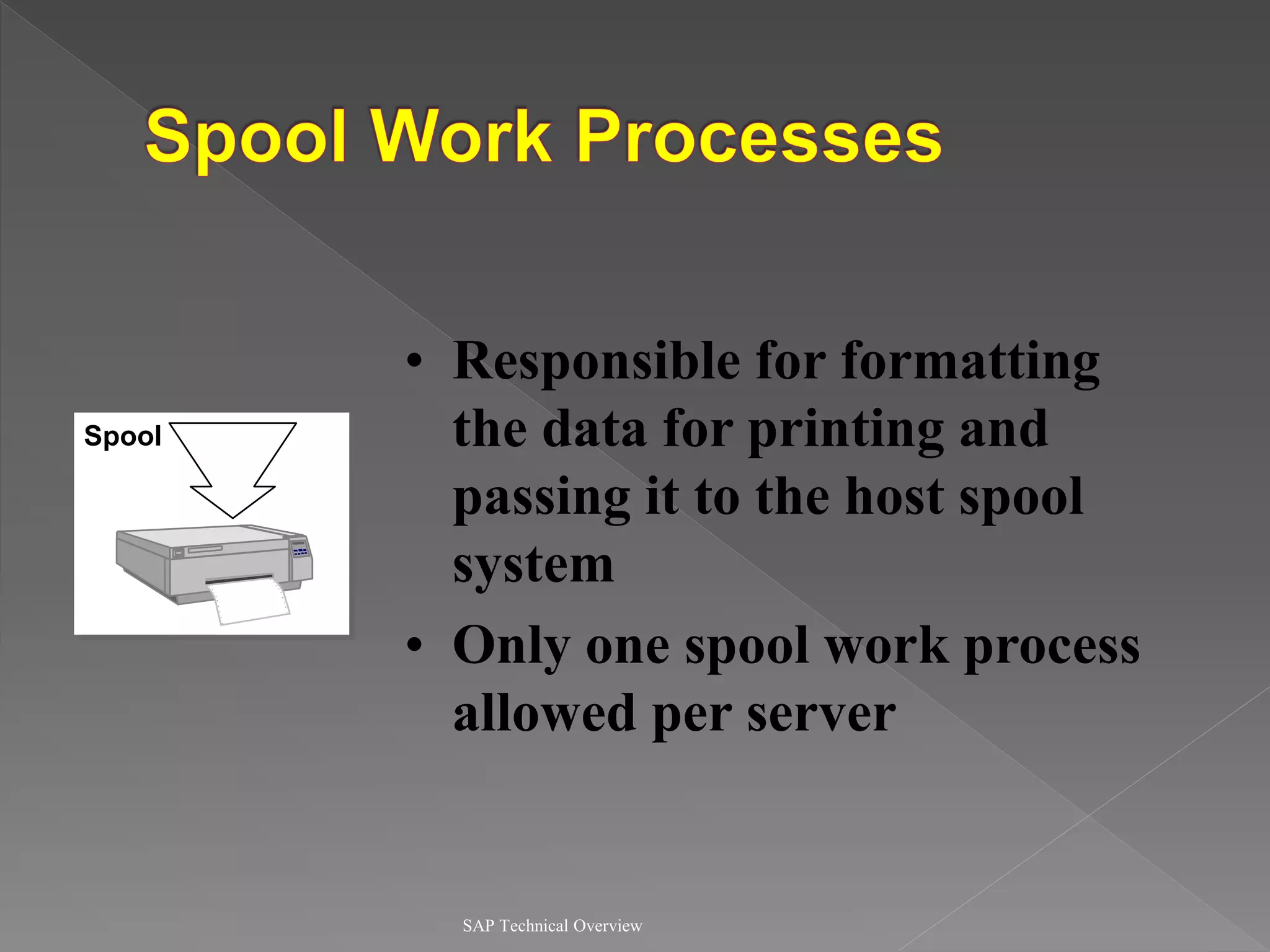
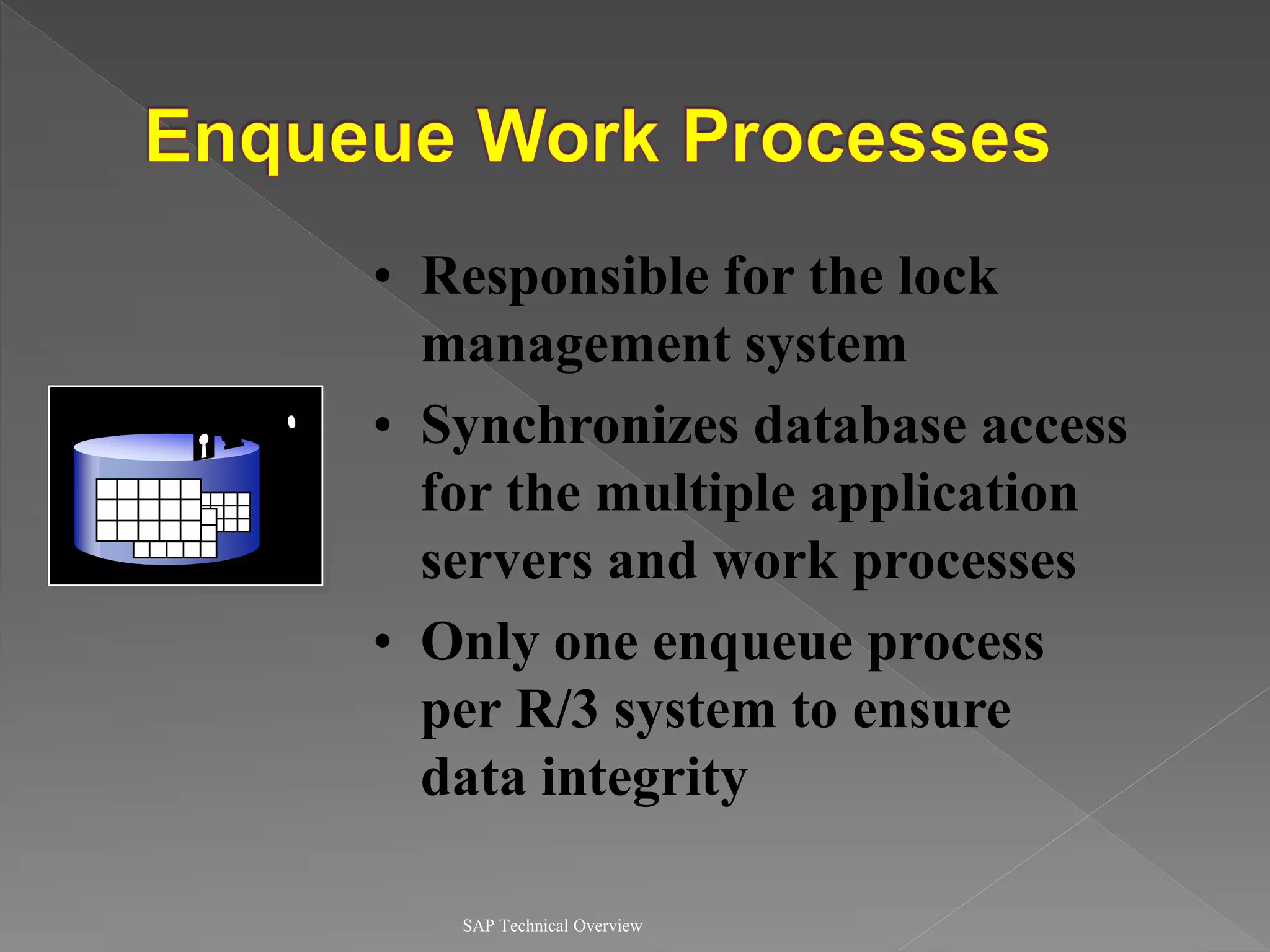
