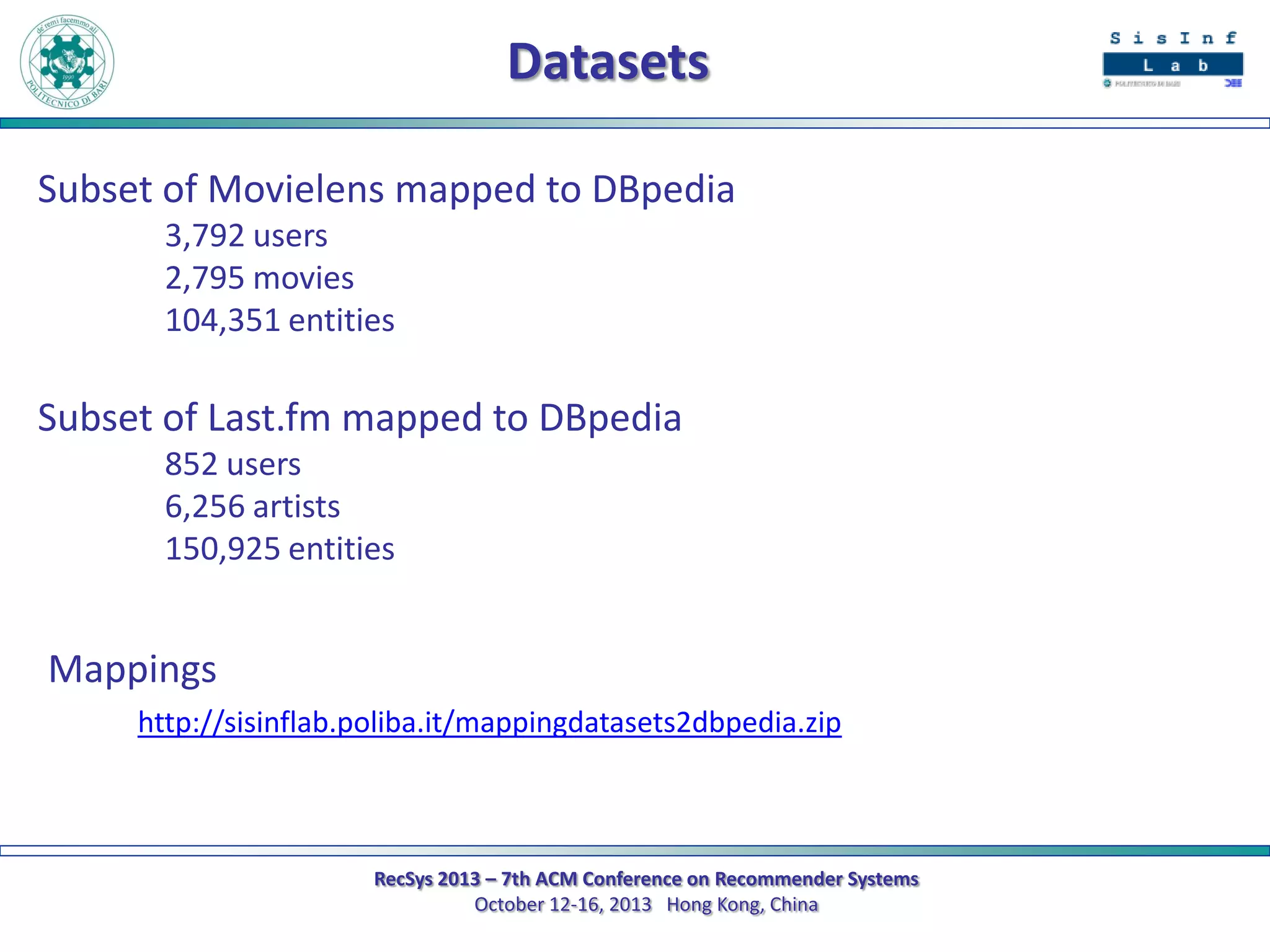
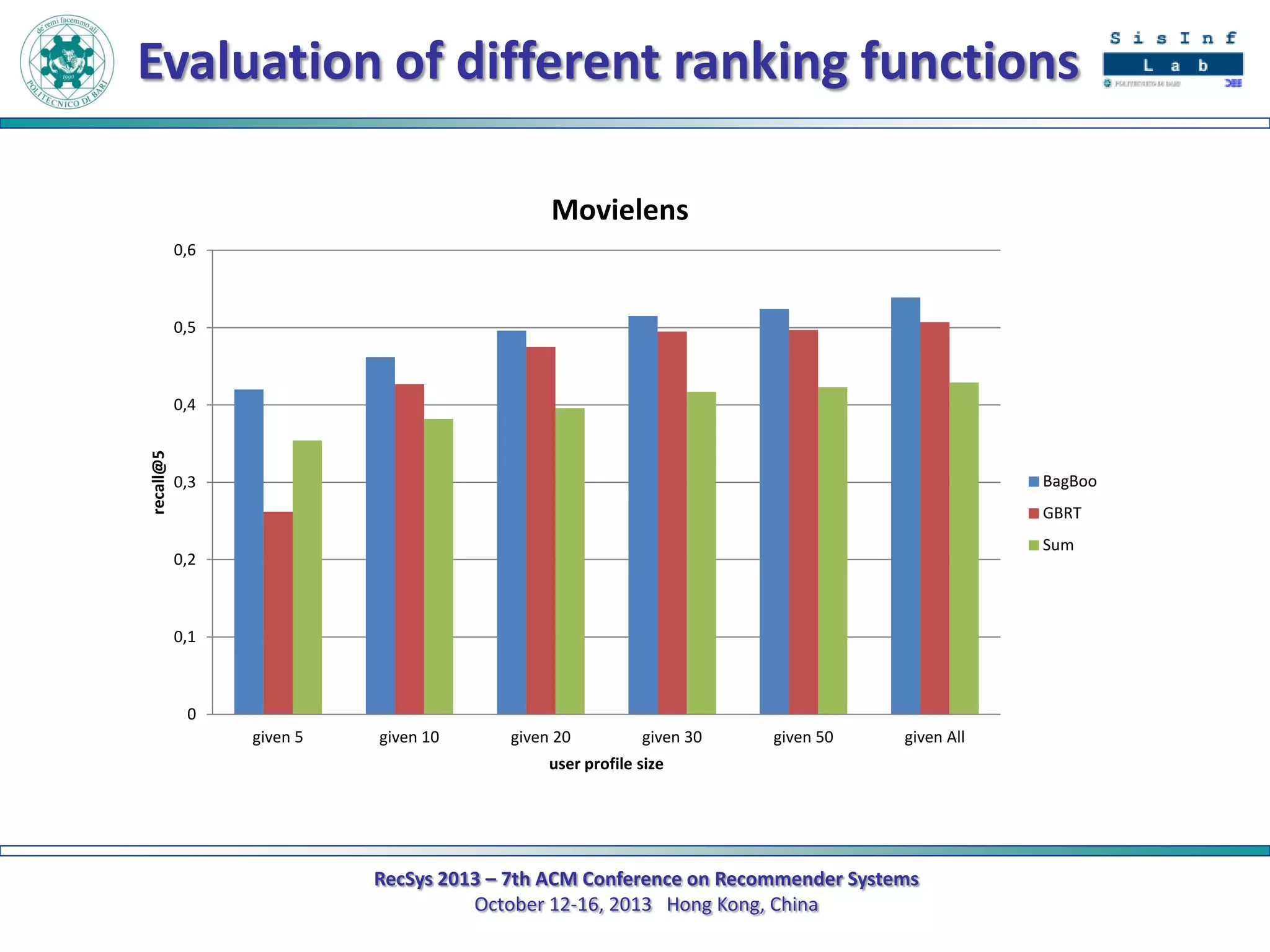
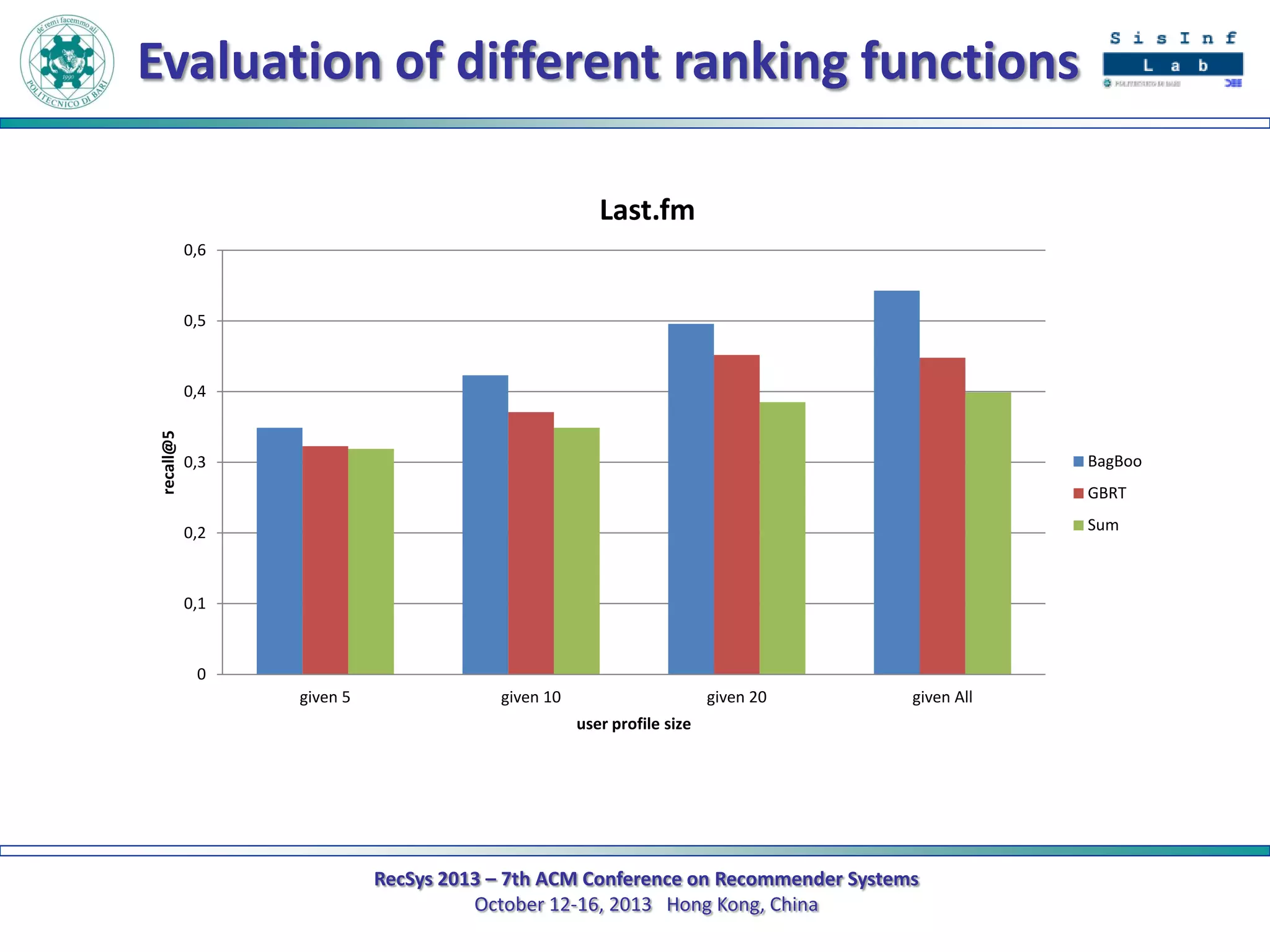
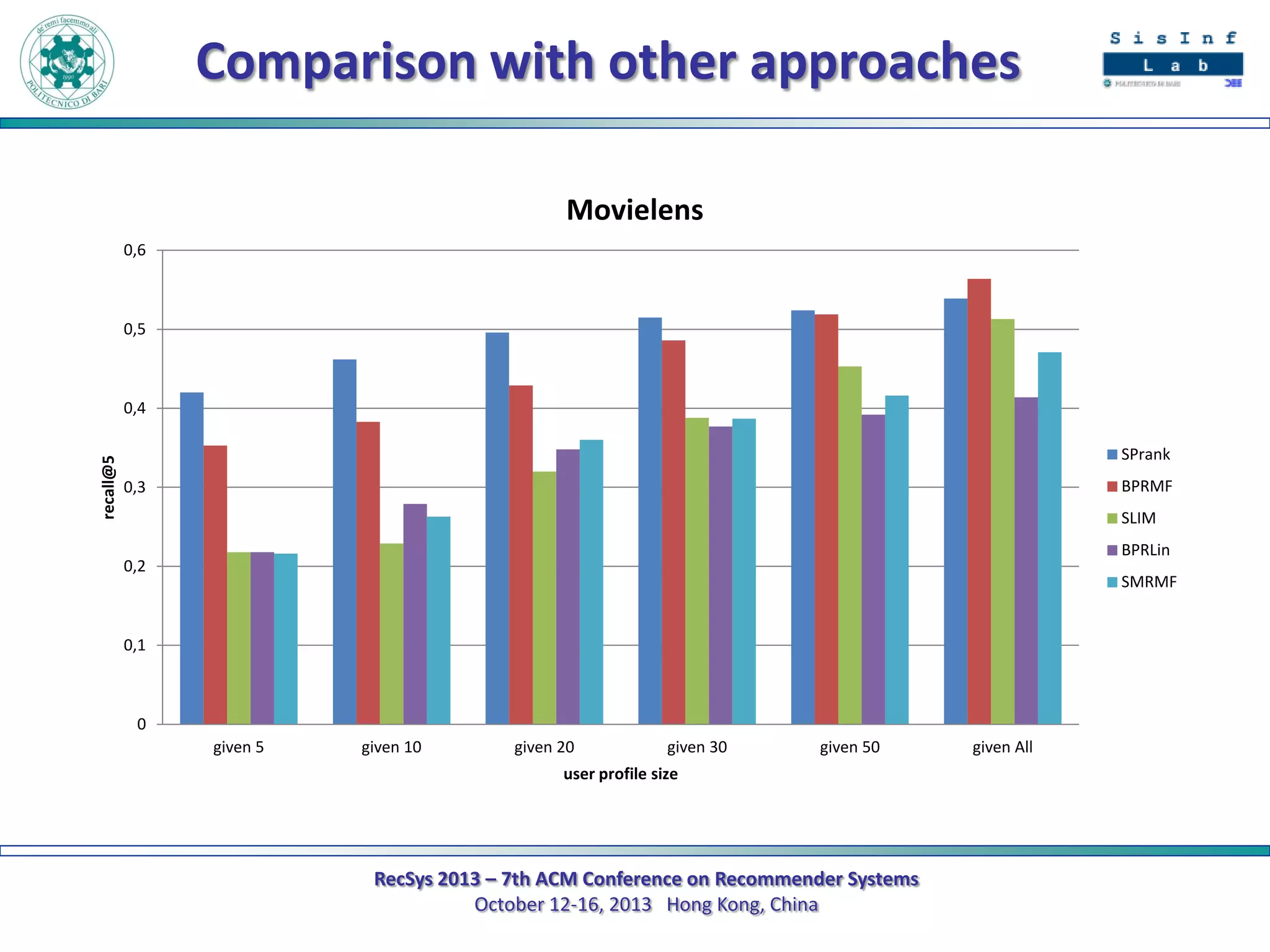
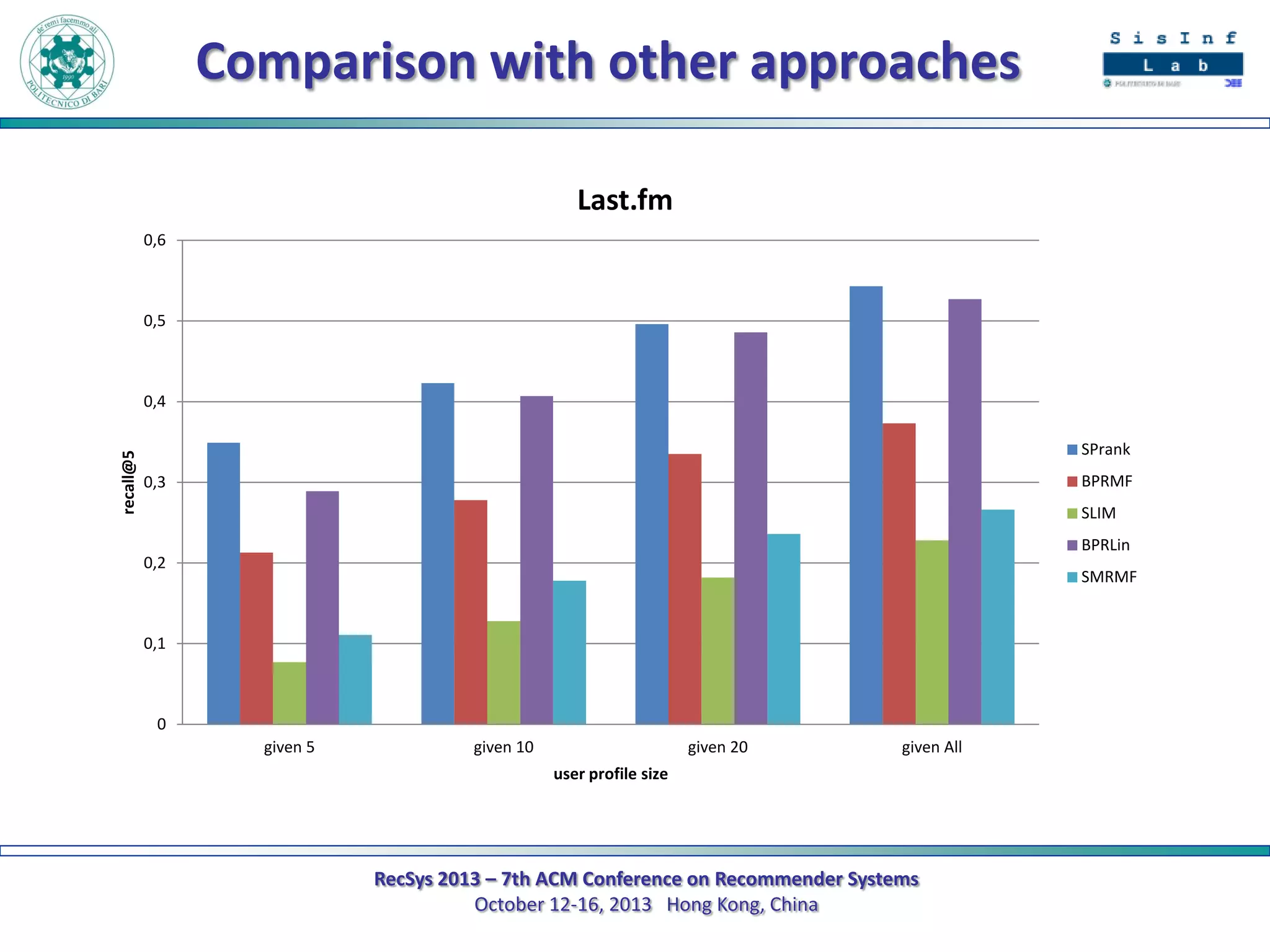
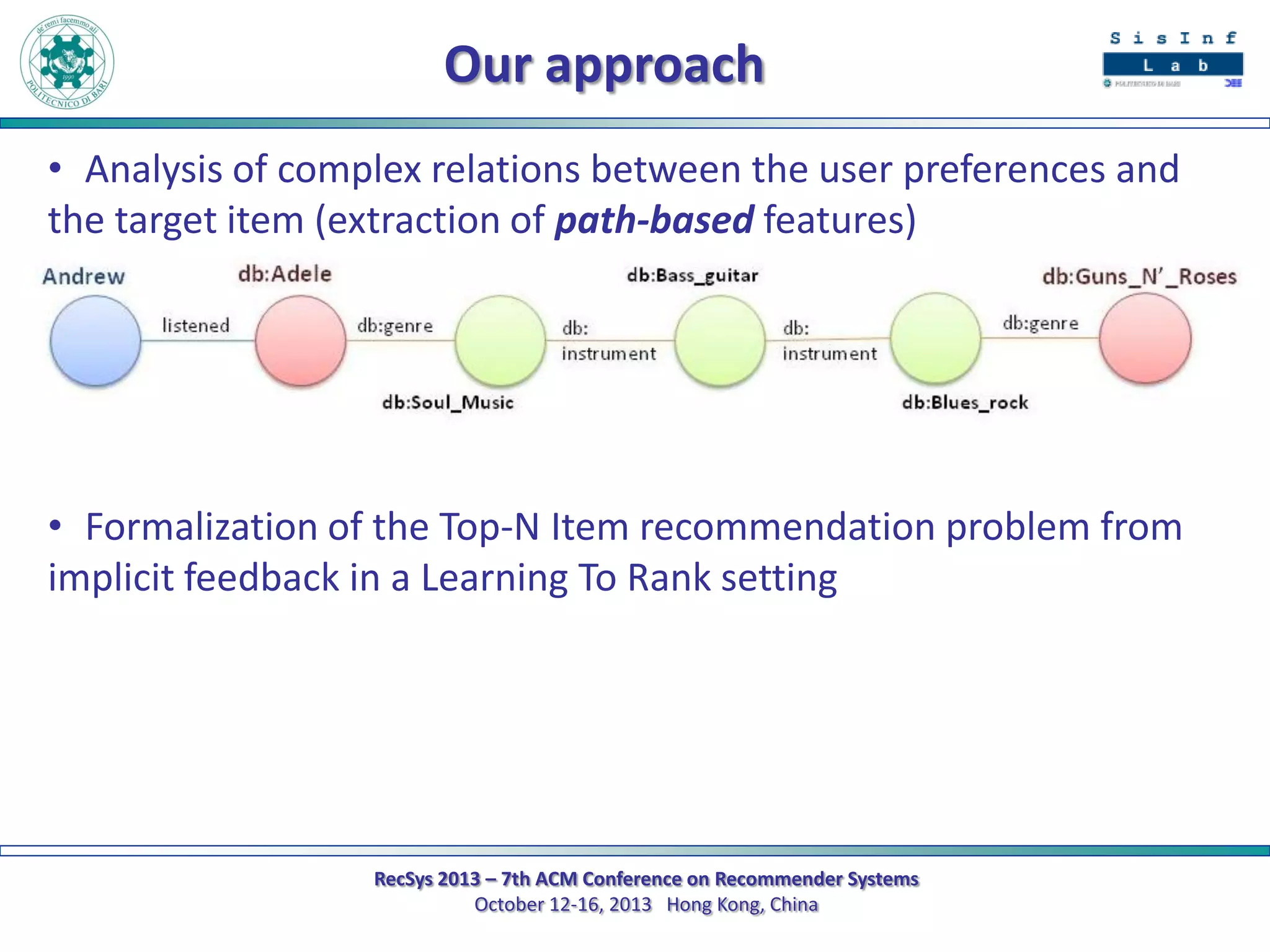
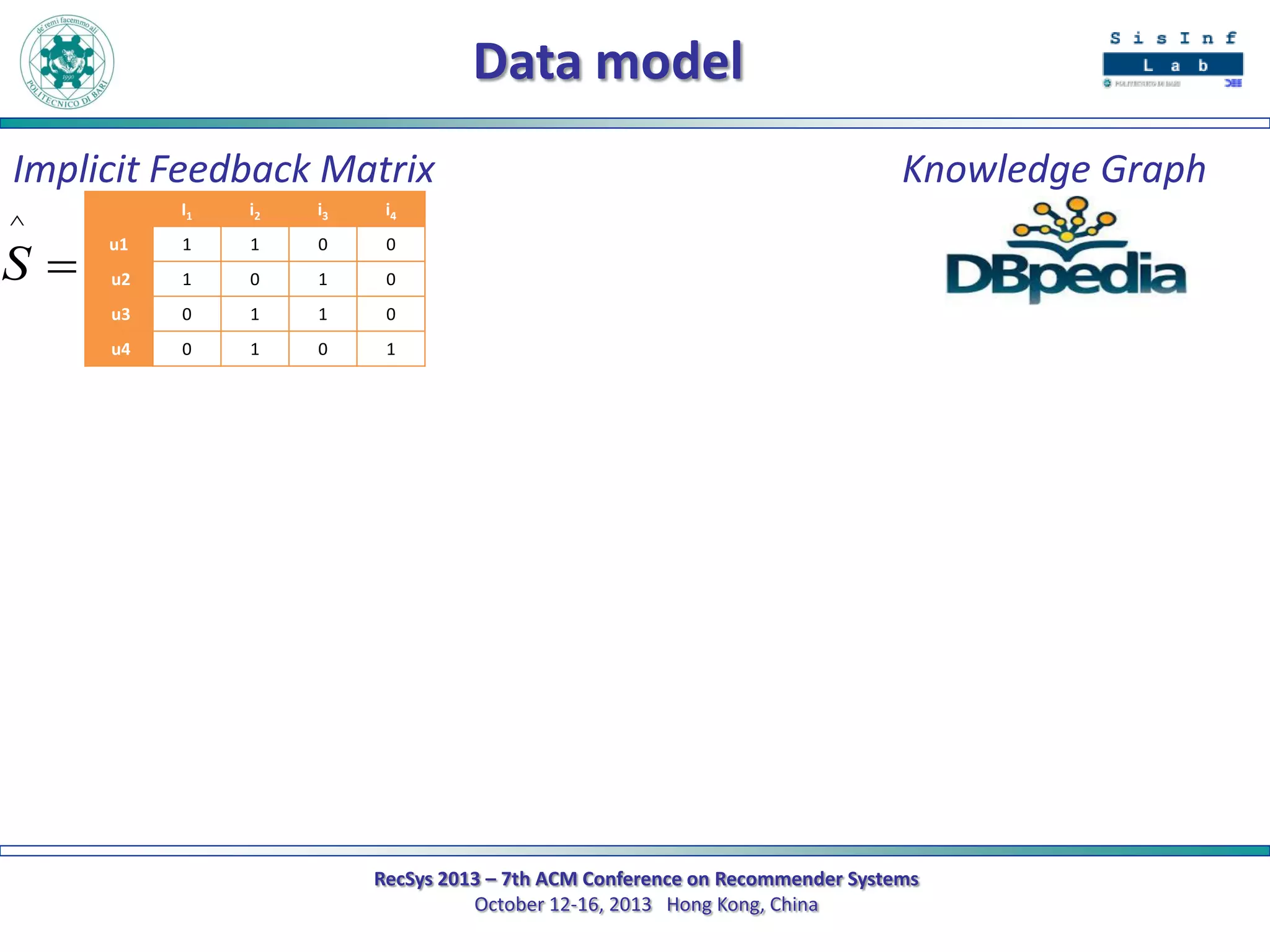
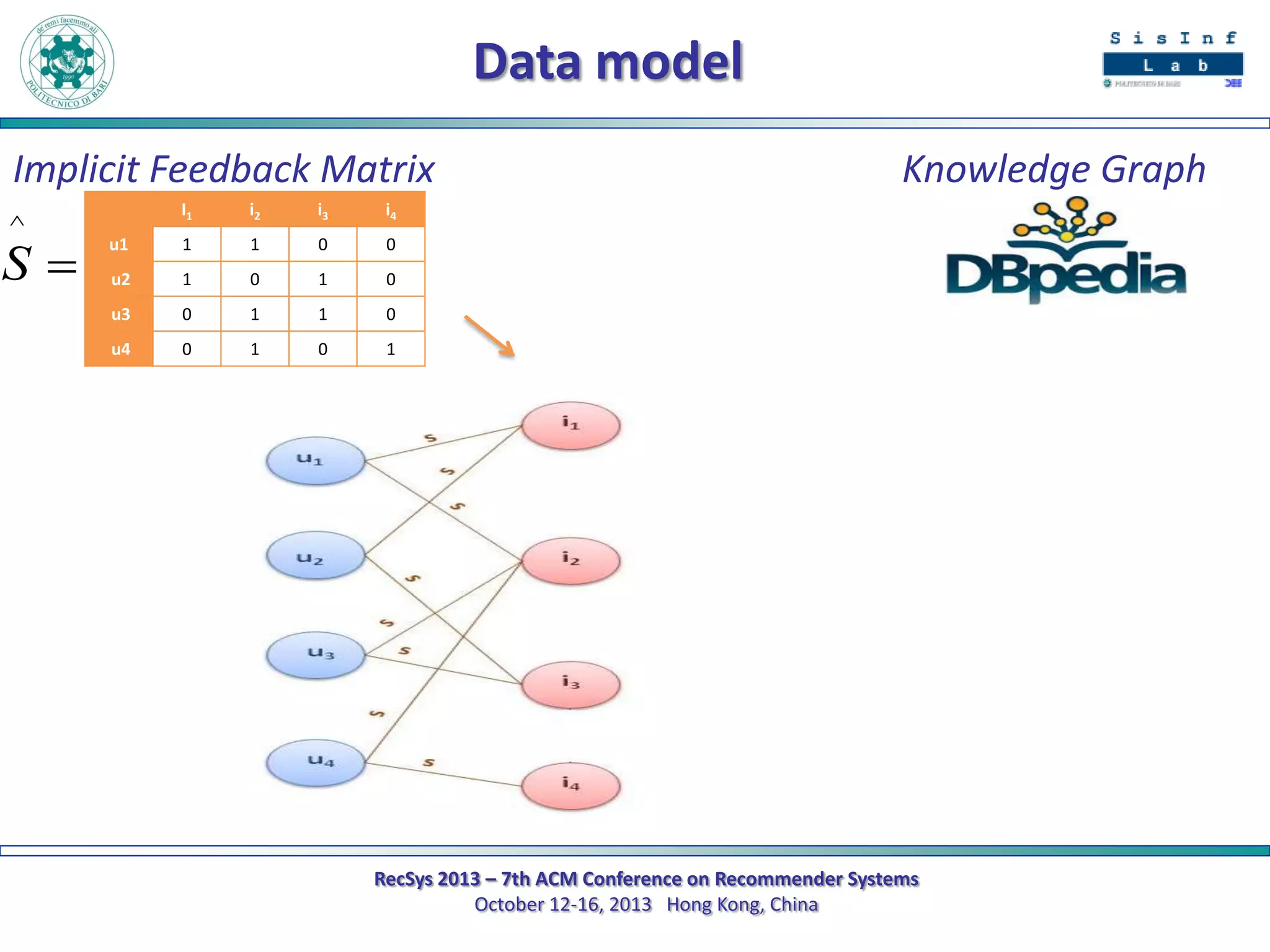
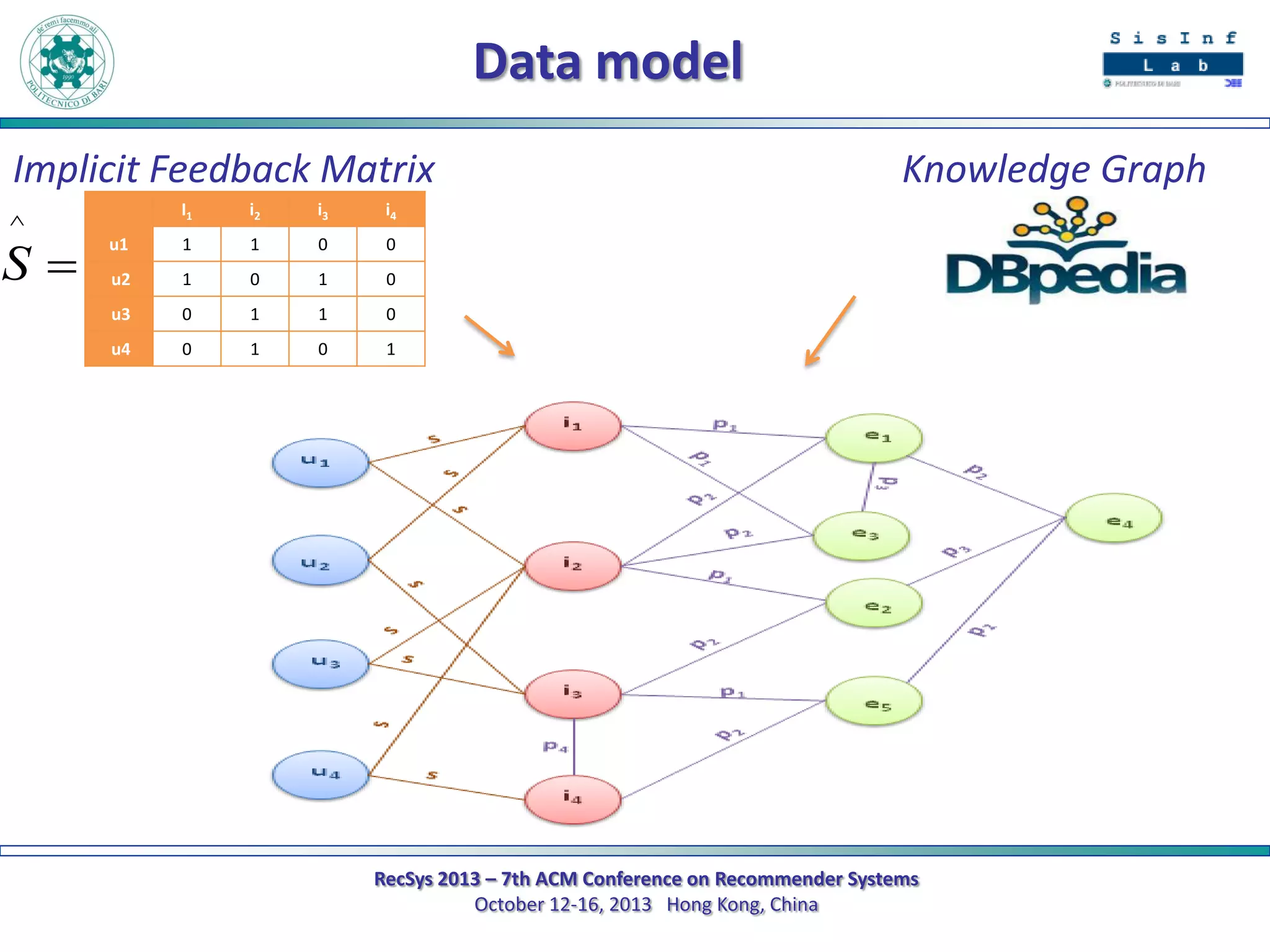
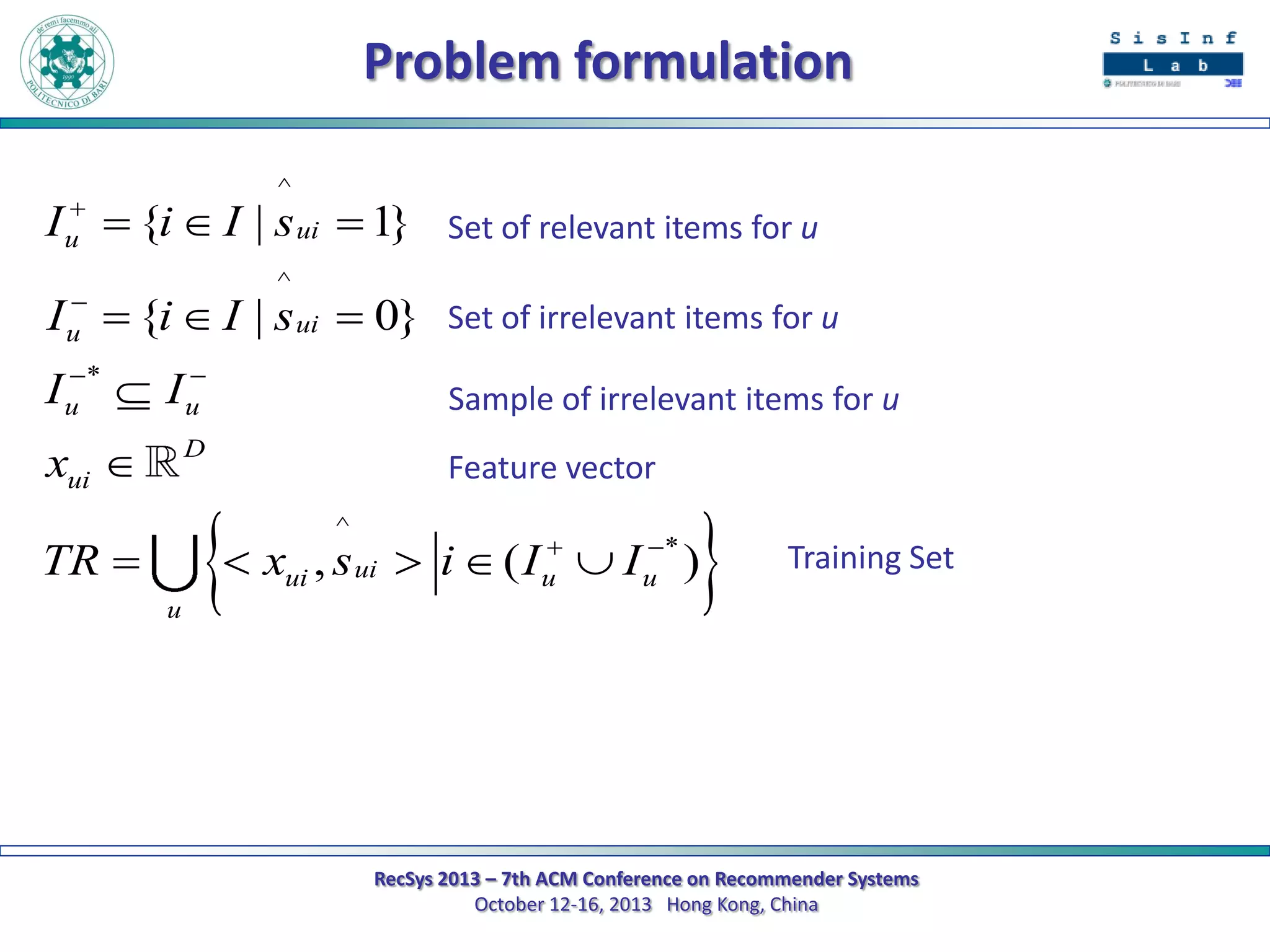
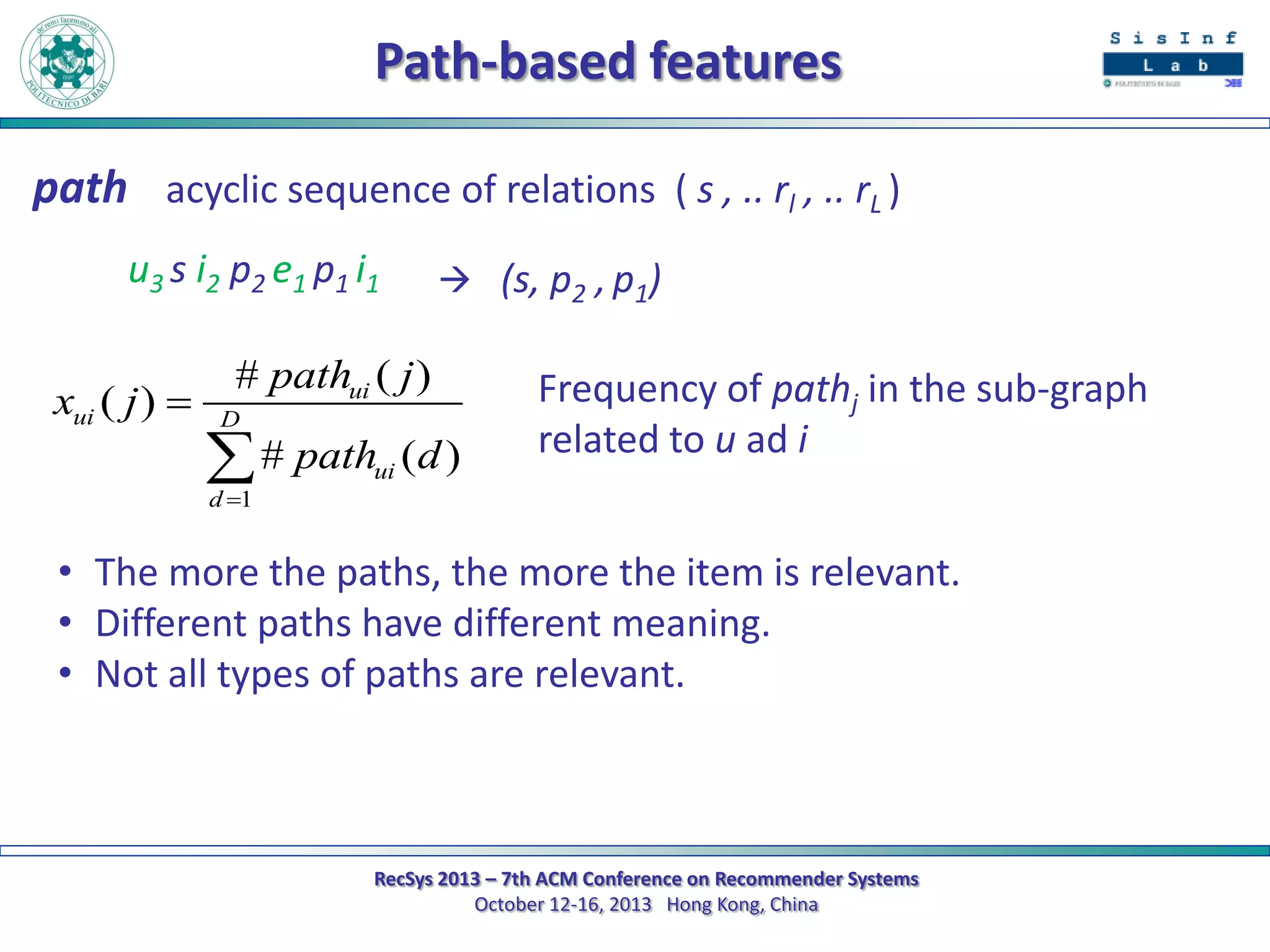
