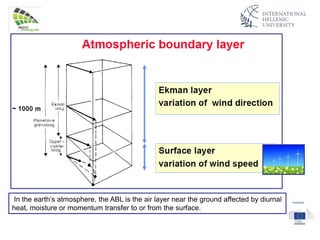
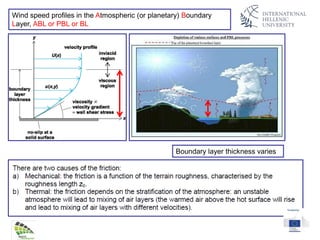
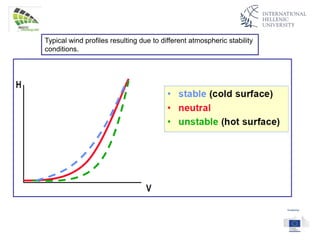
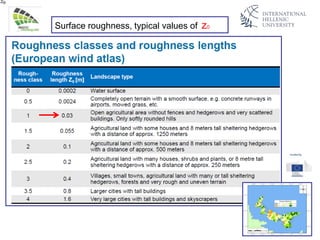
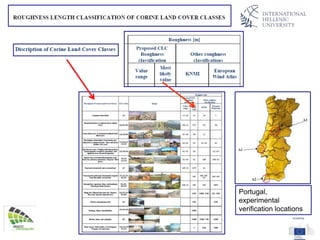
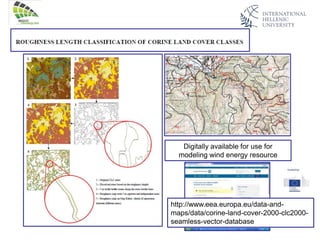
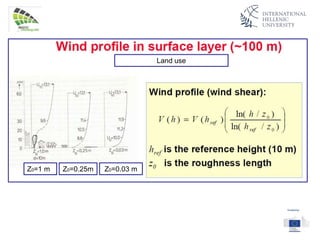
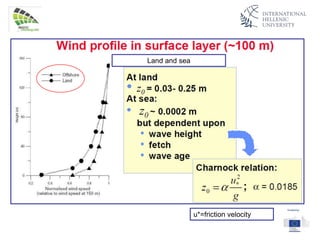
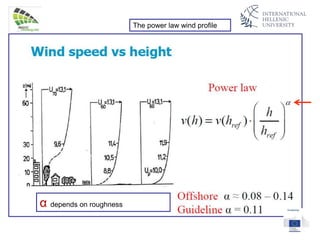
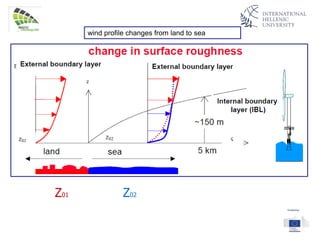
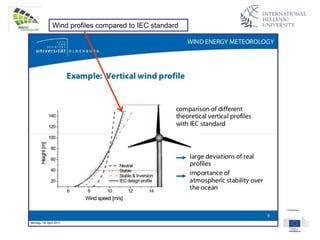
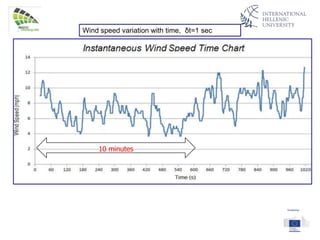
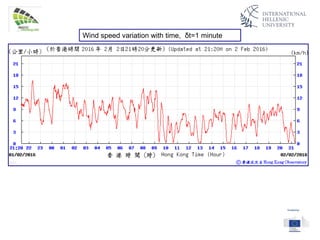
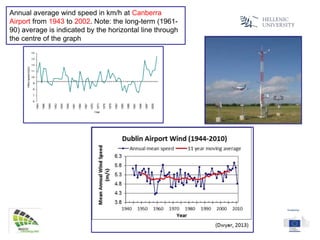
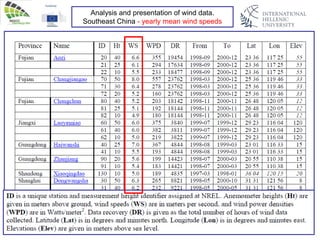
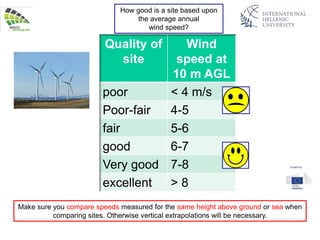
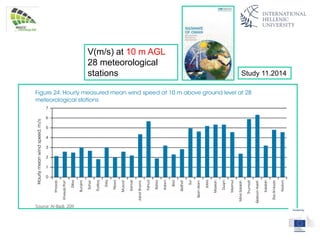
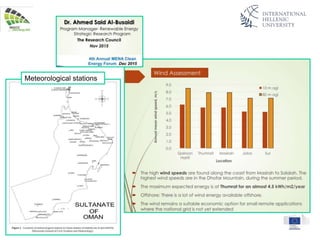
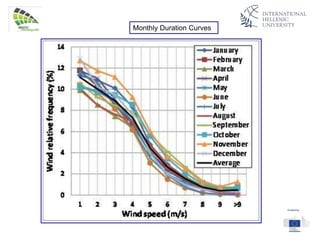
