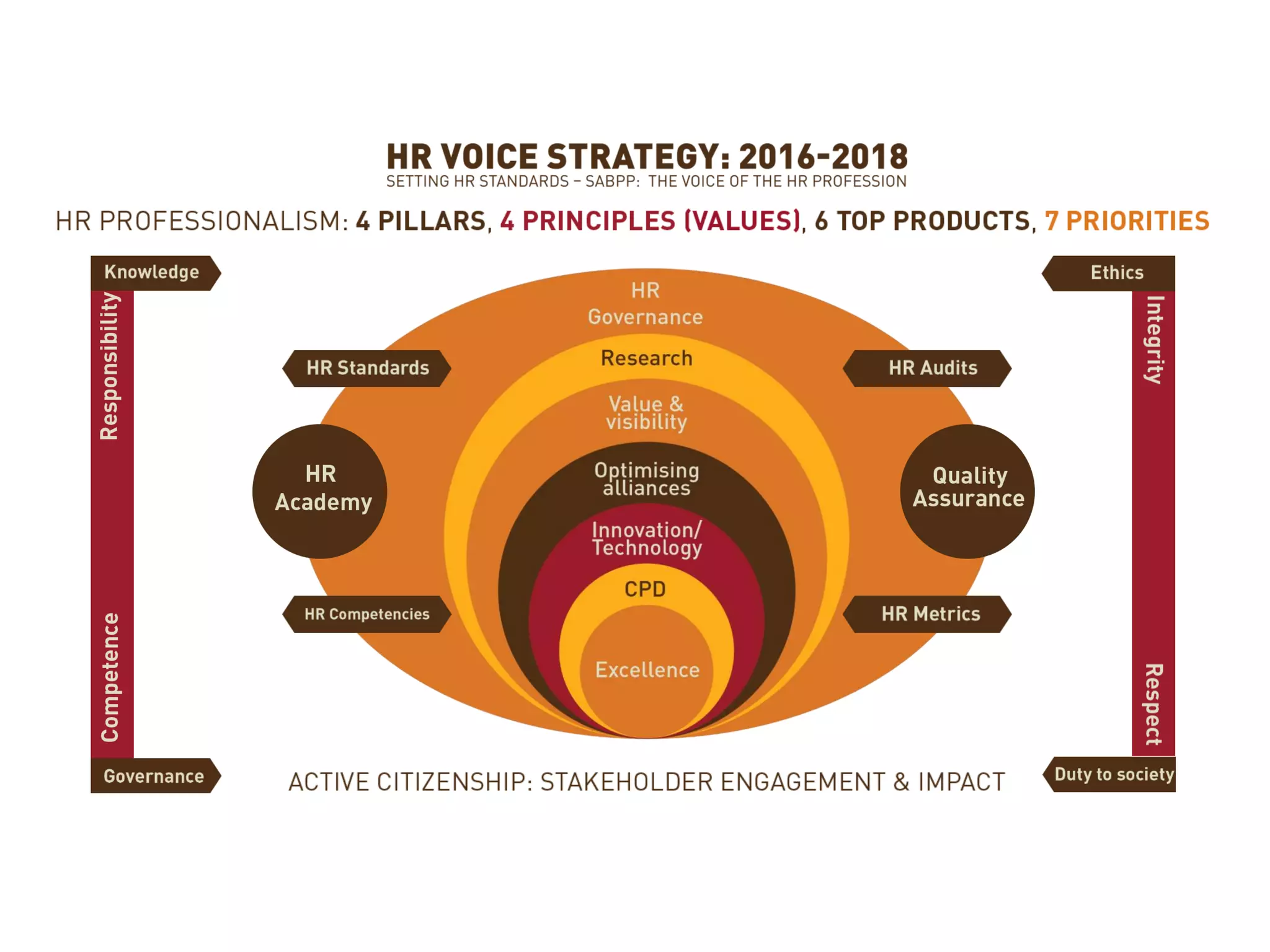
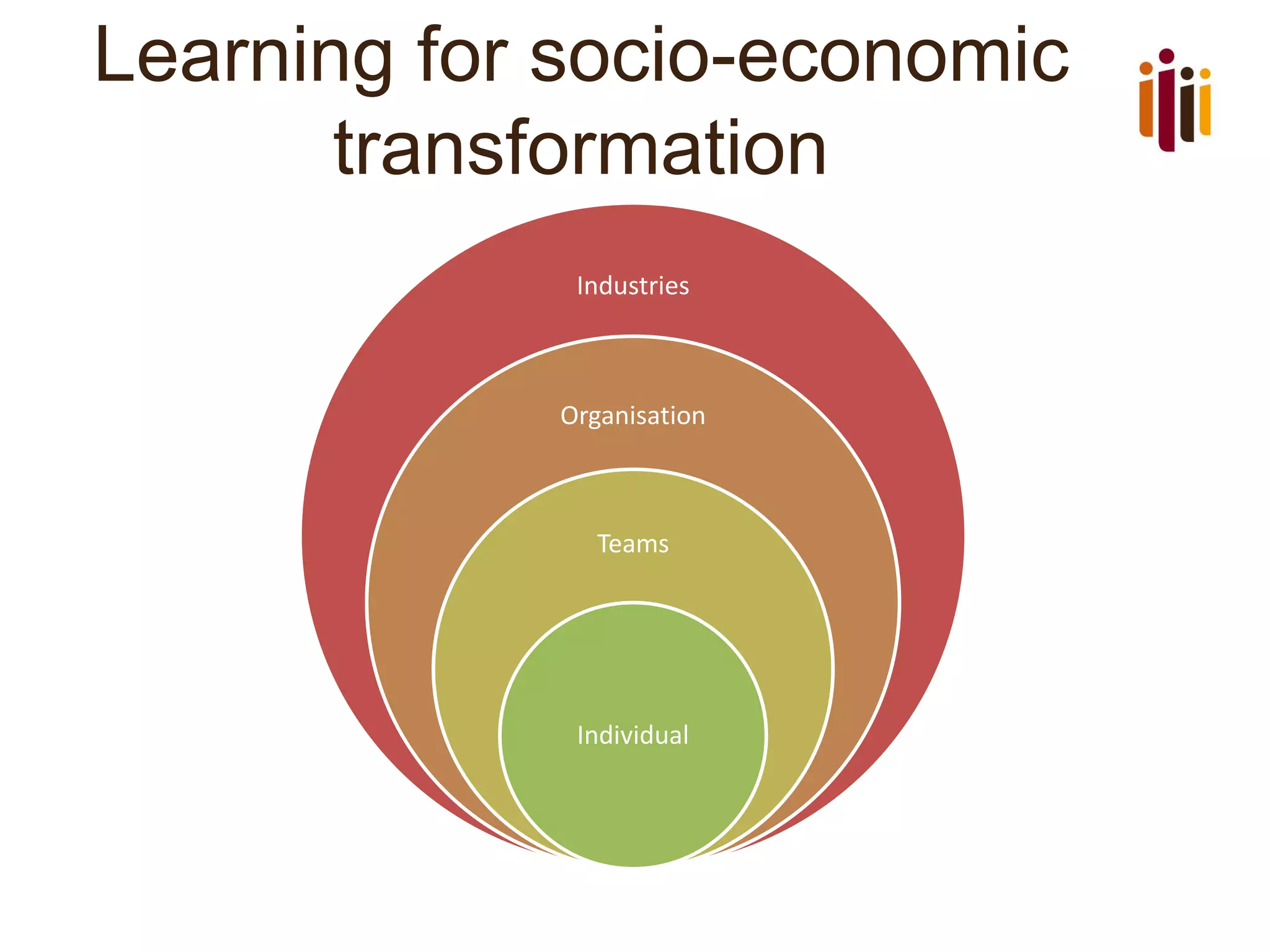
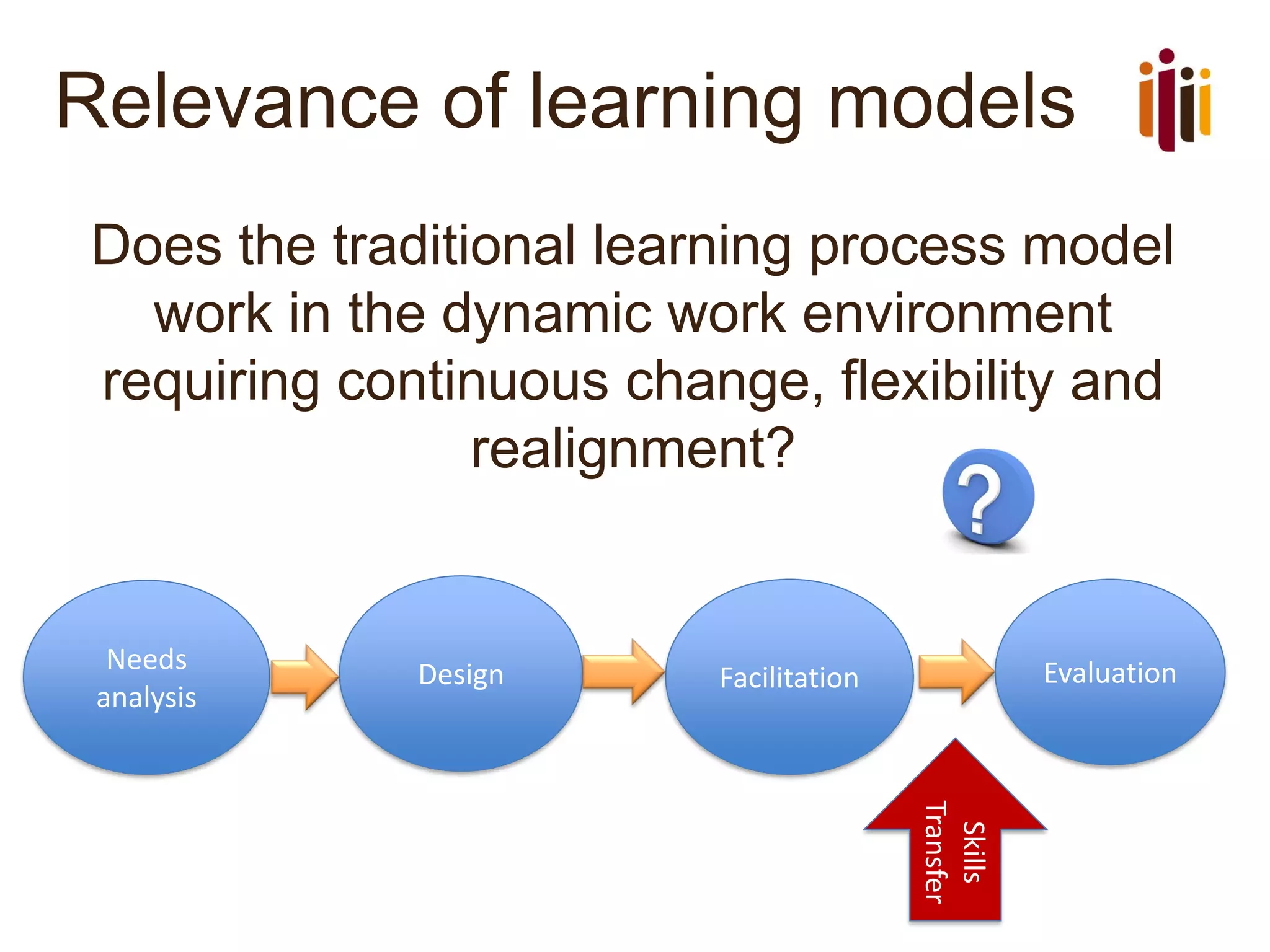
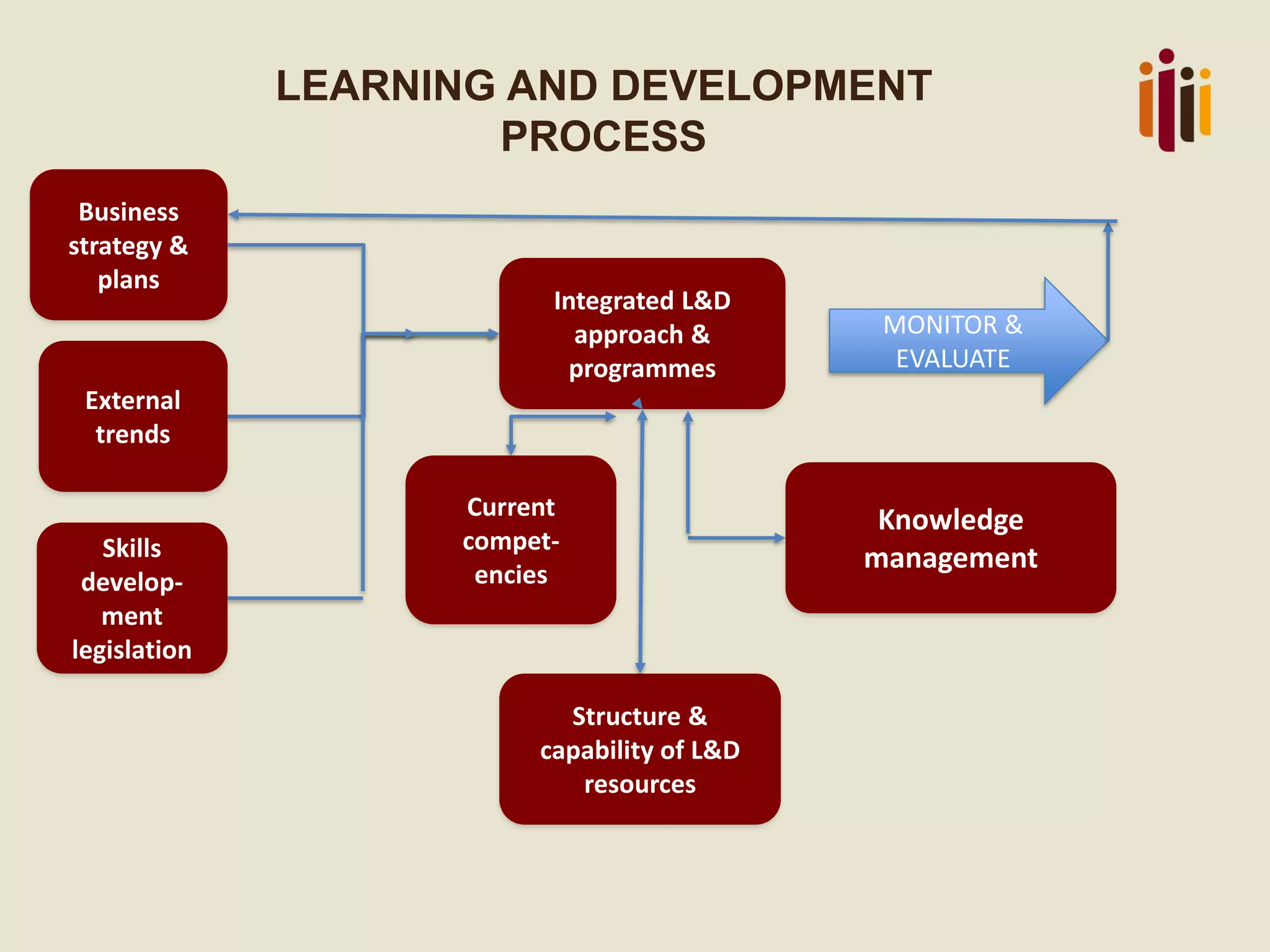
The document discusses the role of learning and development (L&D) in business success. It begins by providing an overview of HR standards and professional practice standards. It then discusses the importance of aligning L&D with business strategy and objectives in order to improve employee performance and measure the impact of L&D interventions. Finally, it emphasizes that L&D should focus on creating a learning culture, capturing knowledge, and driving continuous improvement and innovation.