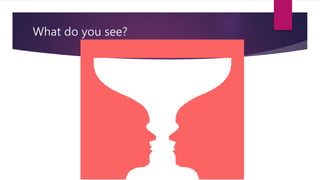
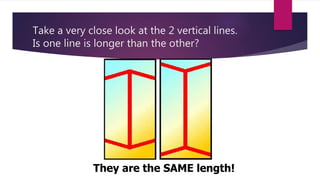
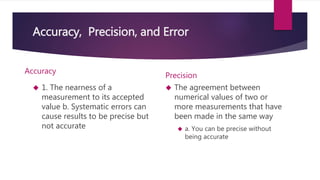
This document provides an overview of key concepts in chemistry. It discusses the differences between observations and inferences, and emphasizes recording observations rather than inferences in lab exercises. It also covers scientific methodology, including variables, controls, and the scientific method. Measurement concepts like accuracy, precision, error, and significant figures are defined. Formulas for calculating percent error are presented. Key terms like independent and dependent variables are introduced.