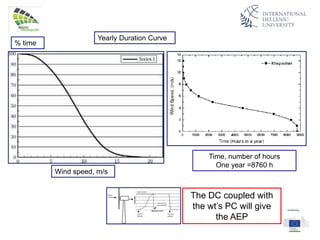
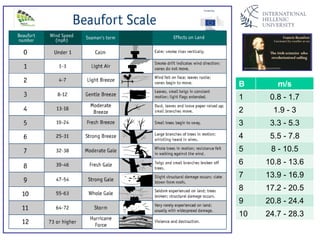
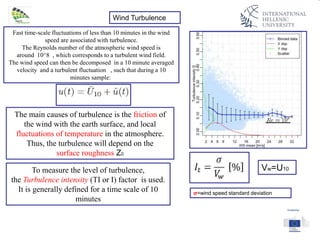
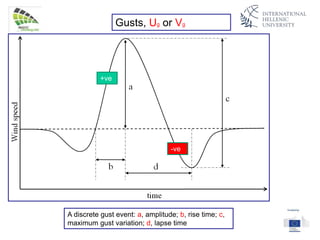
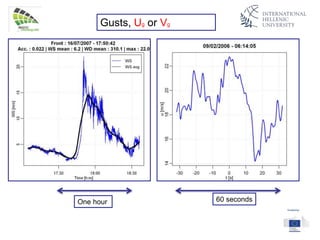
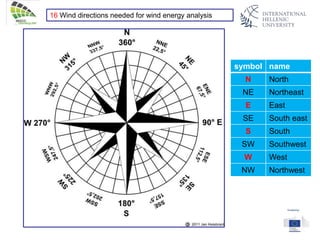
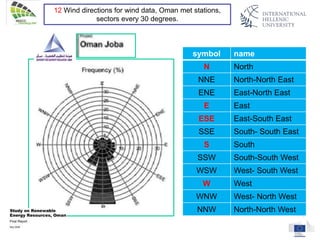
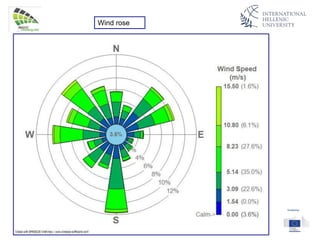
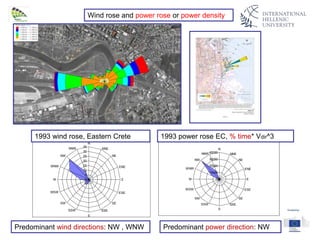
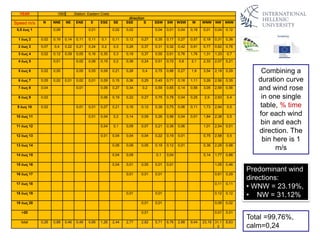
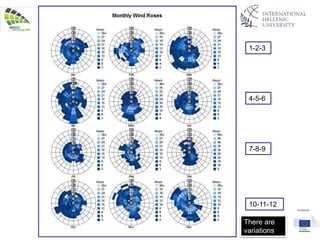
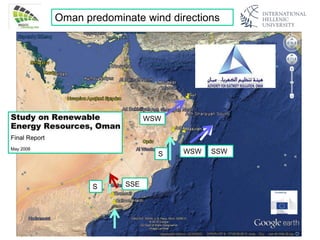
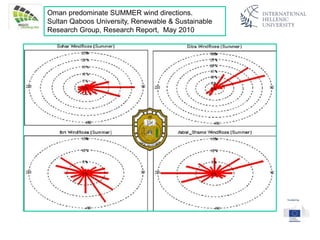
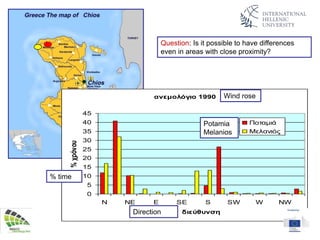
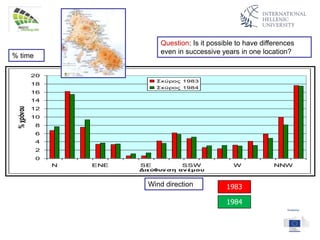
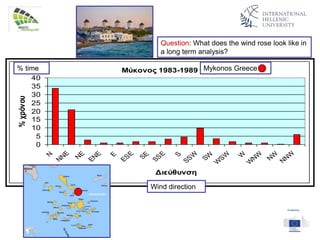
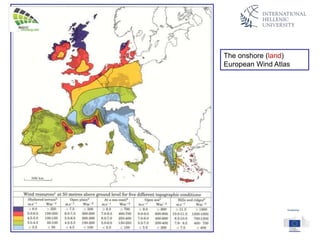
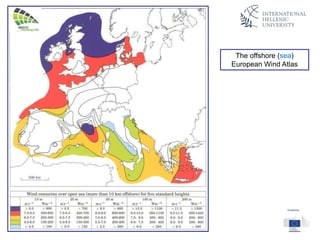
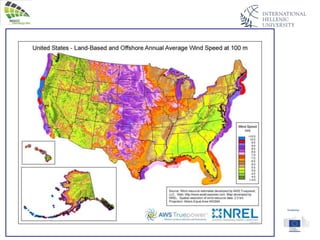
