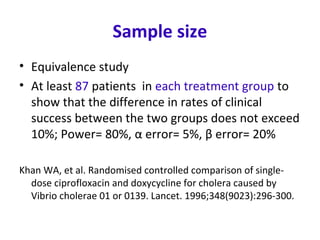
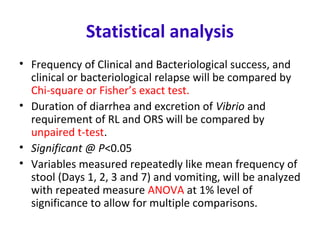
This document describes a randomized controlled trial comparing the effectiveness of azithromycin versus ciprofloxacin for treating cholera in children. The trial aims to evaluate whether a single dose of oral azithromycin is as effective as a single dose of oral ciprofloxacin for resolving diarrhea and stopping the excretion of Vibrio cholerae in children with cholera. Over 87 children between ages 2-12 with acute watery diarrhea will be randomly assigned to receive either azithromycin or ciprofloxacin after rehydration. The primary outcomes will be clinical and bacteriological success after 72 hours. Secondary outcomes include recovery time, fluid requirements, and relapse rates, which will be compared between the