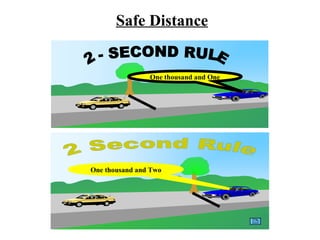
The document provides guidance on safe driving practices including techniques like MSM (Mirrors, Signal, Manoeuvre) and PSL (Position, Speed, Look). It discusses maintaining a safe following distance, defensive driving, the purpose of flyovers and bypasses, and how to handle emergencies. Tips are also given for driving in difficult conditions like rain, fog, or at night.