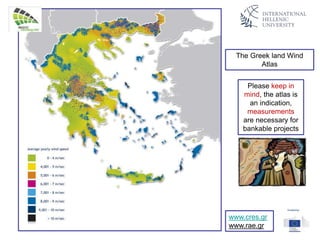
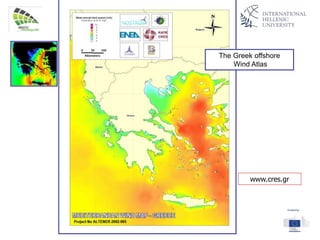
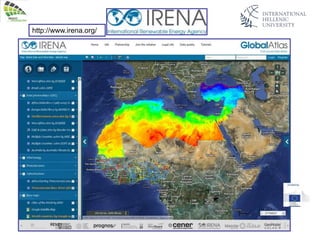
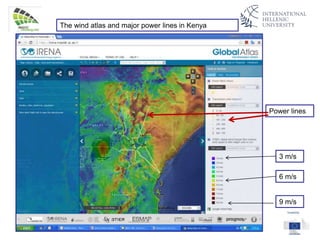
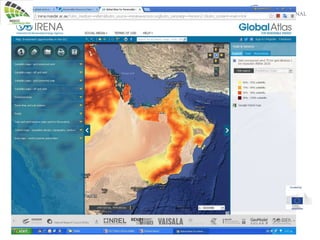
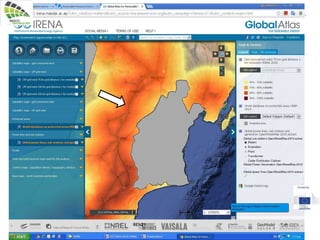
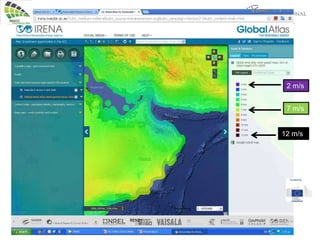
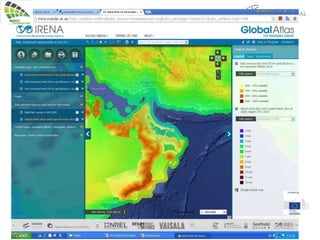
The document discusses wind energy fundamentals, focusing on atmospheric boundary layers, wind speed profiles, and the importance of surface roughness in wind energy estimation. It provides insights into measuring wind characteristics and patterns at meteorological stations, along with examples of wind direction analysis. Additionally, it highlights the variation in wind speeds across different terrains and the influence of local conditions on these measurements.