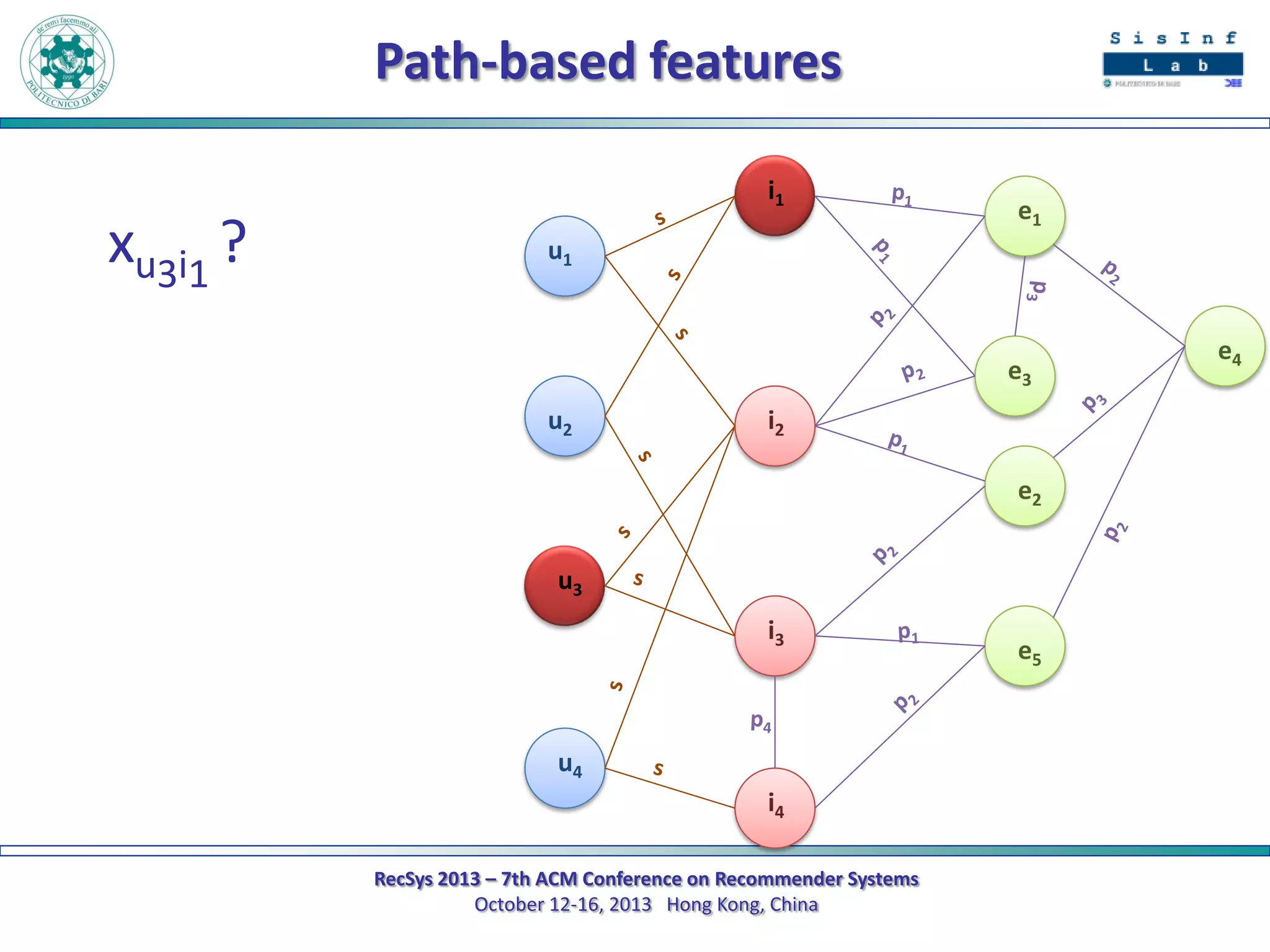
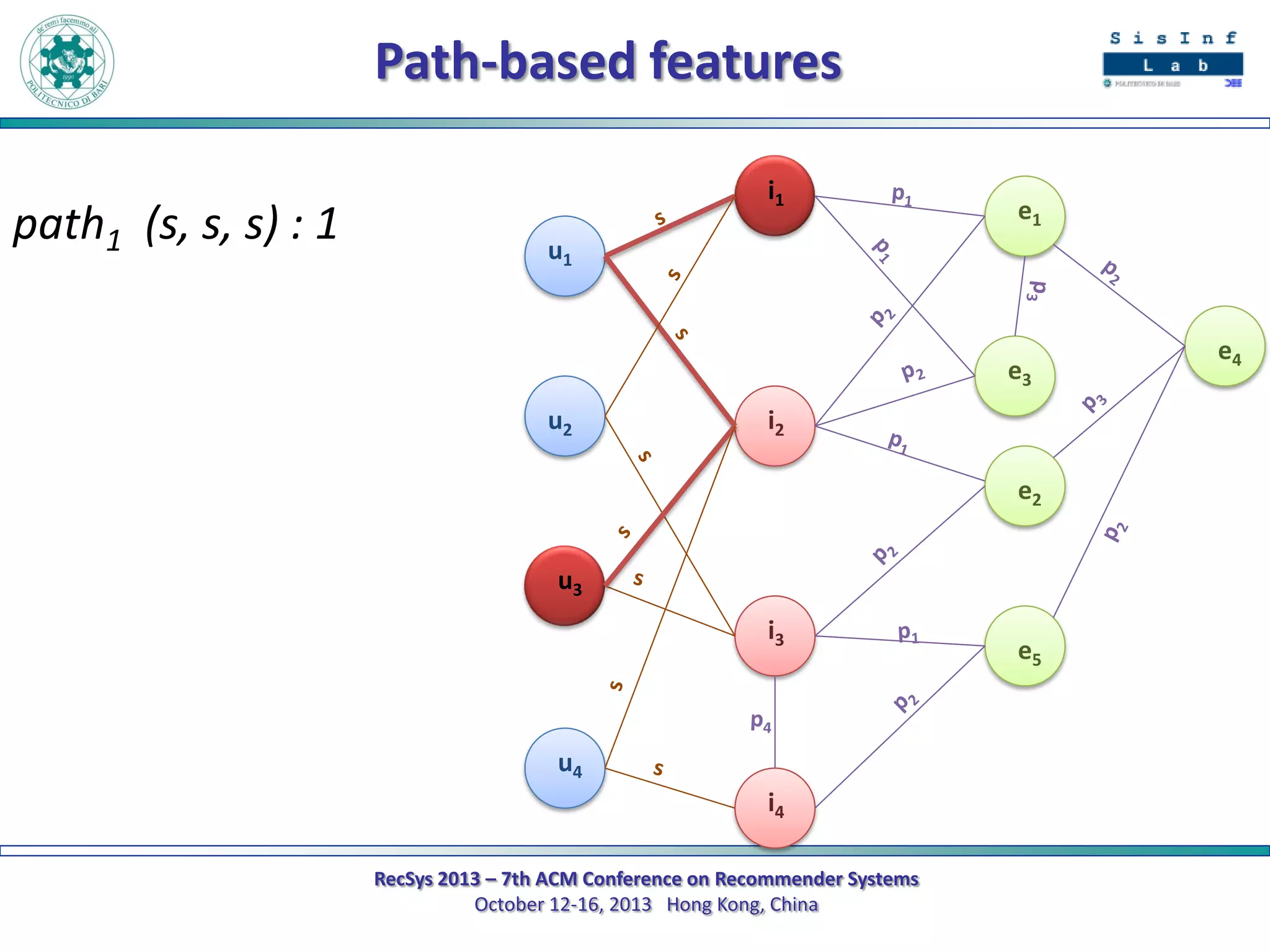
The document describes a new approach called SPrank for top-N recommendations from implicit feedback using linked open data. SPrank analyzes relationships between user preferences and items through path-based features extracted from a knowledge graph. A learning to rank method is used to learn the ranking function from these features. Experimental