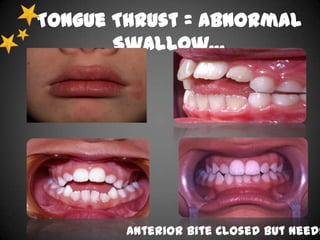
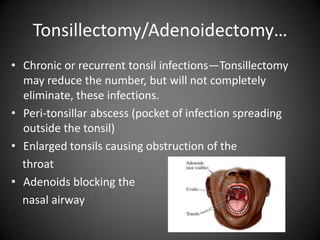
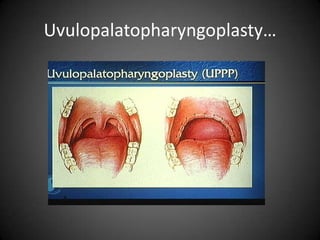
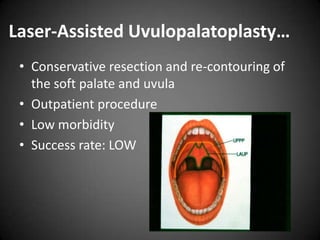
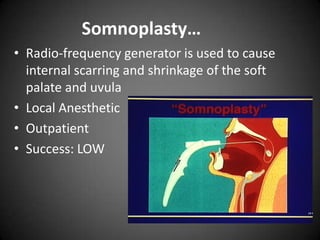
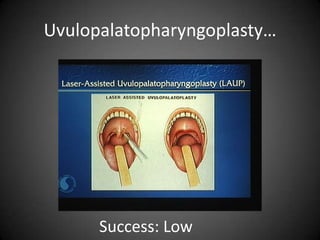
This document discusses various sleep disorders from pediatrics to geriatrics. It provides statistics on common sleep disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy. It describes risk factors, symptoms, and potential health consequences of obstructive sleep apnea, including increased risks of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. The document also discusses screening questionnaires, medical conditions that can contribute to sleep disorders, and various treatment options like tonsillectomy, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, and somnoplasty procedures.





















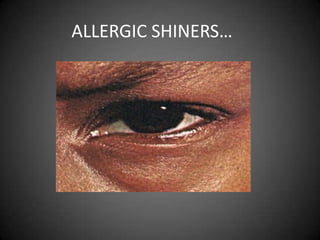
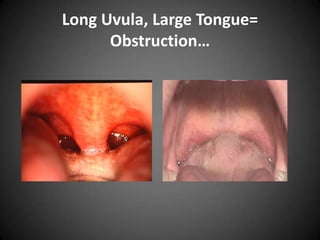
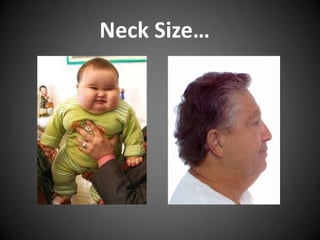














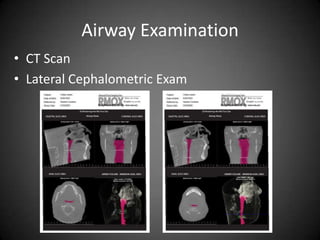















![Sleep…
“[Sleep is] the golden chain that ties
health and our bodies together.”
Thomas Dekker (1572-1632)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sleepdisordersfrompediatricstogeriatricsspreecast332014-140303183549-phpapp02/85/Sandy-Coulson-Sleep-Disorder-Spreecast-75-320.jpg)
