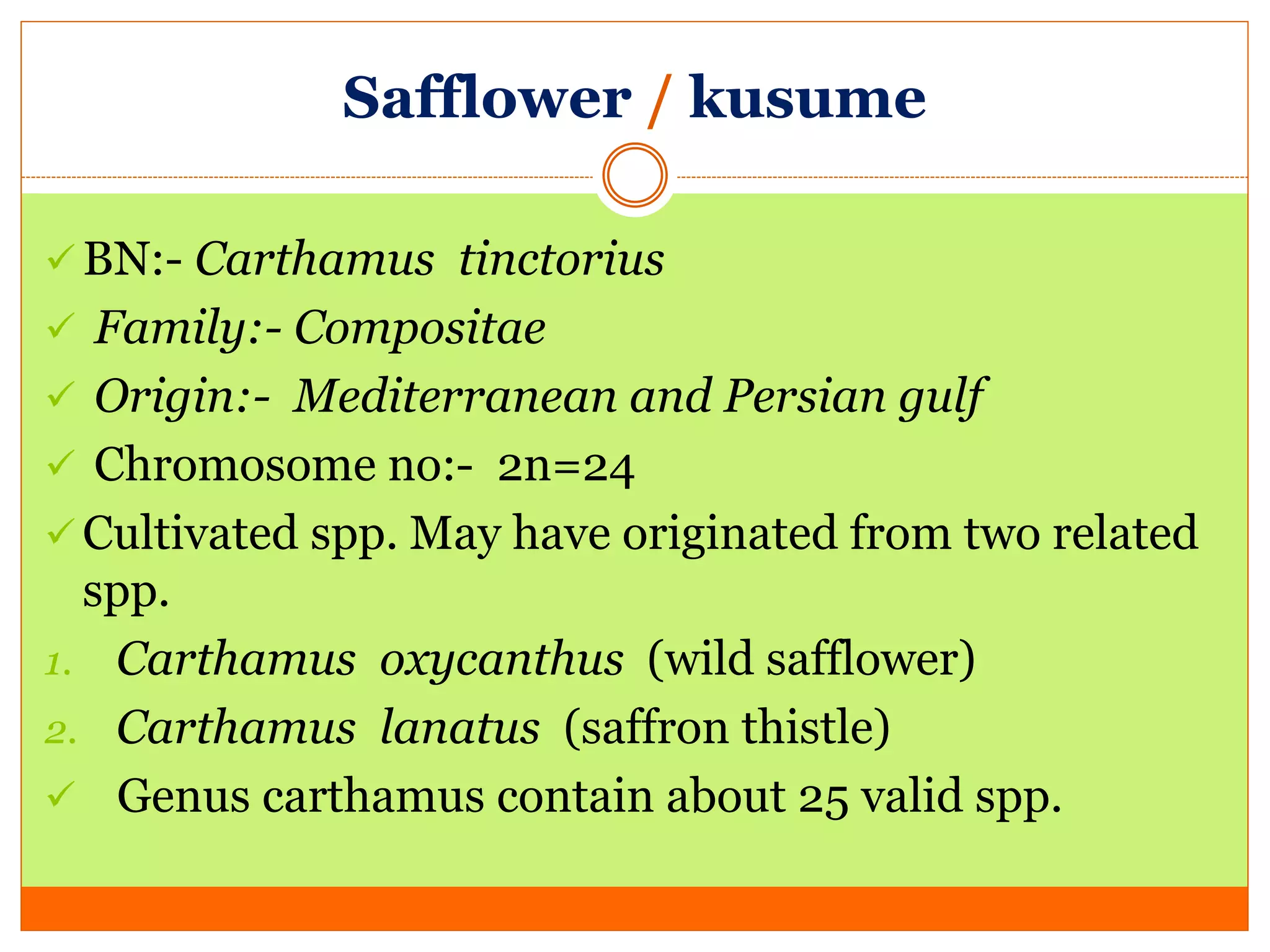
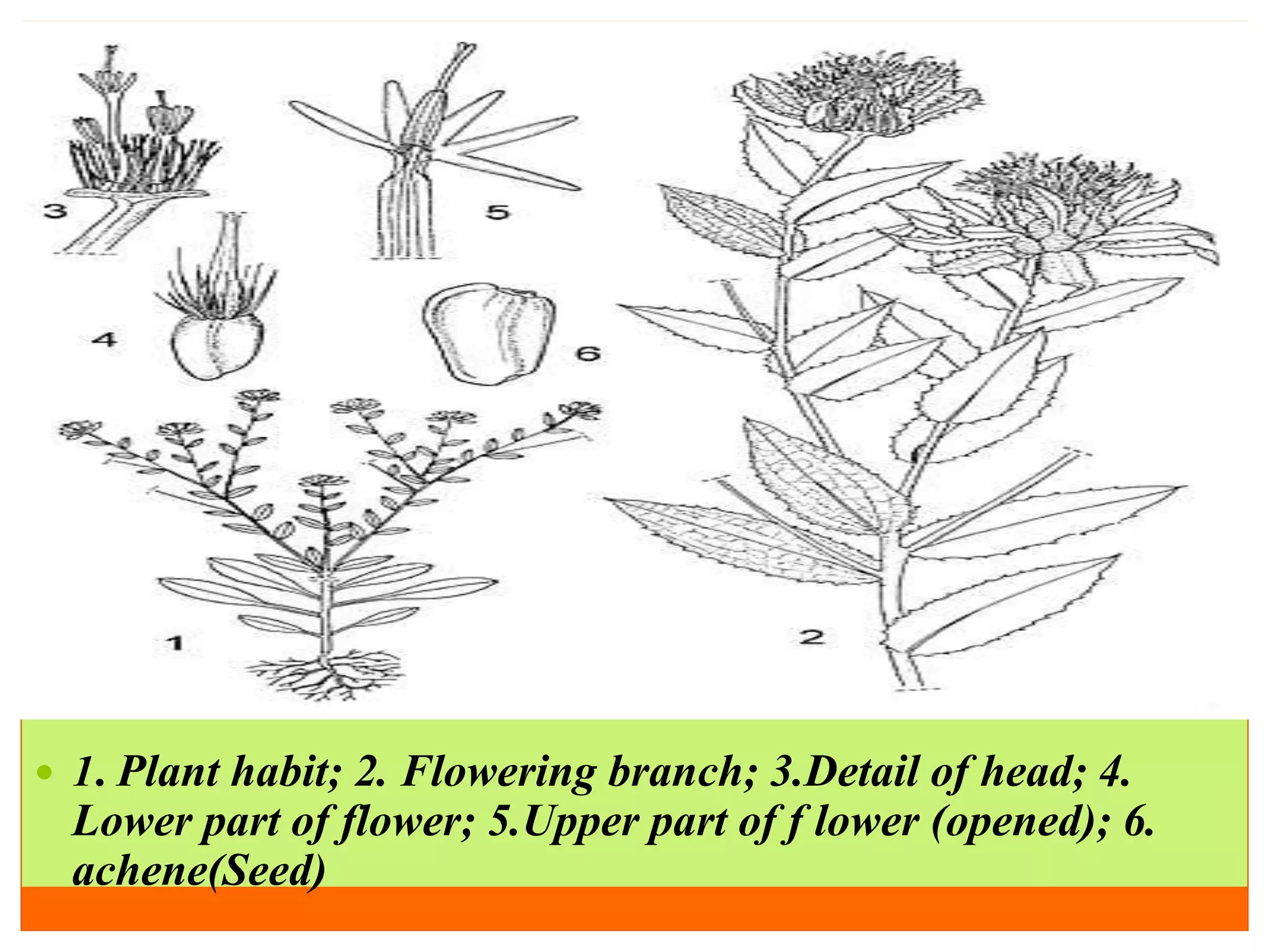
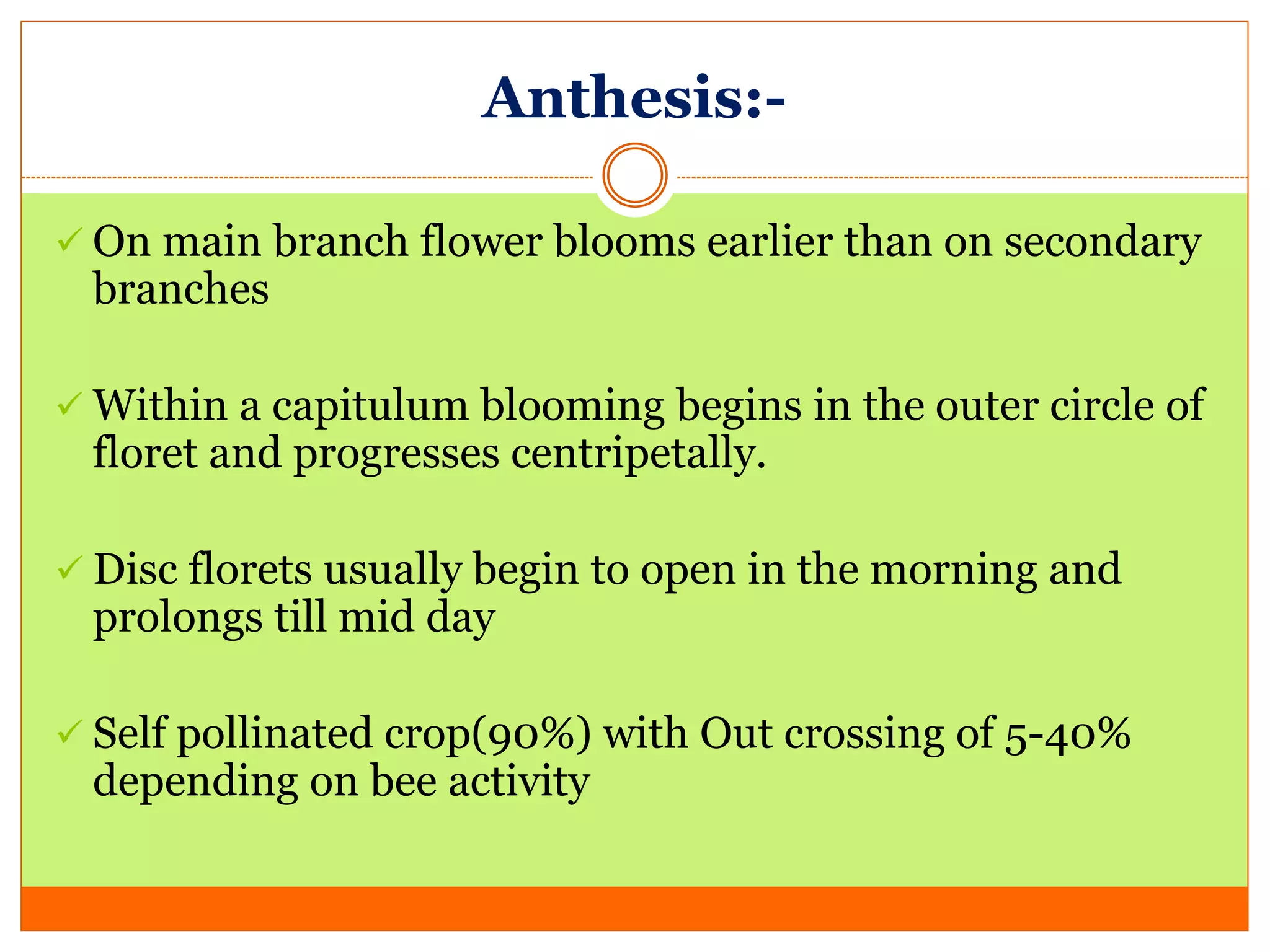
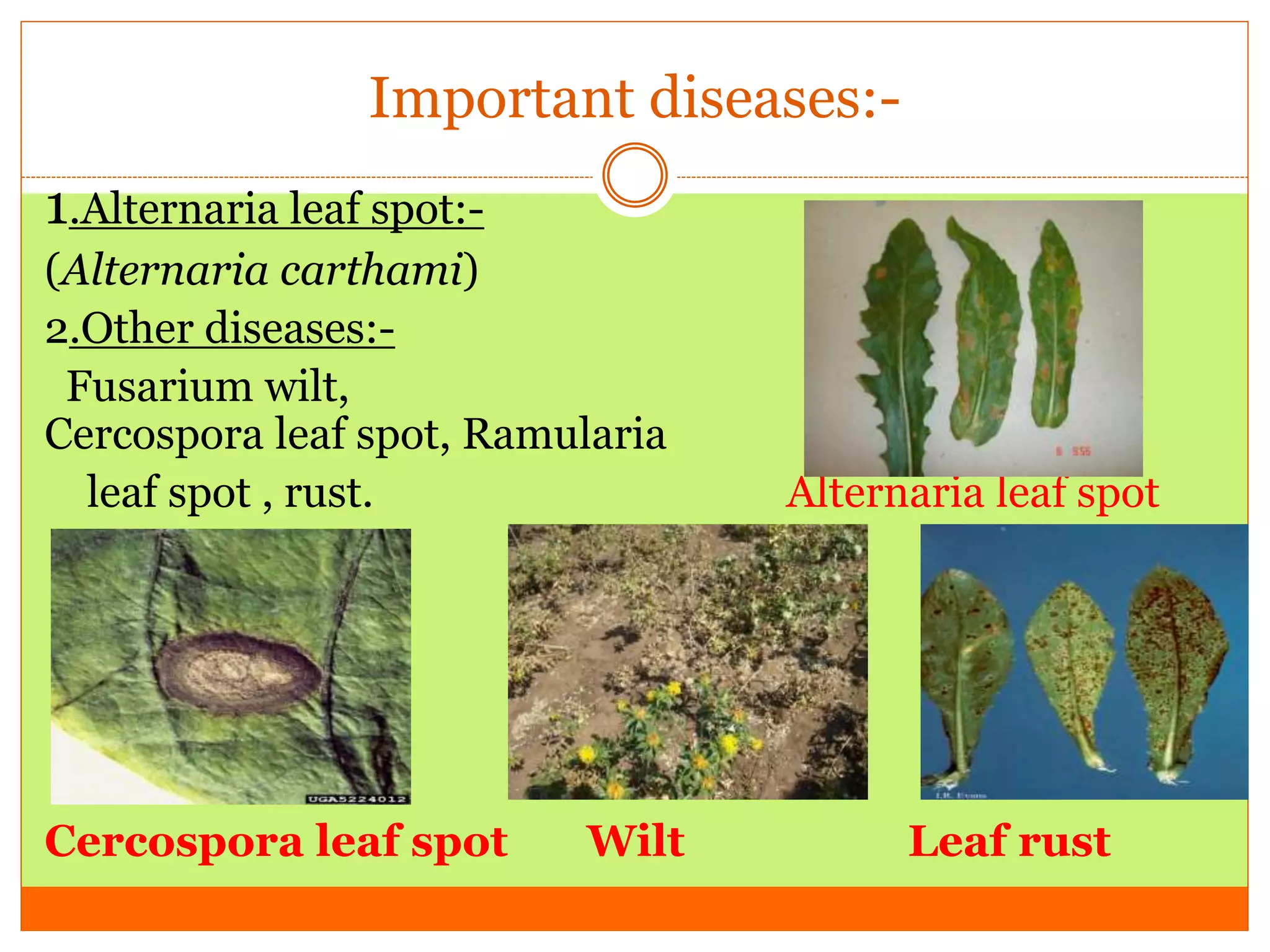
Safflower is an important rabi oilseed crop grown primarily in India and Mexico. The main varieties grown in India are S 144, A1, A2, and A300. Safflower is cultivated for its oil content of 28-32% and protein content of 14-19%. Maharashtra and Karnataka are the major producers of safflower in India. The crop faces pest problems from safflower aphid and diseases like Alternaria leaf spot. Breeding objectives for safflower include developing varieties with higher yields, oil content, thermo-insensitivity and resistance to pests and diseases.