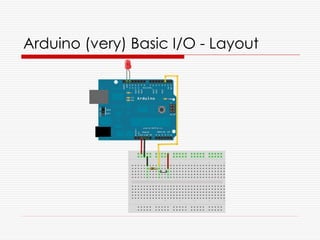
The document discusses hardware hacking, including its definition and various types such as circuit bending, reverse engineering, and toy hacking. It provides guidance on getting started, particularly with Arduino as a microprocessor platform, highlighting its capabilities and related software tools. Additionally, it offers resources and communities for aspiring hardware hackers to explore and connect.


























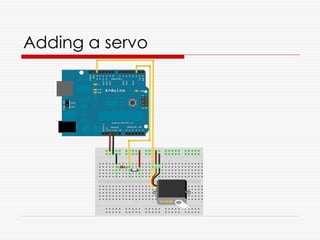
![Update the code
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myServo;
int steps[] = {0,60,120,180};
int currentPos = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(2, INPUT);
myServo.attach(13);
myServo.write(steps[0]);
}
void loop() {
if (HIGH == digitalRead(2)) {
currentPos = (3 == currentPos) ? 0 : currentPos + 1;
myServo.write(steps[currentPos]);
delay(500);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardwarehacking-091130111500-phpapp01/85/Hardware-Hacking-29-320.jpg)

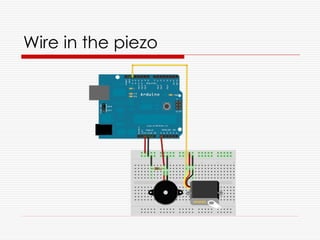
![More code updates
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myServo;
int steps[] = {0,60,120,180};
int currentPos = 0;
const int KNOCKTHRESHOLD = 100;
void setup() {
myServo.attach(13);
myServo.write(steps[0]);
}
void loop() {
if (KNOCKTHRESHOLD <= analogRead(0)) {
currentPos = (3 == currentPos) ? 0 : currentPos + 1;
myServo.write(steps[currentPos]);
delay(500);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardwarehacking-091130111500-phpapp01/85/Hardware-Hacking-32-320.jpg)

![by pieter [iamdoom / bwrah bwrah]- flickr
Photo “Inspiration”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardwarehacking-091130111500-phpapp01/85/Hardware-Hacking-34-320.jpg)