results on movie and music datasets mapped to DBpedia show SPrank outperforms other recommendation techniques, particularly with smaller user profiles.
![Linked Open Data
• Initiative for publishing and connecting data on the Web using
Semantic Web technologies;
• >30 billion of RDF triples from hundreds of data sources;
• Semantic Web done right [ http://www.w3.org/2008/Talks/0617-lod-tbl/#(3) ]
RecSys 2013 – 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems
October 12-16, 2013 Hong Kong, China](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sprankrecsys2013-131017103707-phpapp01/75/Top-N-Recommendations-from-Implicit-Feedback-leveraging-Linked-Open-Data-3-2048.jpg)
![Linked Open Data
• Initiative for publishing and connecting data on the Web using
Semantic Web technologies;
• >30 billion of RDF triples from hundreds of data sources;
• Semantic Web done right [ http://www.w3.org/2008/Talks/0617-lod-tbl/#(3) ]
RecSys 2013 – 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems
October 12-16, 2013 Hong Kong, China](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sprankrecsys2013-131017103707-phpapp01/75/Top-N-Recommendations-from-Implicit-Feedback-leveraging-Linked-Open-Data-4-2048.jpg)





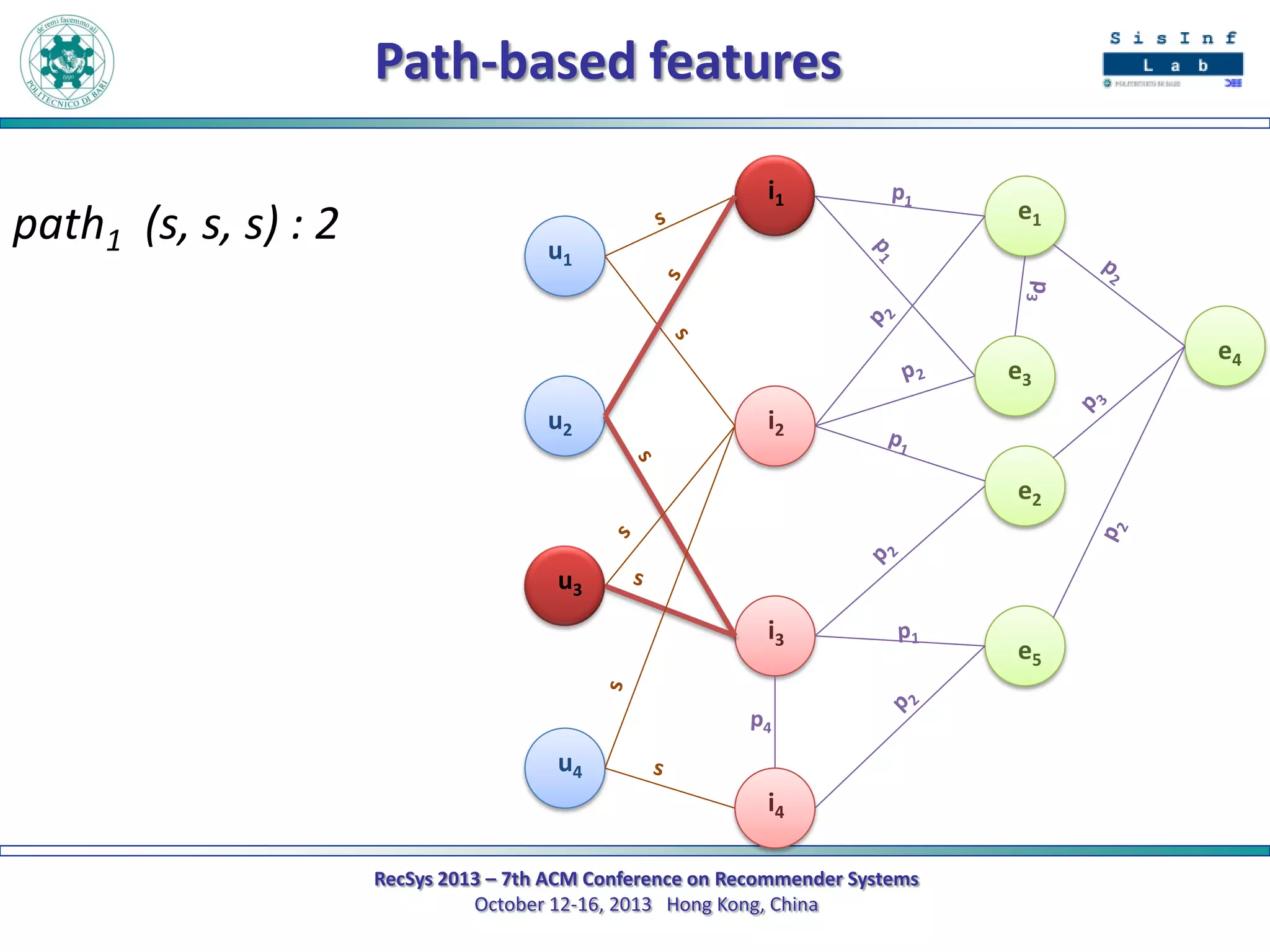
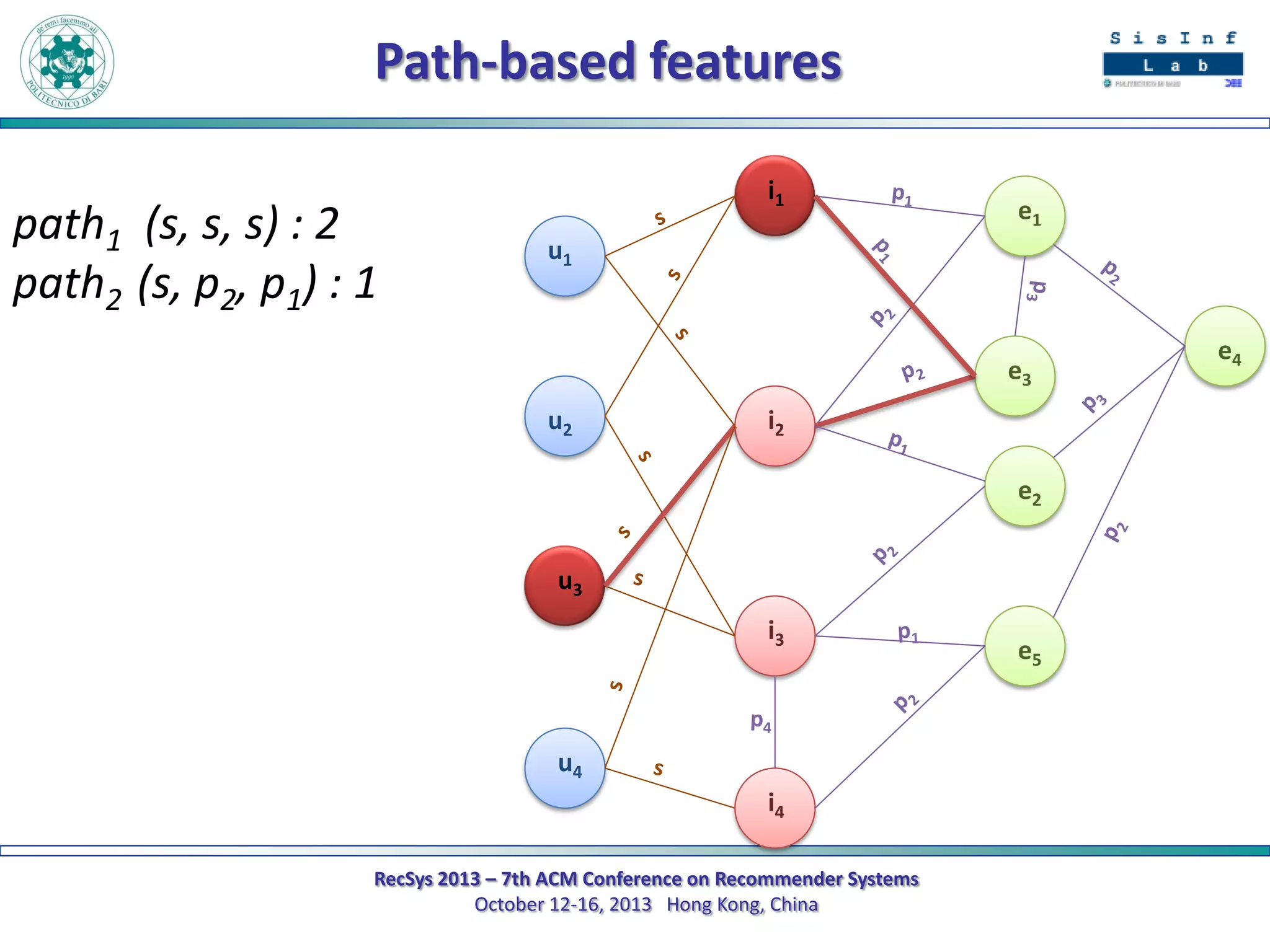
