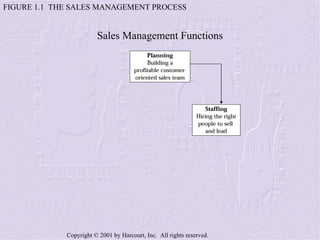
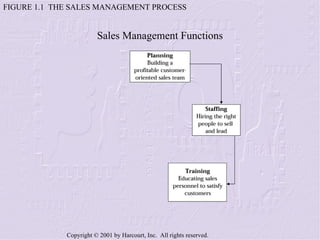
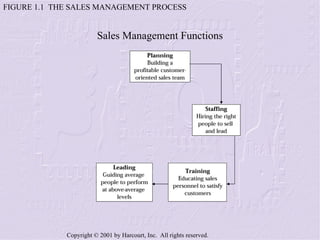
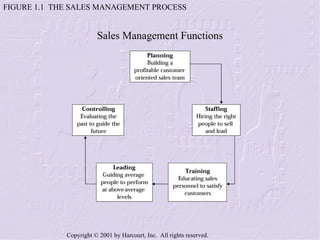
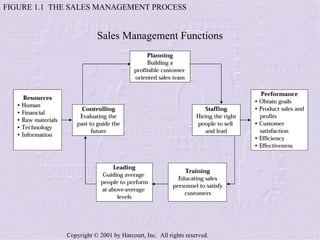
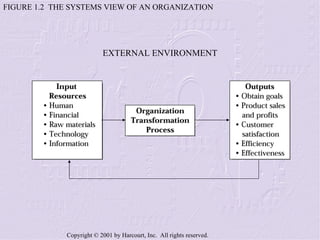
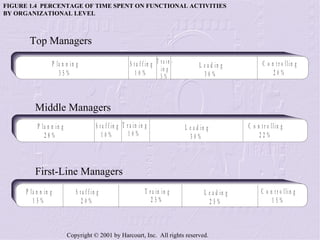
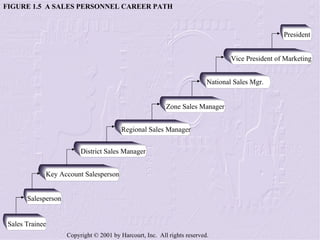
The document provides an overview of sales management, including its nature, rewards, and responsibilities. It discusses the key functions of sales management, which include planning, staffing, training, leading, and controlling organizational resources to effectively achieve sales goals. It also examines the skills required of sales managers and the challenges faced by salespeople promoted to management roles.