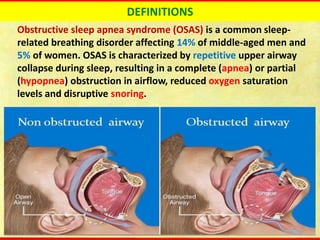
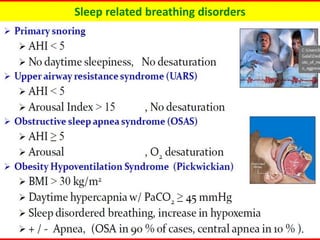
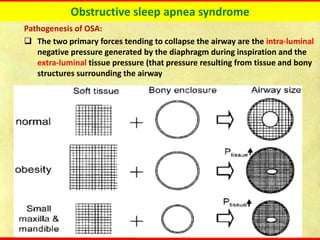
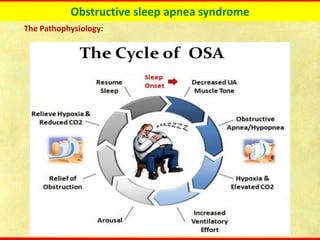
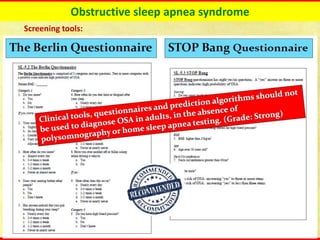
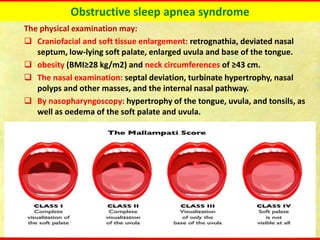
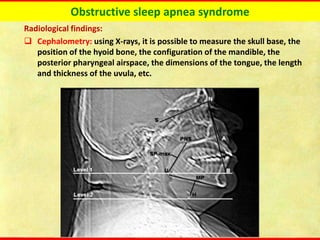
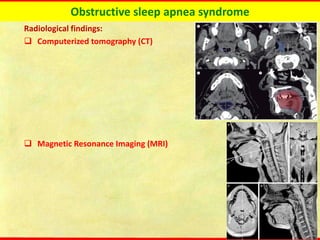
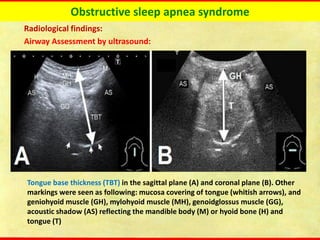
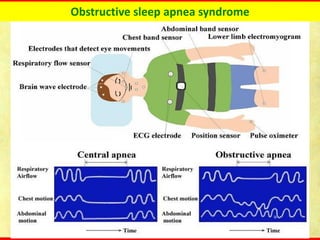
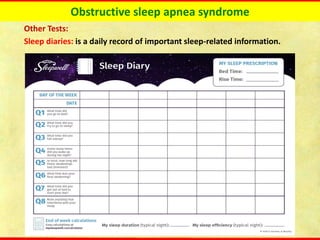
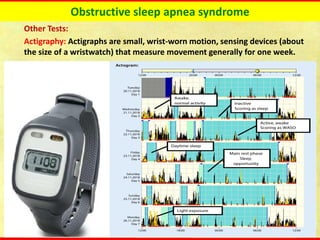
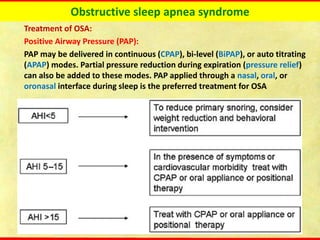
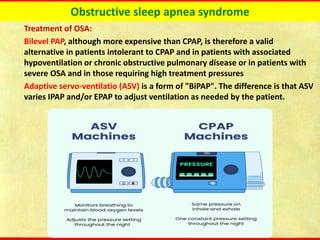
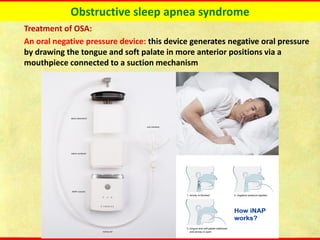
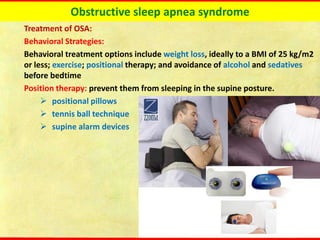
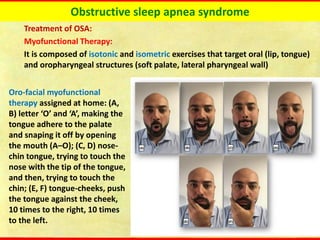
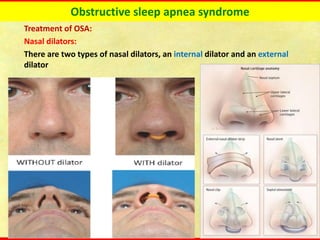
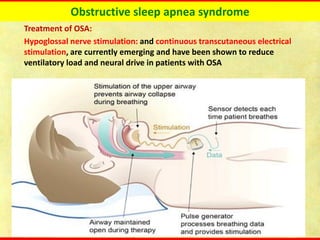
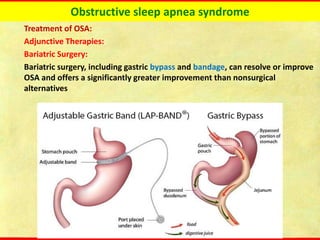
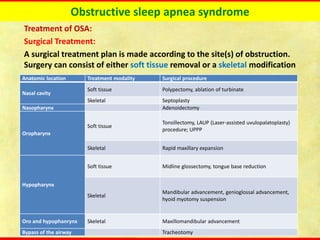
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is a common sleep disorder characterized by repetitive collapse of the upper airway during sleep, resulting in reduced airflow and oxygen levels. It affects 14% of middle-aged men and 5% of women. Polysomnography is the gold standard test used to diagnose OSAS and measure its severity based on the apnea-hypopnea index. Positive airway pressure therapy is the primary treatment, while other options include oral appliances, surgery, and lifestyle changes. Untreated OSAS can cause serious health complications.