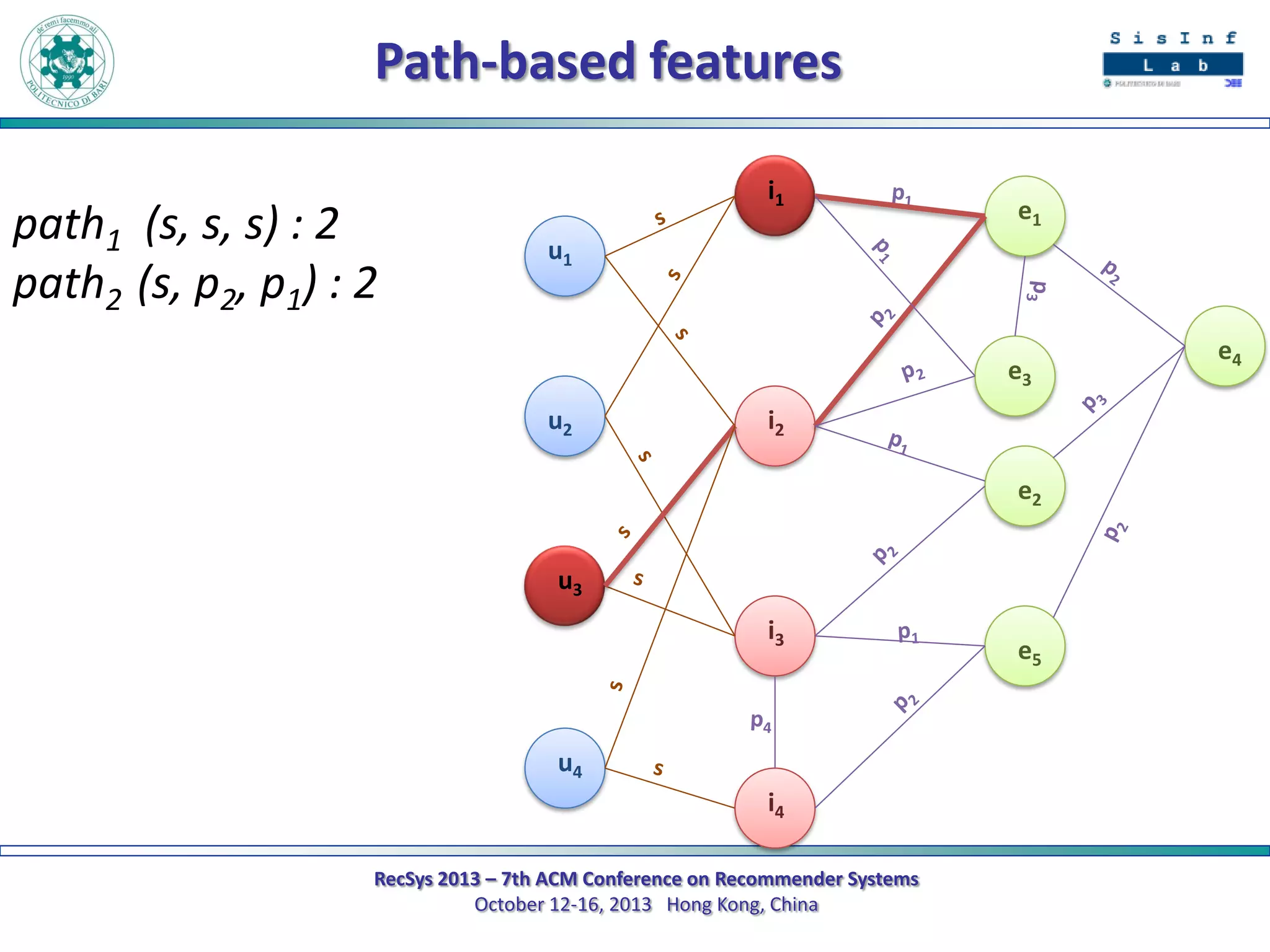
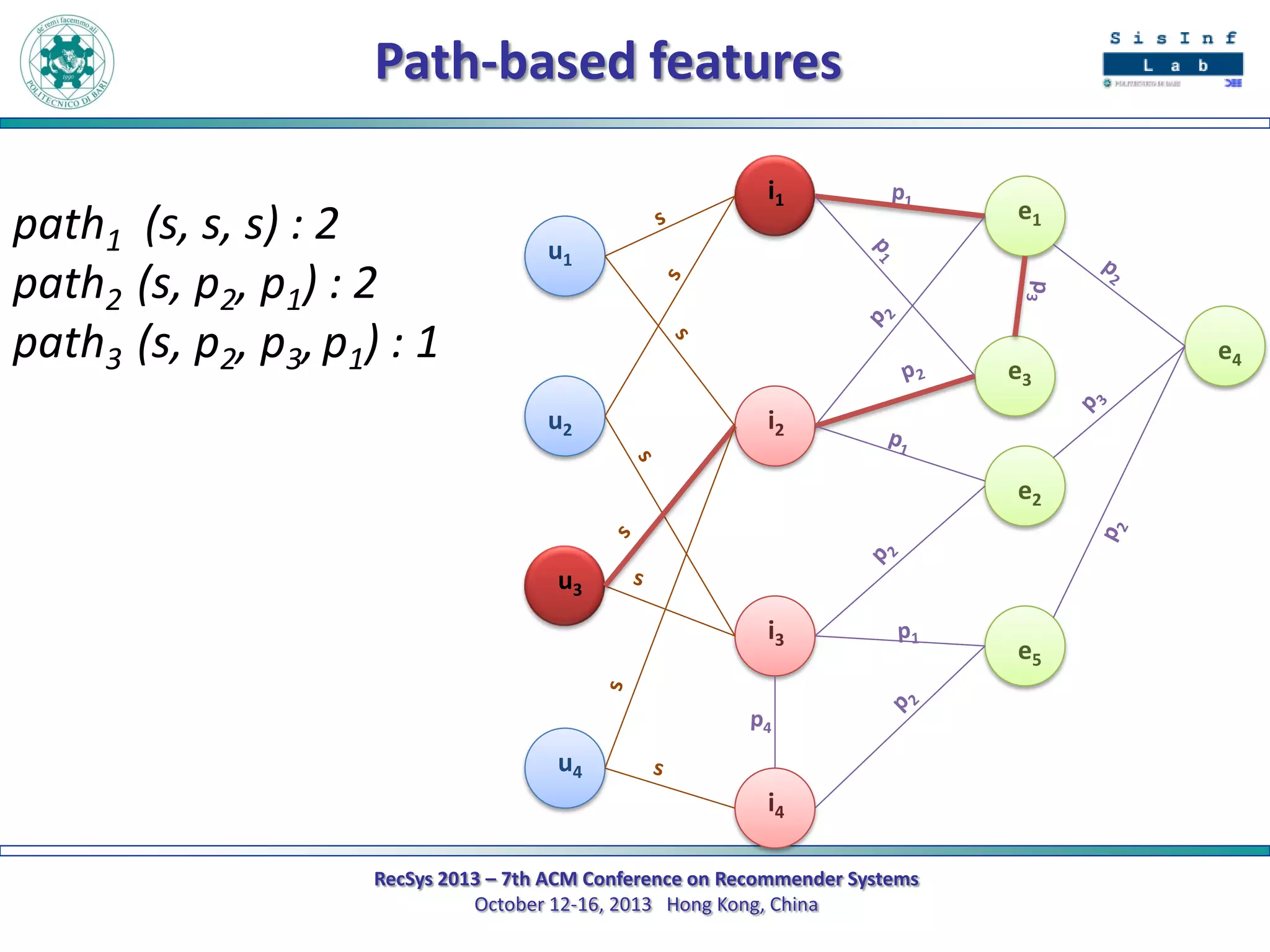
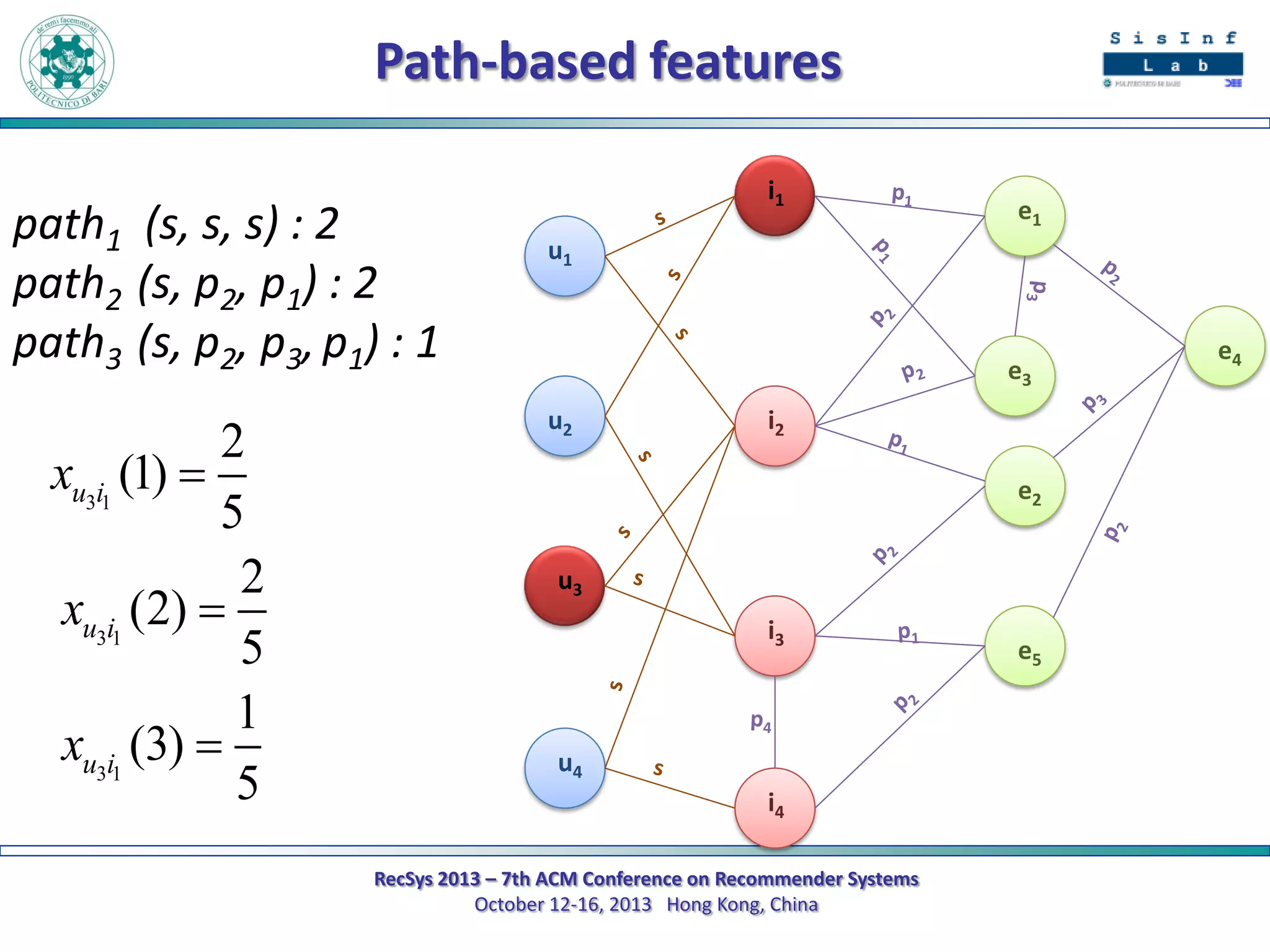

![BagBoo
BagBoo: a scalable hybrid bagging-the-boosting model
[D. Pavlov, A. Gorodilov, C. Brunk CIKM2010]
• Combination of Random Forest (Bagging) and Gradient Boosted
Regression Trees (Boosting)
• Combines the high accuracy of gradient boosting with the resistance
to overfitting of random forests
For b=1 to B:
Tb TR
fb learn GBRT from Tb
1 B
f fb
B b 1
RecSys 2013 – 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems
October 12-16, 2013 Hong Kong, China](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sprankrecsys2013-131017103707-phpapp01/75/Top-N-Recommendations-from-Implicit-Feedback-leveraging-Linked-Open-Data-27-2048.jpg)
![Evaluation Methodology
• Top-N Item recommendation task
• Evaluation methodology similar to:
[Cremonesi, Koren and Turrin, RecSys 2010]
• Evaluation with different user profile size:
given 5
given 10
User
profile
5
User profile
Test Set
10
……
given All
User profile
Test Set
10
Test Set
RecSys 2013 – 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems
October 12-16, 2013 Hong Kong, China](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sprankrecsys2013-131017103707-phpapp01/75/Top-N-Recommendations-from-Implicit-Feedback-leveraging-Linked-Open-Data-28-2048.jpg)