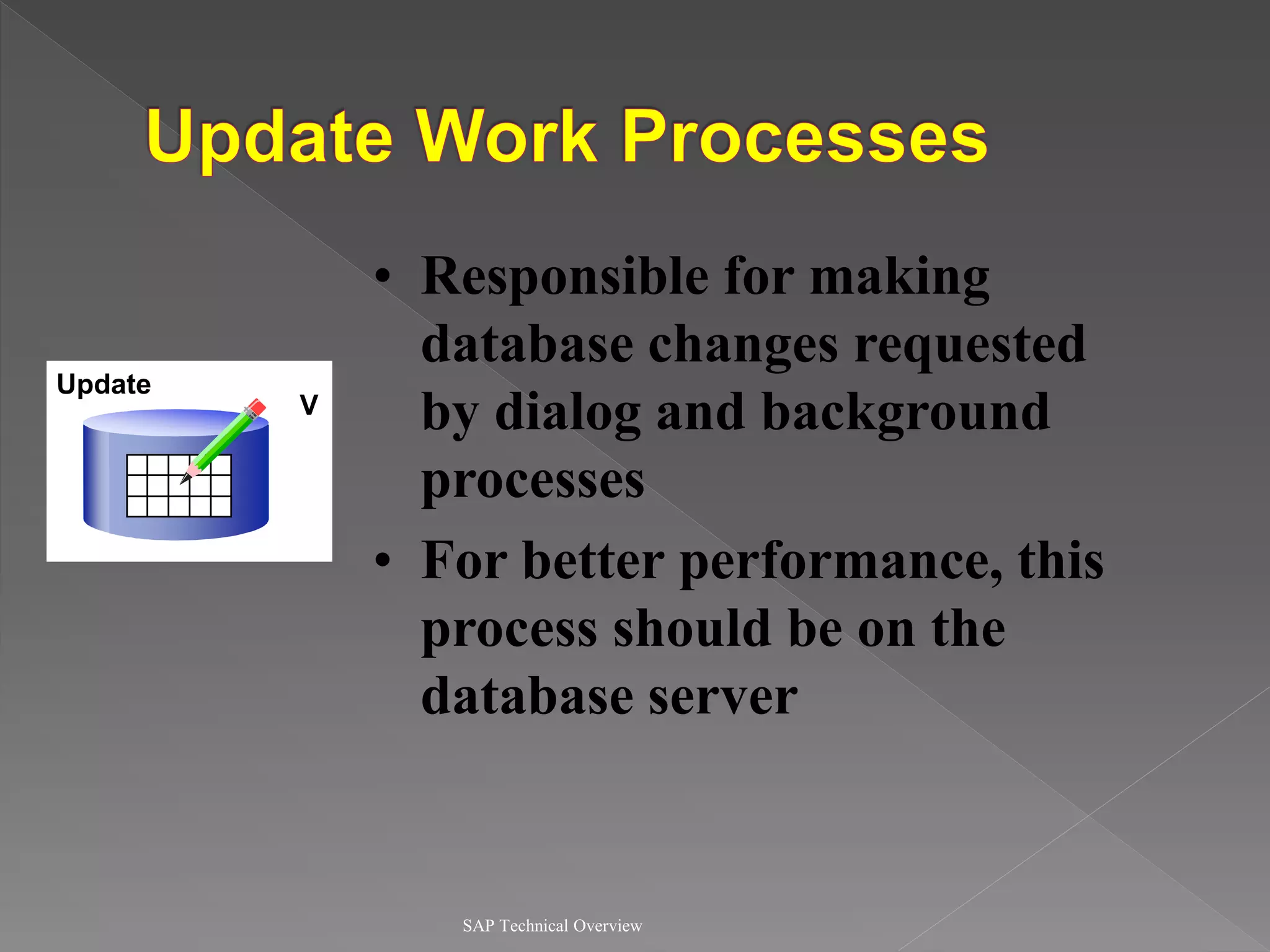
