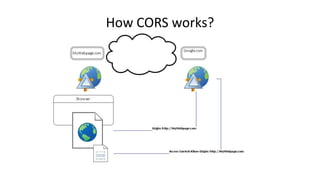
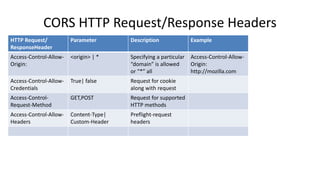
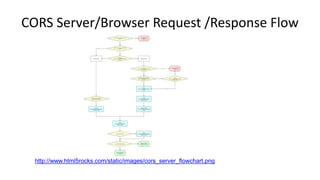
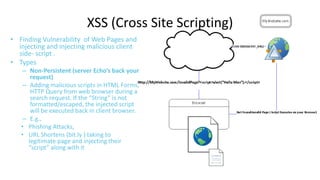
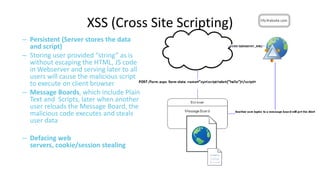
This document discusses cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) and content security policy (CSP) as techniques to improve security in web applications. It begins by explaining the need for the same-origin policy and how CORS helps address limitations of SOP by allowing controlled cross-origin requests. It then discusses cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and how CSP helps prevent XSS by allowing web applications to restrict resources that can be loaded or executed.


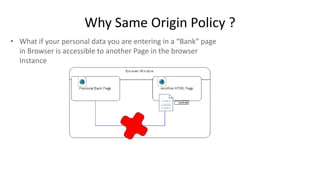

![What are allowed in SOP?
• SOP cannot prevent cross site content inclusions (like images, scripts, css
from different domain
• http://www.google.com/page1 can access http://www.google.com/page2
• http://www.google.com/page1 cannot access http://www.yahoo.com as
the two pages belong to different domain
• <script> is allowed by SOP [file:// ??]
• In a http://www.mypage.com page, you can include<script src=
http://api.google.com/googleplus >.
• Google API page scripts are executed in “Mypage” domain, HTML
Application, it will still have access to “Mypage” DOM elements. So, if the
“Google API scripts” are compromised, it will have bad effect on the
“MyPage” (Will take it to XSS- Cross Site Scripting)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sopcorscspnew-131126075930-phpapp01/85/Browsers_SameOriginPolicy_CORS_ContentSecurityPolicy-5-320.jpg)