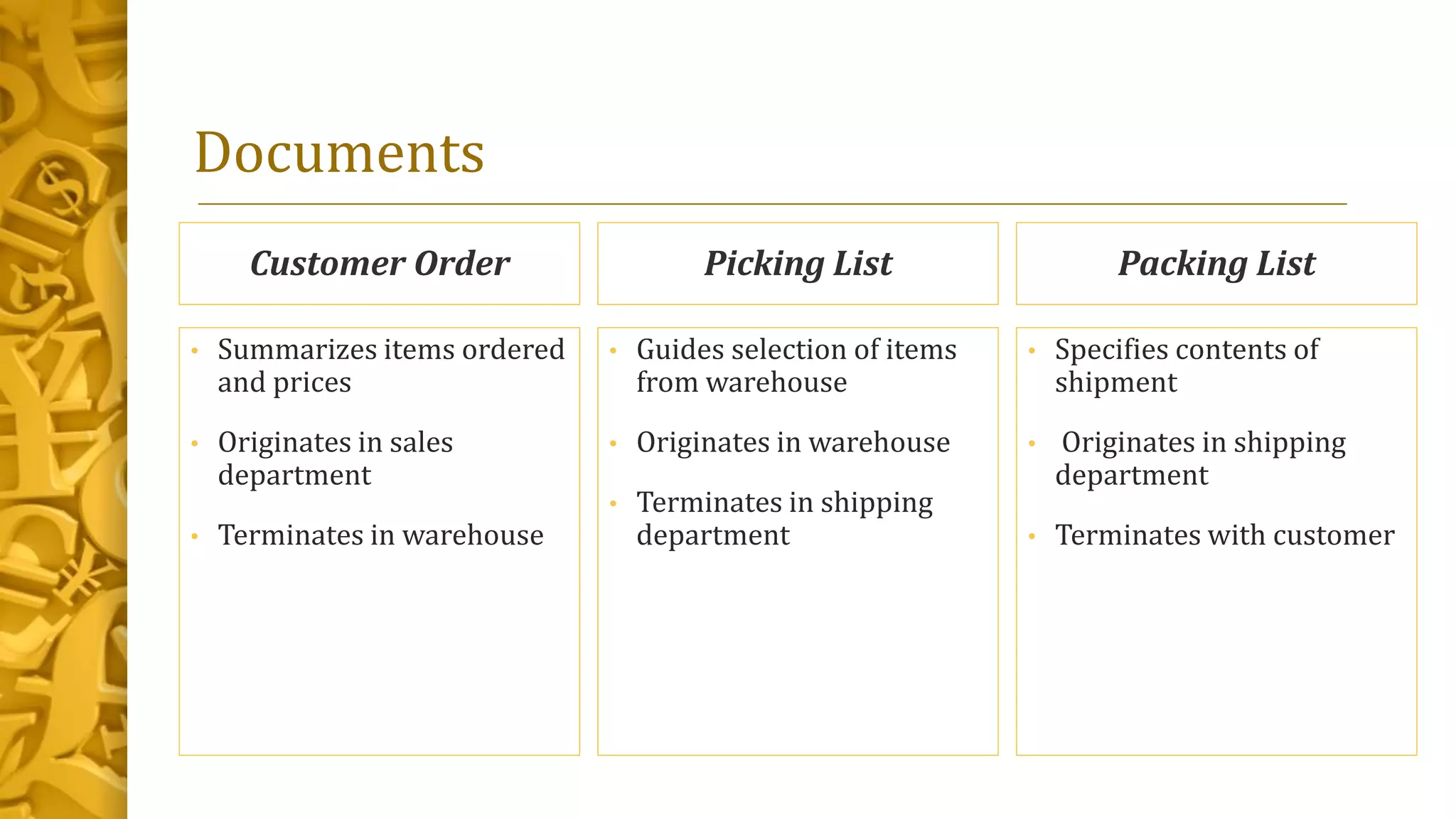
The document describes the sales/collection process and value chain. It discusses the primary and support activities in the value chain. The sales/collection process generally comprises seven steps: taking the customer's order, approving credit, filling the order, shipping the product, billing the customer, collecting payment, and processing uncollectible receivables. It also outlines the flowchart and documents involved in each step, as well as internal controls and how information technology supports the process.