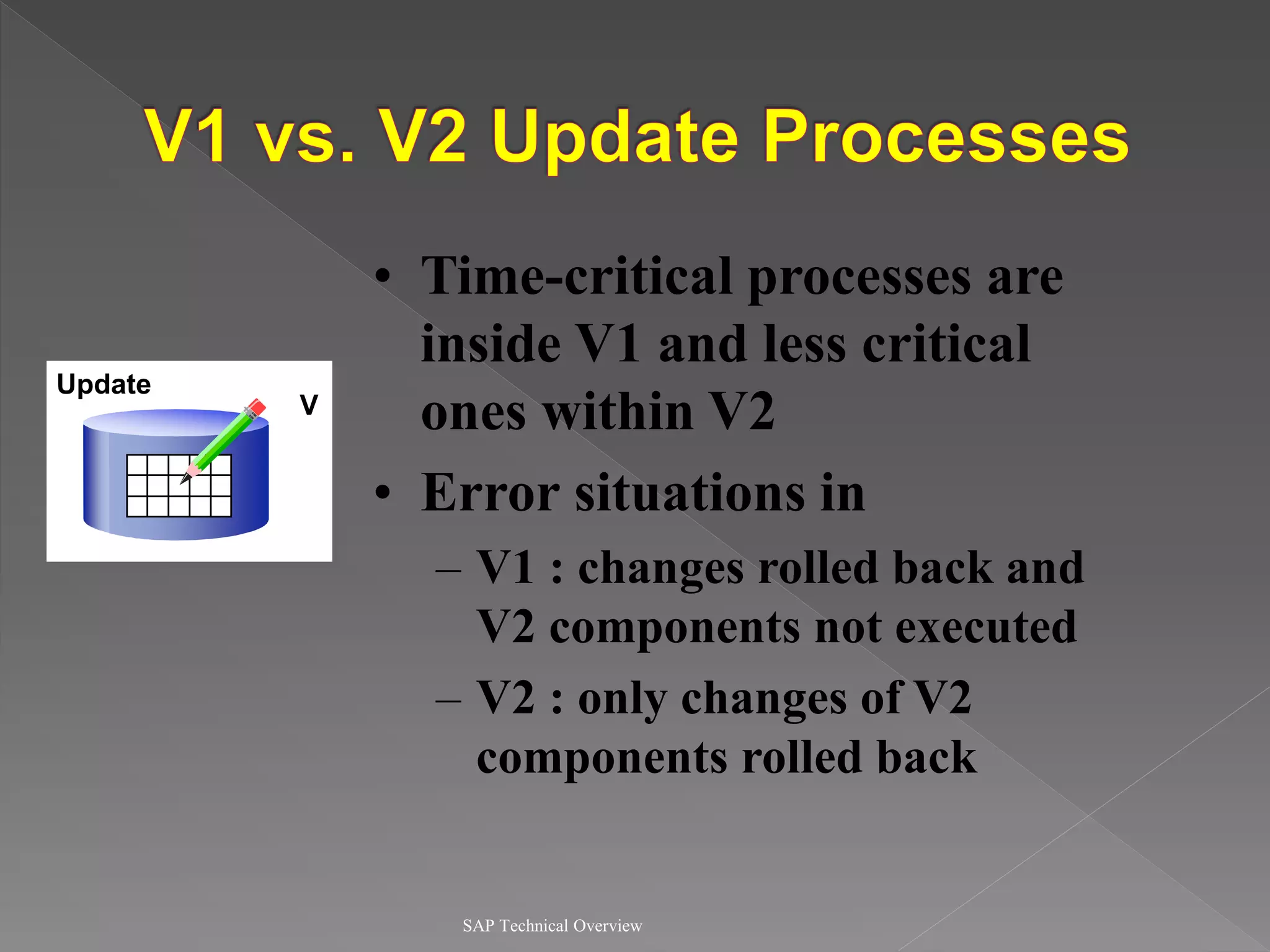
2) It explains the different work processes like dialog, update, enqueue, and batch processes and their roles.
