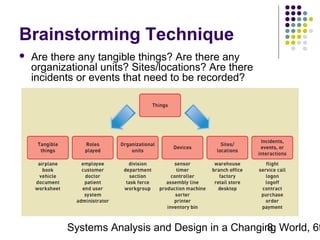
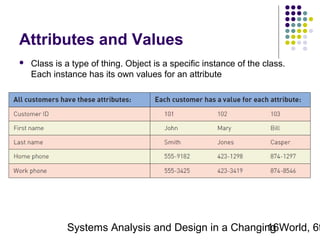
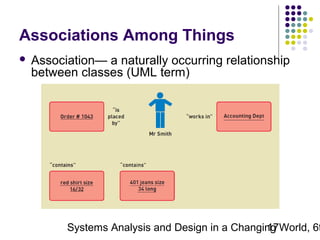
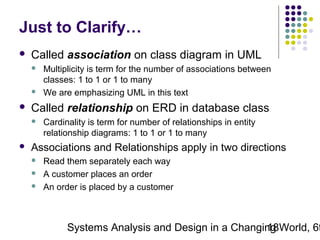
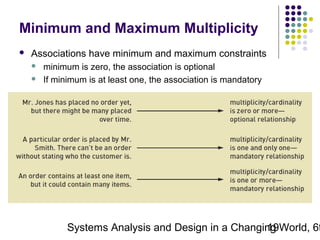
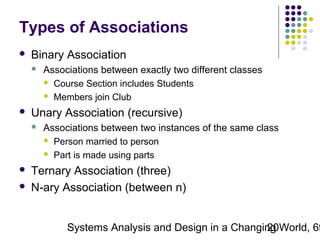
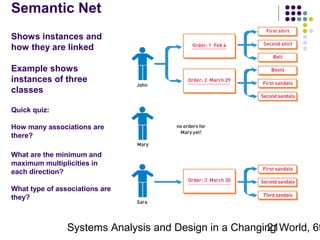
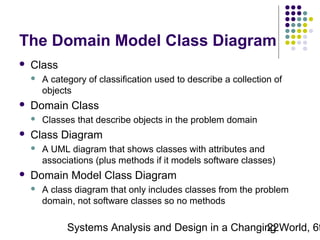
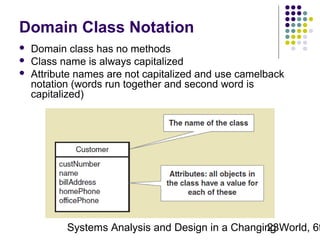
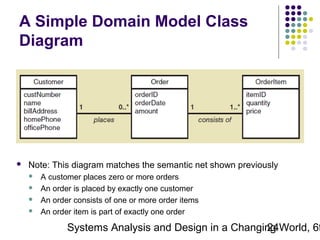
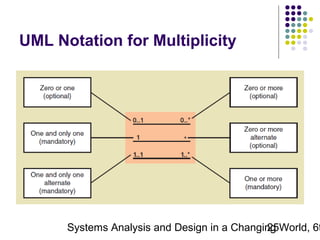
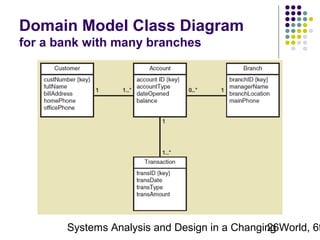
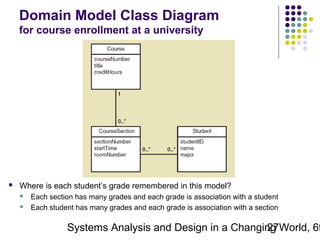
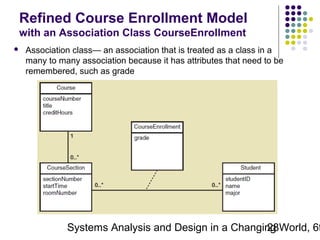
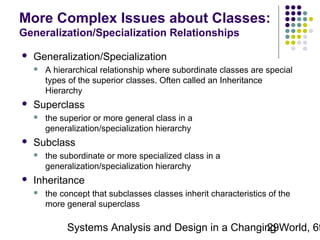
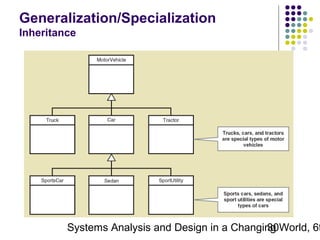
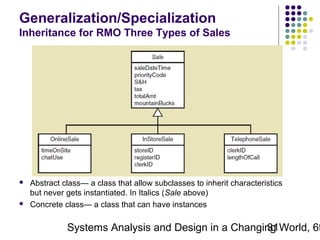
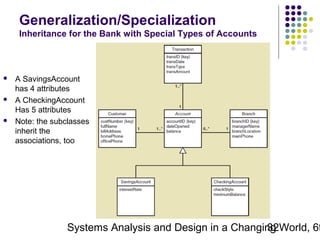
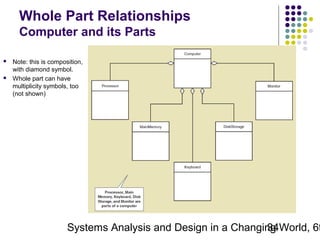
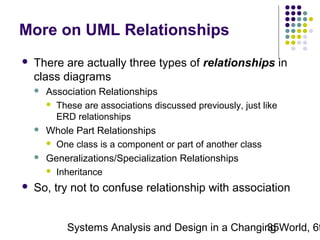
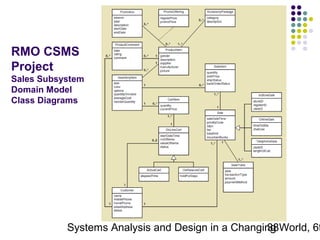
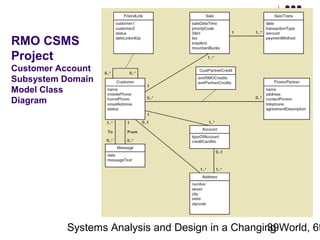
