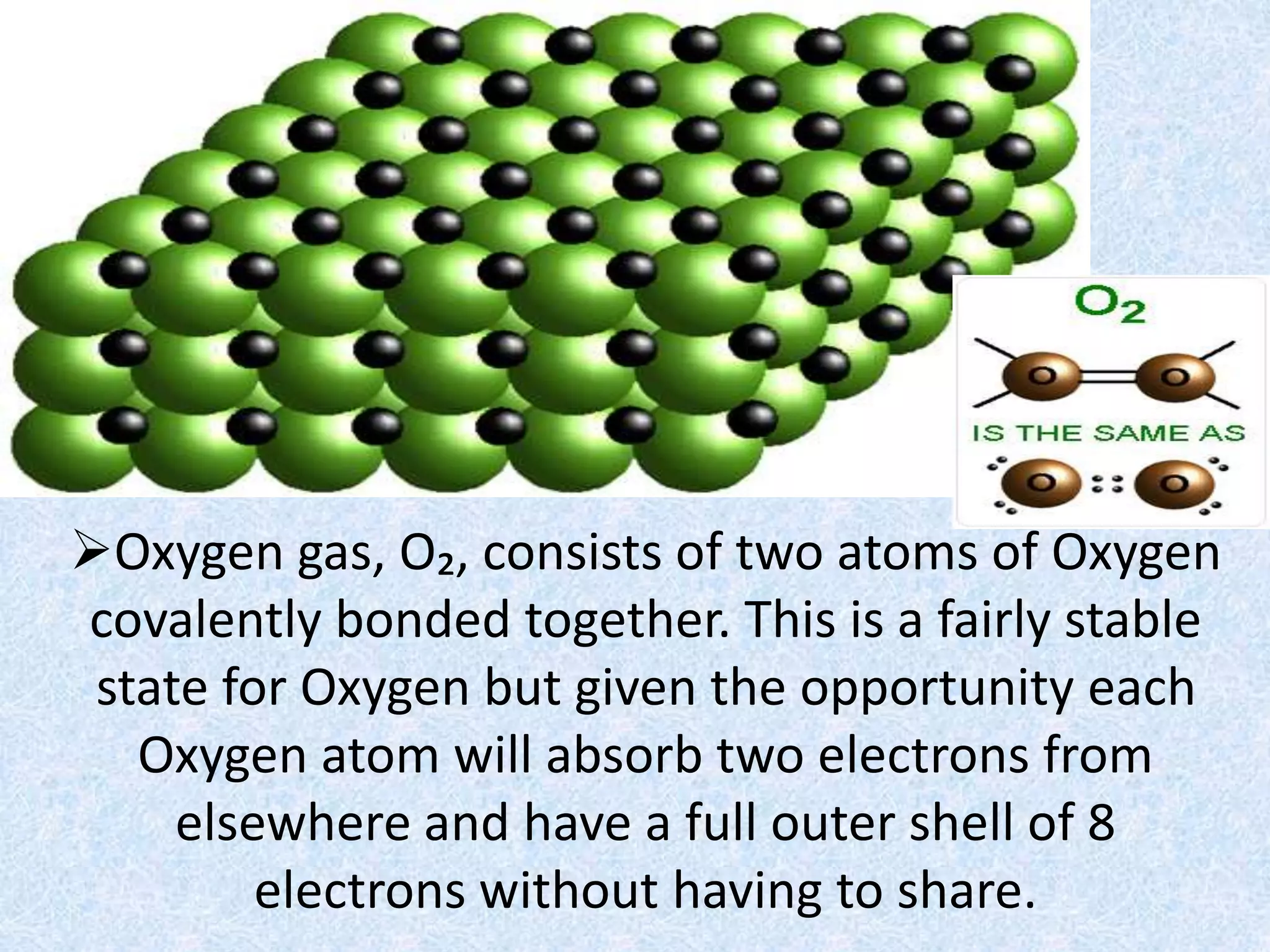
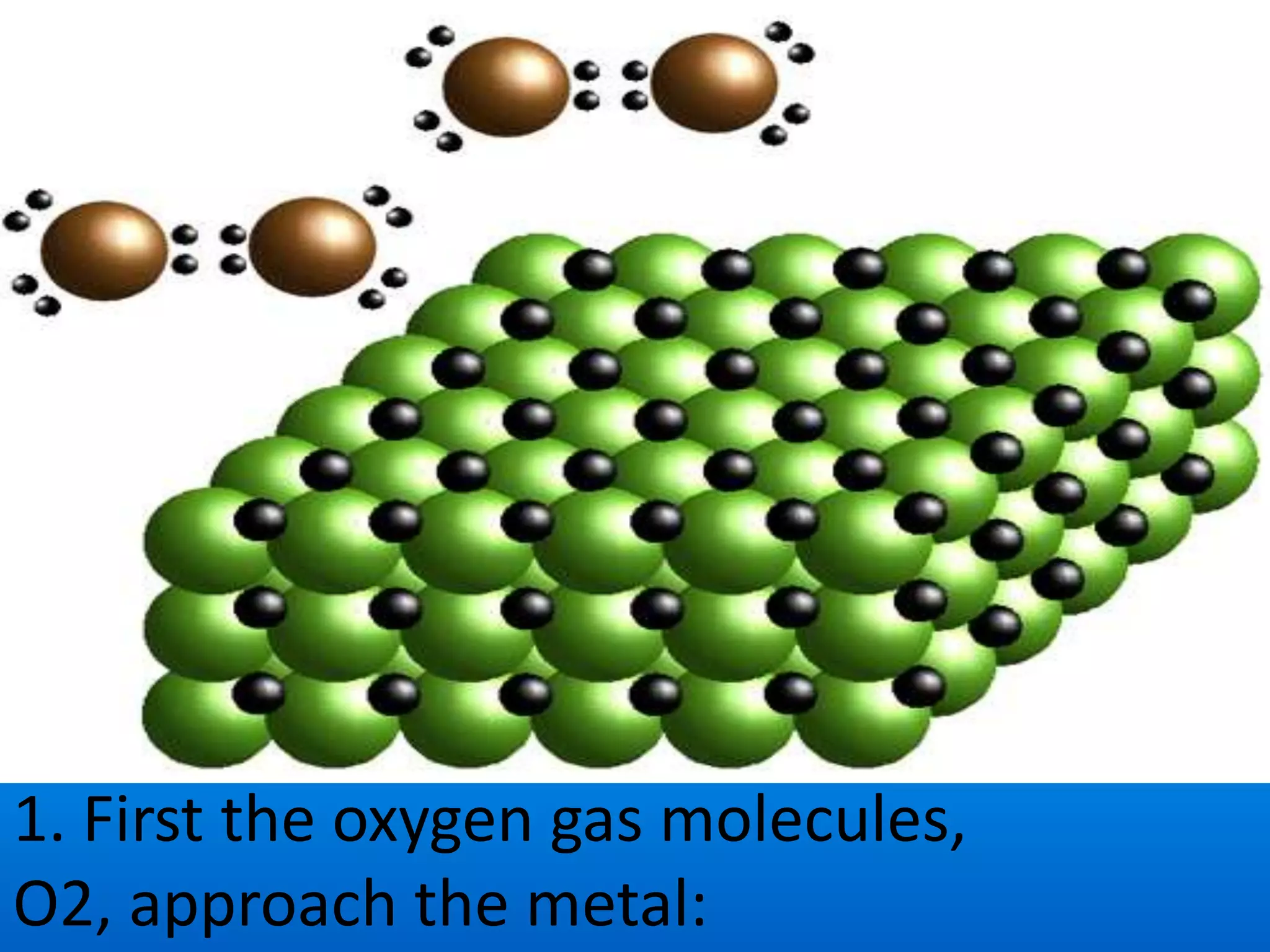
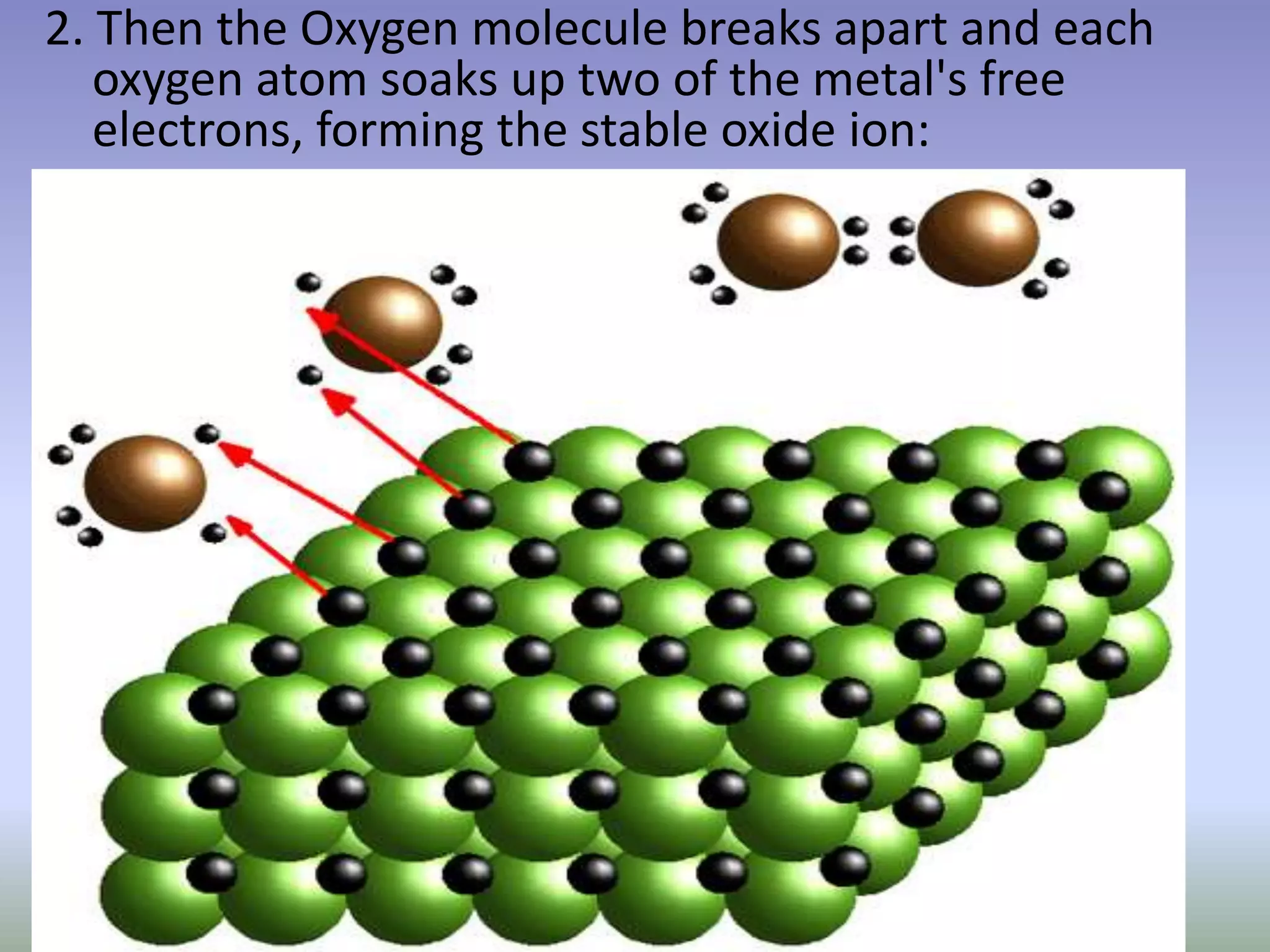