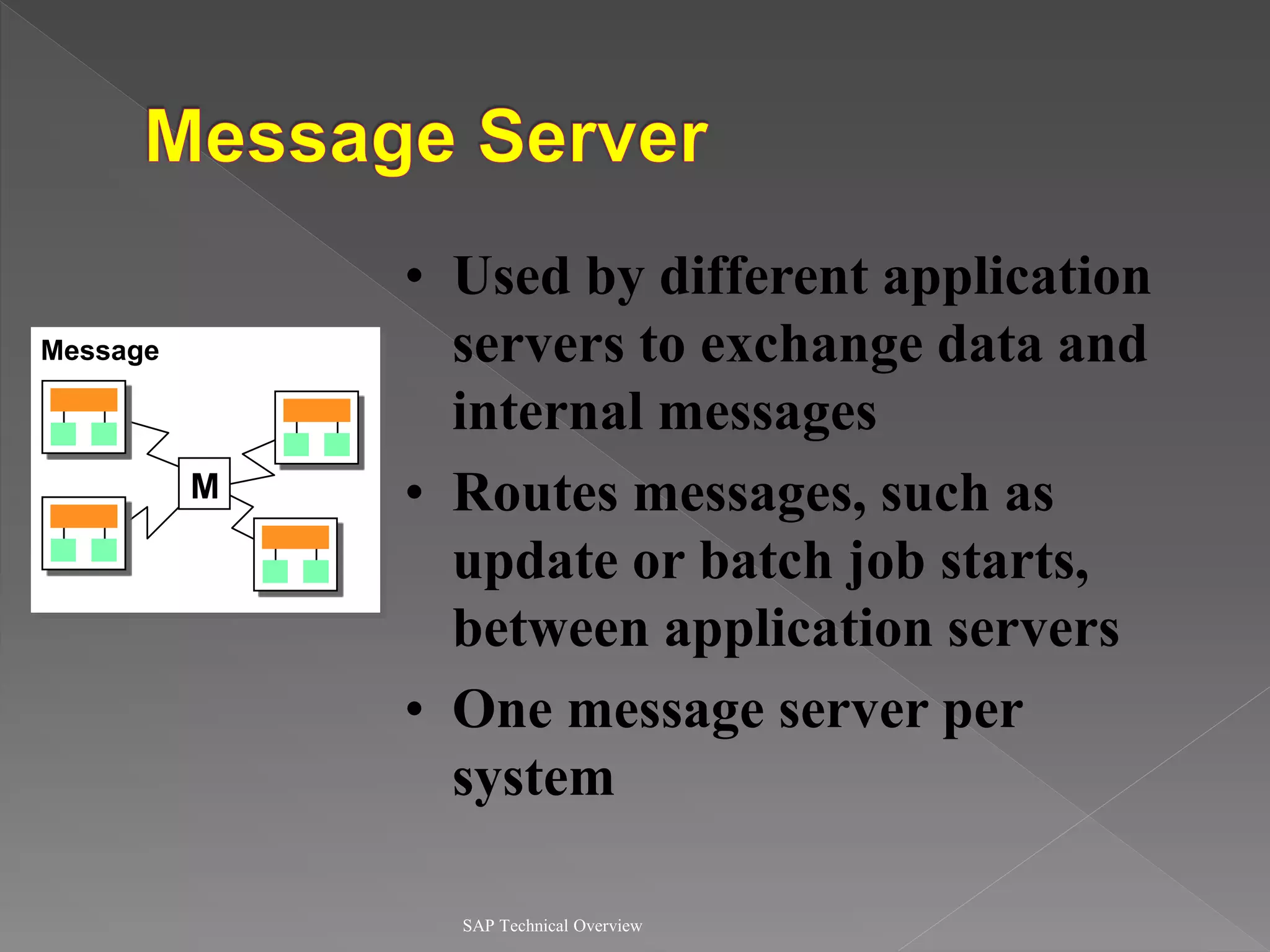
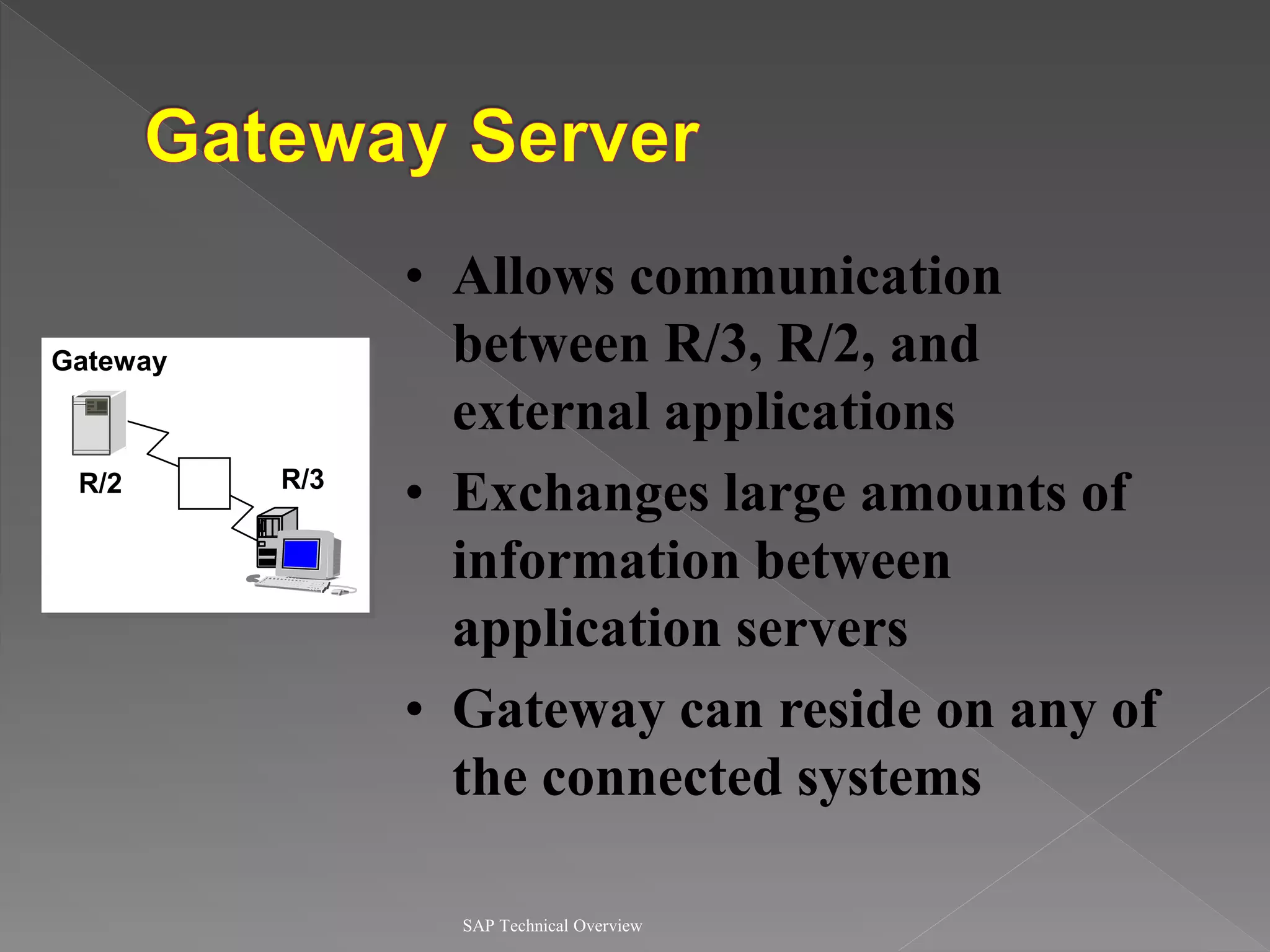
