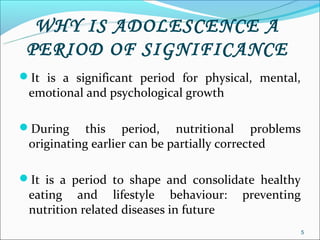
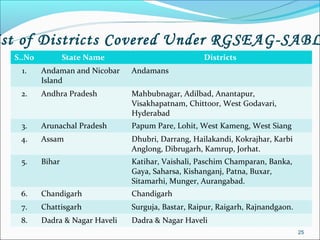
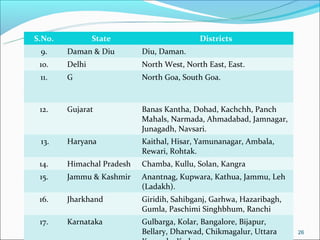
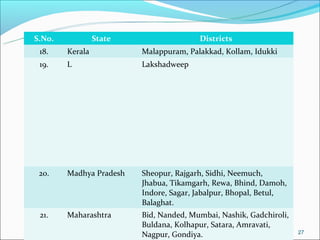
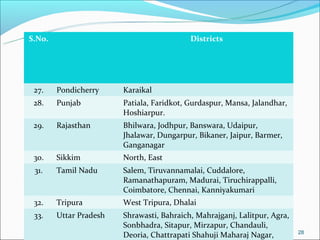
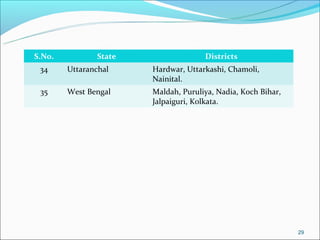
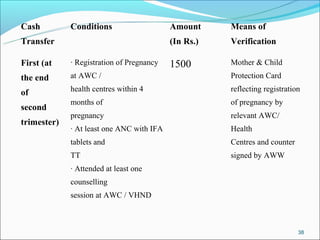
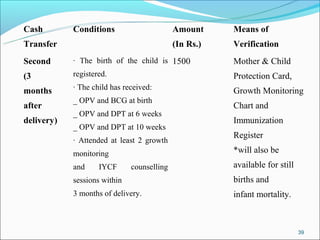
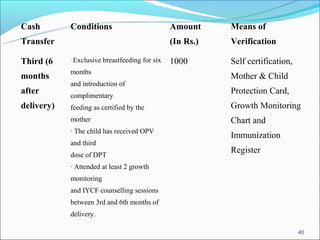
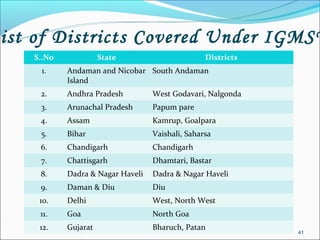
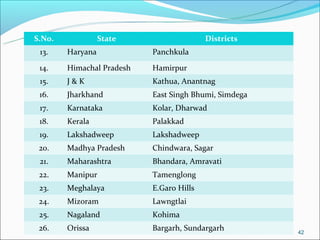
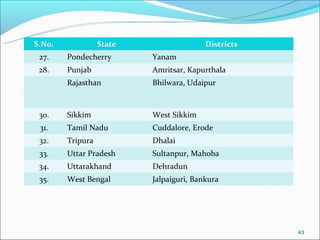
The RGSEAG scheme aims to empower adolescent girls between 11-18 years through nutrition, health education, life skills training, and vocational education. Key services include supplementary nutrition, IFA supplementation, health checkups, and guidance on family welfare and childcare. Implementation occurs through Anganwadi centers with AWWs overseeing peer groups and activities like Kishori Diwas. Monitoring and evaluation ensures proper implementation and record keeping. The scheme aims to improve health, empowerment, and development of adolescent girls in India.