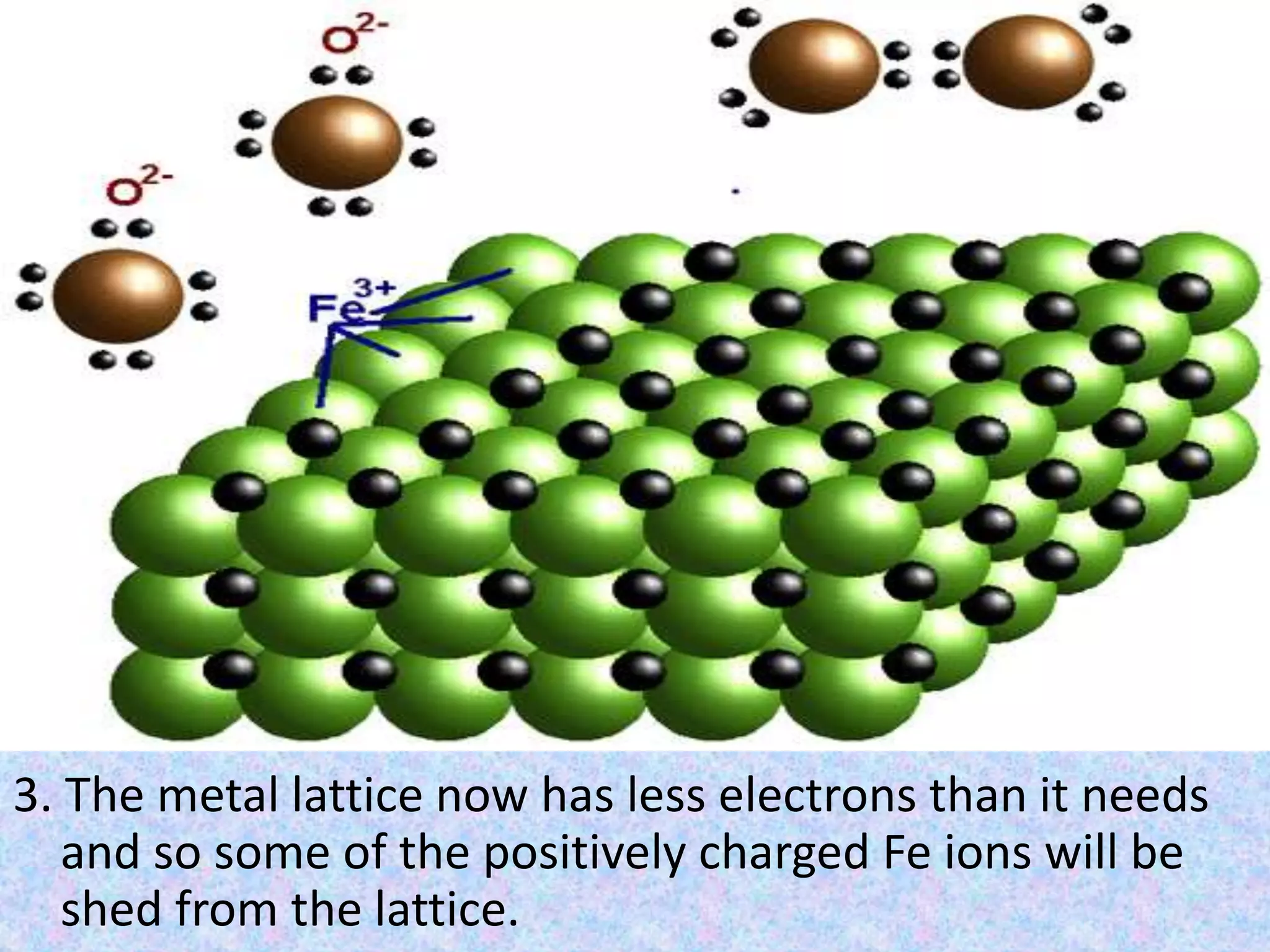
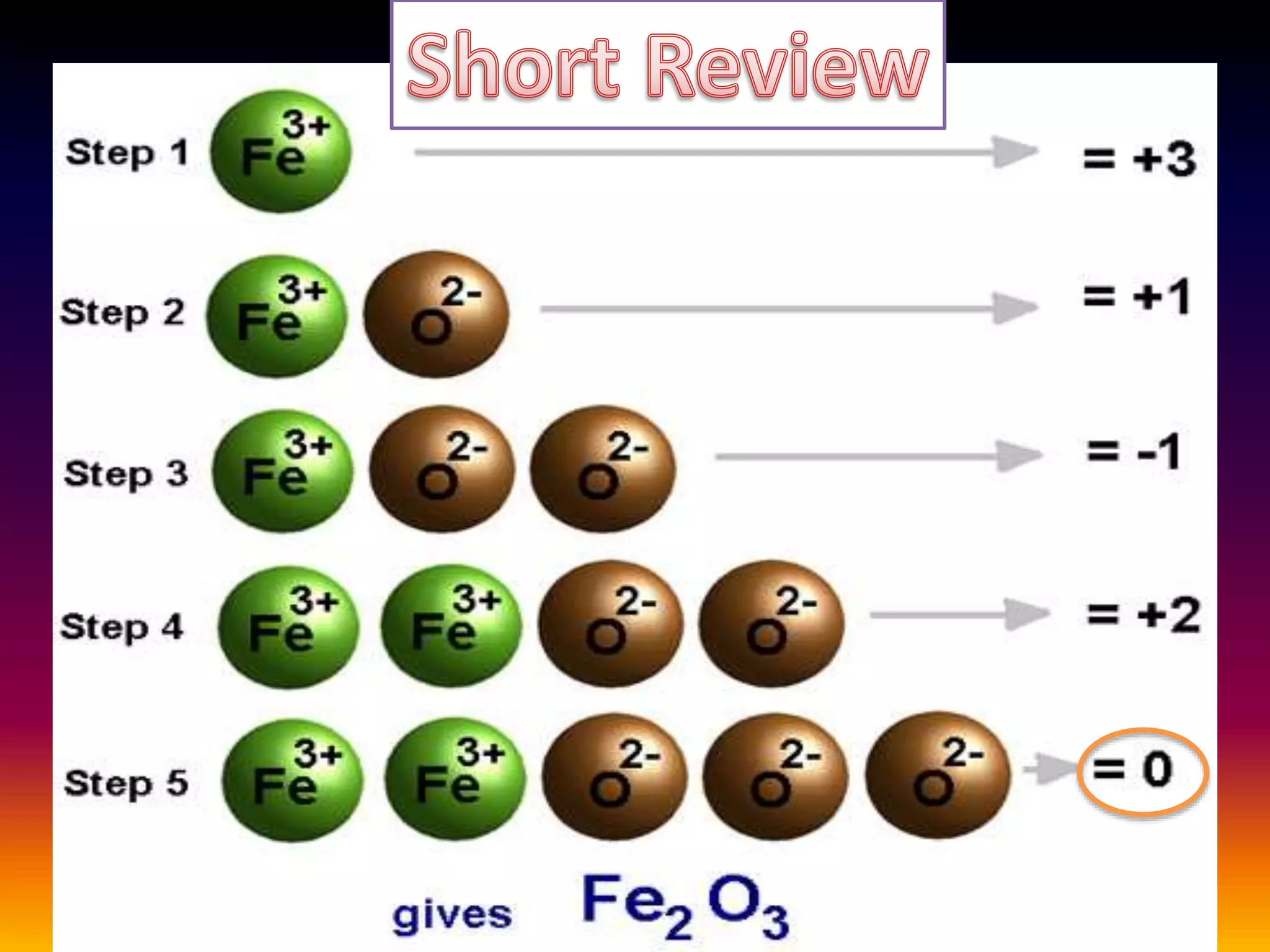
Rust is formed through the oxidation of iron when it is exposed to oxygen and moisture in the air. Oxygen atoms pull electrons from the iron atoms, forming iron oxide and weakening the metal structure. This process can be sped up by placing steel wool in a solution of vinegar and bleach, which contains hypochlorous acid. The acid reacts with the iron, rapidly producing hydrated ferric oxide (rust) that settles to the bottom of the container.