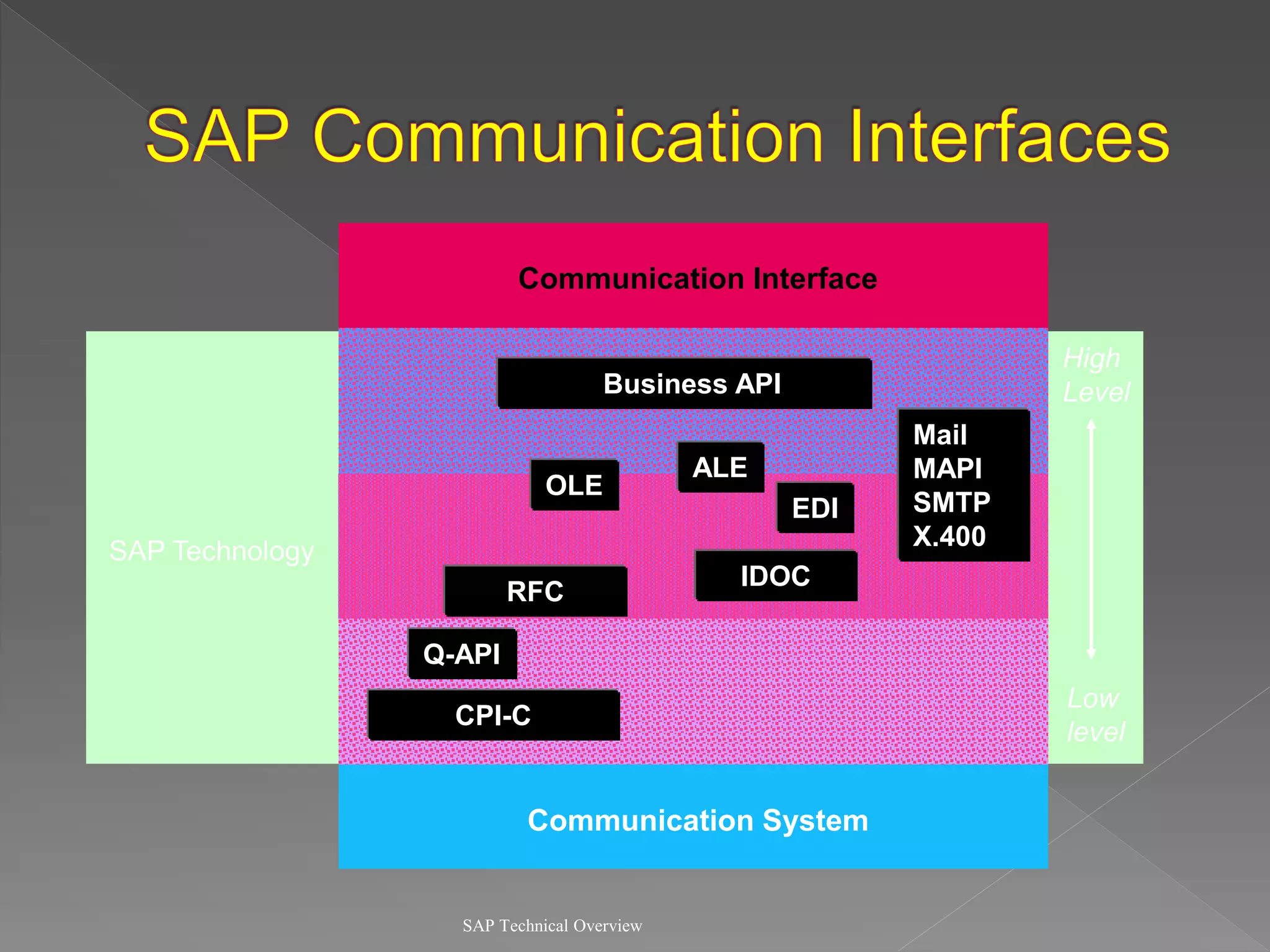