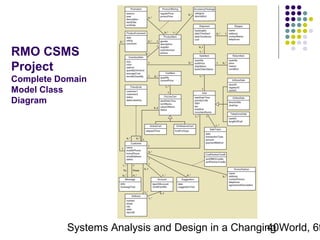
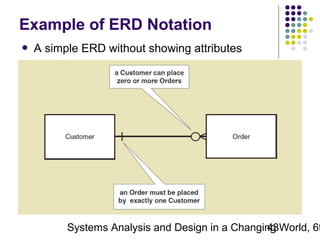
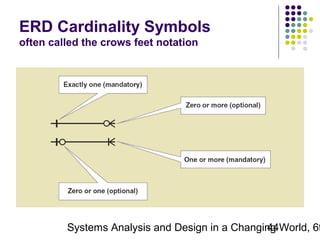
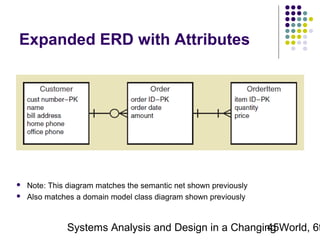
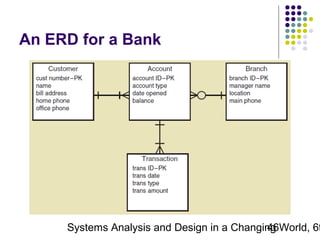
This document discusses domain classes and domain modeling. It begins by explaining how domain classes represent "things" in the problem domain that need to be modeled by the system. Two techniques for identifying domain classes are described: brainstorming and using a noun analysis. The document then discusses how to represent domain classes and their attributes, associations, and relationships in a domain model class diagram. It provides examples of domain model class diagrams for various systems. Finally, it discusses how domain model class diagrams can be developed for subsystems of a large project and how they relate to entity-relationship diagrams.