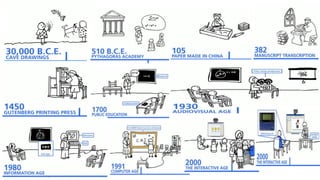
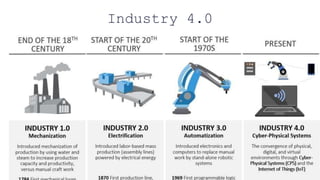
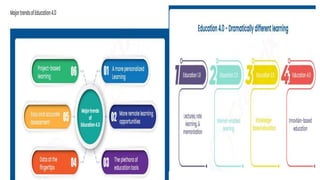
Industry 4.0 refers to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. This fourth industrial revolution is changing how products are made and improving interconnectivity across supply chains. However, for developing countries like India it presents challenges as well, such as the high costs of implementation, lack of data analytics skills and reluctance to innovation. Education 4.0 aims to address these challenges by improving the education system in India through new technologies and a focus on creativity to prepare students for the skills needed in modern Industry 4.0.