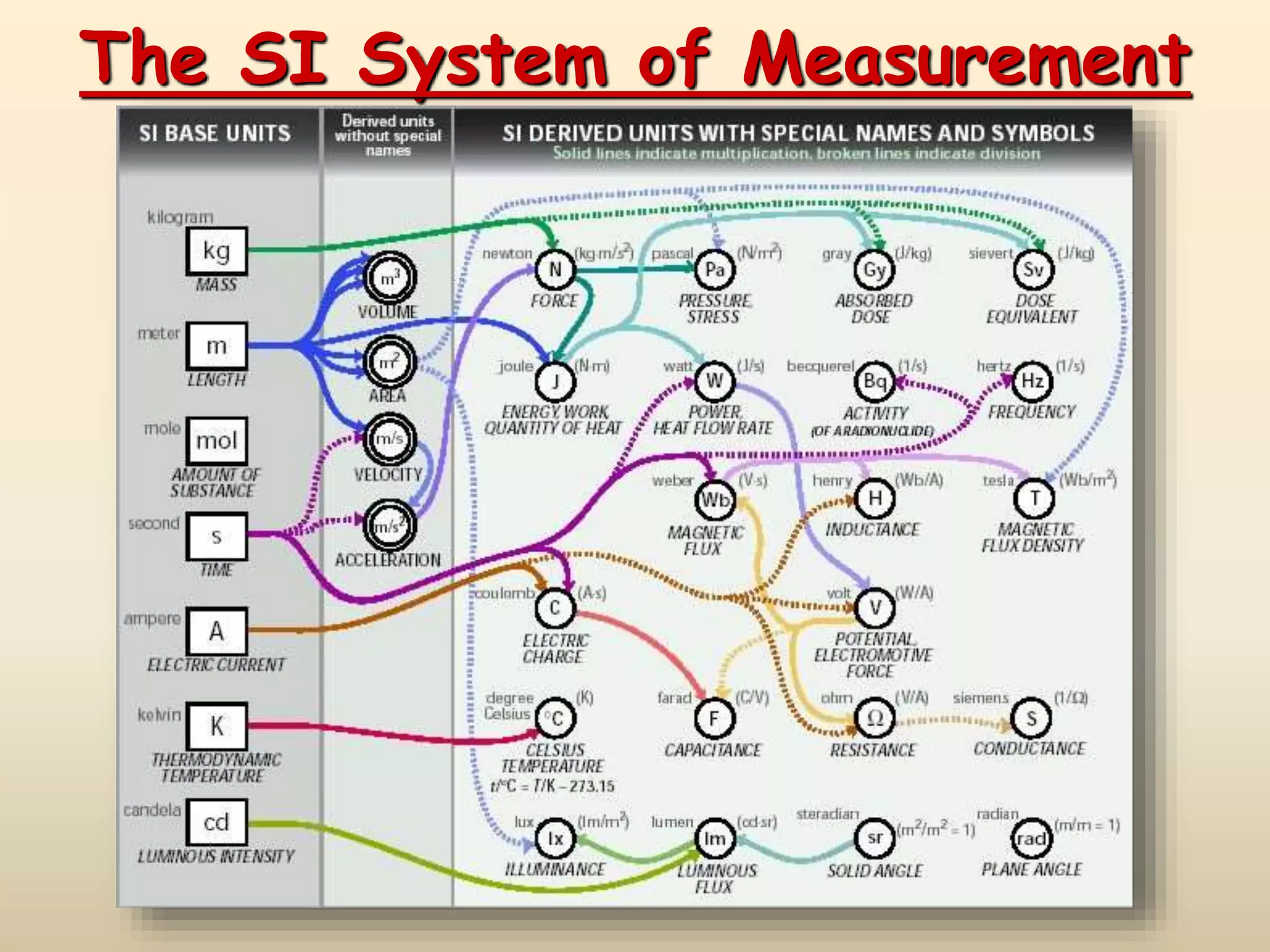
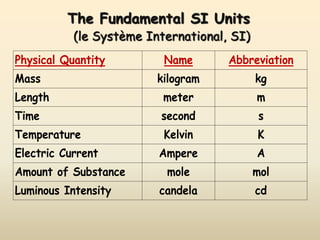
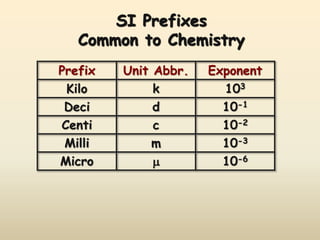
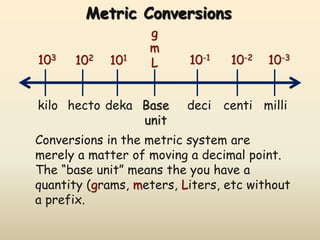
The document discusses the SI system of measurement. It defines a measurement as having two parts - a number and a unit. The SI system establishes standard units for seven base quantities: meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), ampere (electric current), kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity). SI prefixes are used to denote multiples and submultiples of units, such as kilo, centi, and milli. Conversions within the metric system involve moving the decimal place in the number to change the unit, as shown through examples converting between liters and milliliters, grams and milligrams, and kilograms and milligrams.