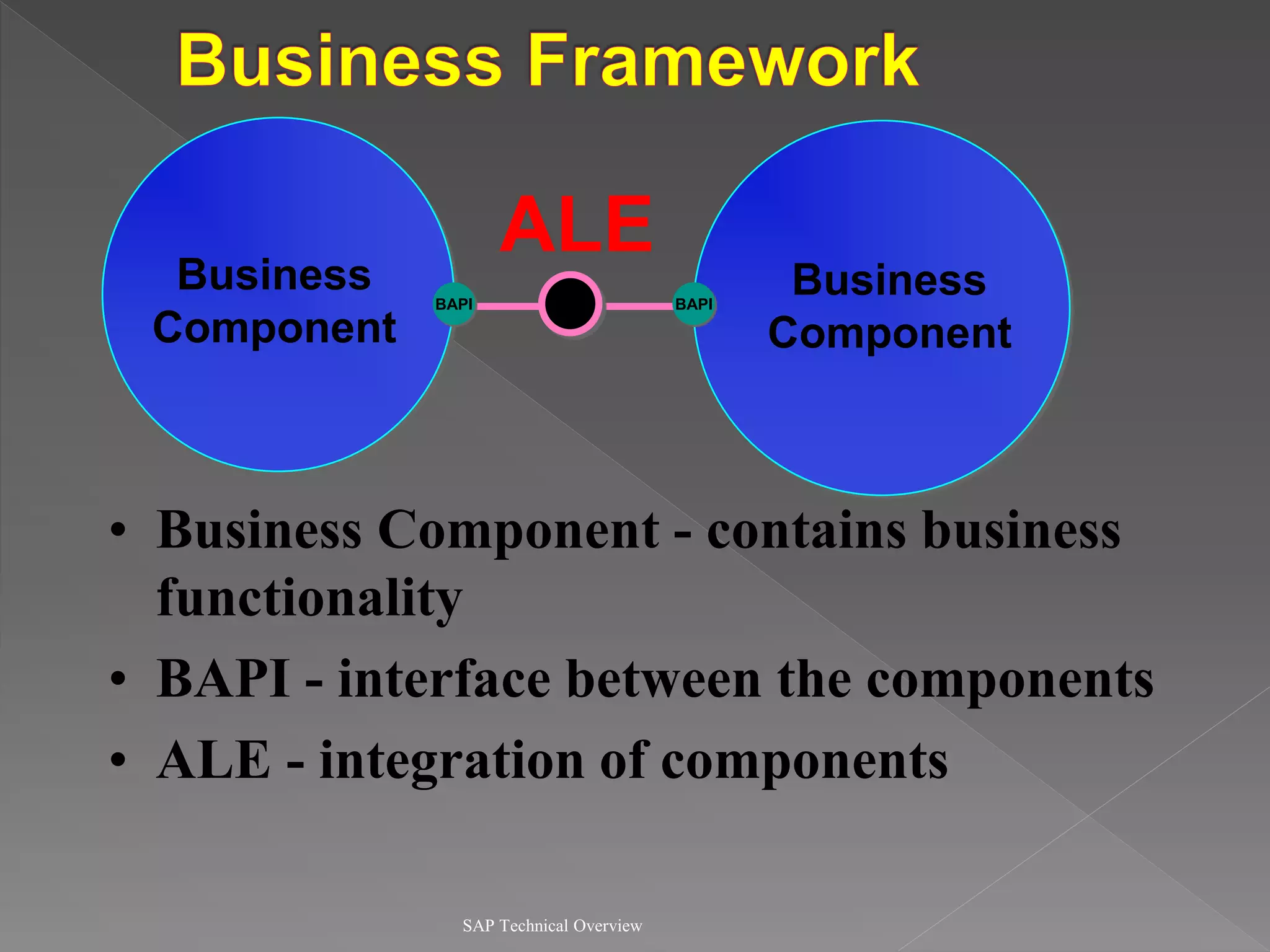
3) It discusses communication interfaces and protocols for integrating different systems as well as business APIs.